Lithium iron phosphate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
iron(2+) lithium phosphate (1:1:1) | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.124.705 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| FeLiO 4P | |
| Molar mass | 157.757 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Lithium iron phosphate, also known as LFP, is an inorganic compound with the formula LiFePO
4. It is a gray, red-grey, brown or black solid that is insoluble in water. The material has attracted attention as a candidate component of lithium iron phosphate batteries,[1] which are related to Li-ion batteries). It is targeted for use in power tools, electric vehicles, and solar energy installations.[2] It is also used in OLPC XO education laptops.
Most lithium batteries (Li-ion) used in 3C (computer, communication, consumer electronics) products use cathodes of other lithium materials, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO
2) lithium manganese oxide (LiMn
2O
4), and lithium nickel oxide (LiNiO
2). The anodes are generally made of carbon.
Lithium iron phosphate exists naturally in the form of the mineral triphylite, but such material have insufficient purity for use in batteries.
LiMPO
4
With general chemical formula of LiMPO
4, LiFePO
4 adopts the olivine structure. M includes not only Fe but also Co, Mn and Ti. The first commercial LiMPO
4 was C/LiFePO
4 and therefore, refer to the whole group of LiMPO
4 as lithium iron phosphate, LiFePO
4. However, more than one olivine-type phase may be used as a battery's cathode material. Olivine compounds such as A
yMPO
4, Li
1-xMFePO
4, and LiFePO
4-zM have the same crystal structures as LiMPO
4 and may replace in a cathode. All may be referred to as “LFP”.
Manganese, phosphate, iron, and lithium also form an olivine structure. This structure is a very useful contributor to the cathode of lithium rechargeable batteries.[3] This is due to the olivine structure created when lithium is combined with manganese, iron, and phosphate (as described above). The olivine structures of lithium rechargeable batteries are significant, for they are affordable, stable, and can be safely stored as energy.[4]
History and production
LiFePO
4 was proposed as a candidate for use in batteries in 1996 by Goodenough et al.[5][6] These workers demonstrated the reversible extraction of lithium from LiFePO
4 and insertion of lithium into FePO
4. Neutron diffraction confirmed that LFP was able to ensure the security of large input/output current of lithium battery.[7]
The material can be produced by heating a variety of iron and lithium salts with phosphates or phosphoric acid. Many related routes have been described including those that use hydrothermal synthesis.[8]
Physical and chemical properties
LFP batteries have an operating voltage of 3.3 V, charge density of 170mAh/g, high power density, long cycle life and stability at high temperatures.
In LiFePO
4, lithium has a +1 charge, iron +2 charge balancing the 3- charge for phosphate. Upon removal of Li, the material converts to the ferric form FePO4.[9]
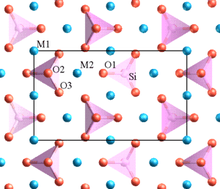
The iron atom and 6 oxygen atoms form an octahedral coordination sphere, described as FeO
6, with the Fe ion at the center. The phosphate groups, PO
4, are tetrahedral. The three-dimensional framework is formed by the FeO
6 octahedra sharing O corners. Lithium ions reside within the octahedral channels in a zigzag manner. In crystallography, this structure is thought to belong to the Pmnb space group of the orthorhombic crystal system. The lattice constants are: a = 6.008 Å, b = 10.334 Å, and c = 4.693 Å. The volume of the unit cell is 291.4 Å3.
In contrast to two traditional cathode materials - LiMnO
4 and LiCoO
2, lithium ions of LiMPO
4 migrate in the lattice's one-dimensional free volume. During charge/discharge, the lithium ions are extracted concomitant with oxidation of Fe:
Extraction of lithium from LiFePO
4 produces FePO
4 with a similar structure. FePO
4 adopts a Pmnb space group with a unit cell volume of 272.4 3, only slightly smaller that of its lithiated precursor. Extraction of lithium ions reduces the lattice volume, as is the case with lithium oxides. LiMPO
4's corner-shared FeO
6 octahedra are separated by the oxygen atoms of the PO
43- tetrahedra and cannot form a continuous FeO
6 network, reducing conductivity.
A nearly close-packed hexagonal array of oxides centers provides relatively little free volume for Li+ ions to migrate within. For this reason, the ionic conductivity of Li+ is relatively low at ambient temperate. The details of the lithiation of FePO4 and the delithiation of LiFePO4 have been examined. Two phases of the lithiated material are implicated.[9][10]
Applications
LFP's major commercial advantages are that it poses few safety concerns such as overheating and explosion, as well as long cycle lifetimes, high power density and has a wider operating temperature range. Power plants and automobiles use LFP.
BAE has announced that their HybriDrive Orion 7 hybrid bus uses about 180 kW LFP battery cells. AES has developed multi-trillion watt battery systems that are capable of subsidiary services of the power network, including spare capacity and frequency adjustment. In China, BAK and Tianjin Lishen are active in the area.
Comparison
Although LFP has 25% less capacity than other lithium batteries due to its material structure, it has 70% more than nickel-hydrogen batteries.
The major differences between LFP batteries and ordinary lithium batteries are that LFP batteries do not have safety concerns such as overheating and explosion, that they have 4 to 5 times longer cycle lifetimes than the lithium batteries 8 to 10 times higher discharge power.
LFP batteries have drawbacks including higher costs given less time on the learning curve. The energy density is significantly lower than LiCoO
2 (although higher than the nickel-metal hydride battery).
Lithium cobalt oxide has multiple disadvantages. It is one of the more expensive components of traditional li-ion batteries. The cobalt in LiCoO
2 is listed as a possible human carcinogen by IARC. LiCoO
2 can experience problems with runaway overheating and outgassing, particularly in lithium polymer battery packs.
LFP batteries do not need the sophisticated charge monitoring in traditional Li-ion, but still benefit from balance charging on a regular basis, especially in repeated high-current discharge rate uses like electric-powered flying model aircraft.
Intellectual property
The root patents of LFP compounds are held by four organizations. University of Texas-Austin for the discovery of the material. Hydro-Québec, Université de Montréal and the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS) for the carbon coating that enhance its conductivity and actually makes LFP suitable for industrial developments.[11] These patents underlie mature mass production technologies. The largest production capacity is up to 250 tons per month. The key feature of Li
1-xMFePO
4 from A123 is the nano-LFP, which modifies its physical properties and adds noble metals in the anode, as well as the use of special graphite as the cathode.
The main feature of LiMPO
4 from Phostech is increased capacitance and conductivity by an appropriate carbon coating. The special feature of LiFePO
4 • zM from Aleees a high capacitance and low impedance obtained by the stable control of the ferrites and crystal growth. This improved control is realized by applying strong mechanical stirring forces to the precursors in high oversaturation states, which induces crystallization of the metal oxides and LFP.
In patent lawsuits in the US in 2005 and 2006, the University of Texas at Austin|University of Texas-Austin and Hydro-Québec claimed that LiFePO
4 as the cathode infringed their patents, US 5910382 and US 6514640. The patent claims involved a unique crystal structure and a chemical formula of the battery cathode material.
On April 7, 2006, A123 filed an action seeking a declaration of non-infringement and invalidity UT's patents. A123 separately filed two ex parte Reexamination Proceedings before the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO), in which they sought to invalidate the patents based upon prior art.
In a parallel court proceeding, UT sued Valence Technology, Inc. ("Valence") - a company that commercializes LFP products that alleged infringement.
The USPTO issued a Reexamination Certificate for the '382 patent on April 15, 2008 and for the '640 patent on May 12, 2009, by which the claims of these patents were amended. This allowed the current patent infringement suits filed by Hydro-Quebec against Valence and A123 to proceed. After a markman hearing, on April 27, 2011 the Western District Court of Texas held that the claims of the reexamined patents had a narrower scope than as originally granted.
On Dec 9th, 2008, the European Patent Office revoked Dr. Goodenough’s patent numbered 0904607. This decision basically reduced the patent risk of using LFP in European automobile applications. The decision is believed to be based on the lack of novelty.[12]
The first major large settlement was the lawsuit between NTT and the University of Texas-Austin (UT). In October 2008,[13] NTT announced that they would settle the case in the Japan Supreme Civil Court for $30 million. As part of the agreement UT agreed that NTT did not steal the information and that NTT would share its LFP patents with UT. NTT’s patent is also for an olivine LFP, with the general chemical formula of A
yMPO
4 (A is for alkali metal and M for the combination of Co and Fe), now used by BYD Company. Although chemically the materials are nearly the same, from the viewpoint of patents, A
yMPO
4 of NTT is different from the materials covered by UT. A
yMPO
4 has higher capacity than LiMPO
4. At the heart of the case was that NTT engineer Okada Shigeto, who had worked in the UT labs developing the material, was accused of stealing UT’s intellectual property.
Research
Power density
LFP has two shortcomings: low conductivity and low lithium diffusion constant, both of which limit the charge/discharge rate. Adding conducting particles in delithiated FePO
4 raises its electron conductivity. For example, adding conducting particles with good diffusion capability like graphite and carbon [14] to LiMPO
4 powders significantly improves conductivity between particles, increases the efficiency of LiMPO
4 and raises its reversible capacity up to 95% of the theoretical values. LiMPO
4 shows good cycling performance even under charge/discharge current as large as 5C.[15]
Stability
Coating LFP with inorganic oxides can make LFP’s structure more stable and increase conductivity. Traditional LiCoO
2 with oxide coating shows improved cycling performance. This coating also inhibits dissolution of Co and slows the decay of LiCoO
2 capacity. Similarly, LiMPO
4 with an inorganic coating such as ZnO[16] and ZrO
2,[17] has a better cycling lifetime, larger capacity and better characteristics under rapid discharge. The addition of a conductive carbon increases efficiency. Mitsui Zosen and Aleees reported that addition of conducting metal particles such as copper and silver increased efficiency.[18] LiMPO
4 with 1 wt% of metal additives has a reversible capacity up to 140mAh/g and better efficiency under high discharge current.
Metal substitution
Substituting other metals for the iron or lithium in LiMPO
4 can also raise efficiency. Substituting zinc for iron increases crystallinity of LiMPO
4 because zinc and iron have similar ion radii.[19] Cyclic voltammetry confirms that LiFe
1-xM
xPO
4, after metal substitution, has higher reversibility of lithium ion insertion and extraction. During lithium extraction, Fe (II) is oxidized to Fe (III) and the lattice volume shrinks. The shrinking volume changes lithium’s returning paths.
Synthesis processes
Mass production with stable and high quality still faces many challenges.
Similar to lithium oxides, LiMPO
4 may be synthesized by a variety of methods, including: solid-phase synthesis, emulsion drying, sol-gel process, solution coprecipitation, vapor phase deposition, electrochemical synthesis, electron beam irradiation, microwave process, hydrothermal synthesis, ultrasonic pyrolysis and spray pyrolysis. example, in the emulsion drying process, the emulsifier is first mixed with kerosene.
Next, the solutions of lithium salts and iron salts are added to this mixture. This process produces nanocarbon particles.[20] Hydrothermal synthesis produces LiMPO
4 with good crystallinity. Conductive carbon is obtained by adding polyethylene glycol to the solution followed by thermal processing.[21] Vapor phase deposition produces a thin film LiMPO
4.[22] In flame spray pyrolysis FePO4 is mixed with Lithium carbonate and glucose and charged with electrolytes. The mixture is then injected inside a flame and filtered to collect the synthesized LiFePO
4.[23]
See also
References
- ↑ Park, O. K.; Cho, Y.; Lee, S.; Yoo, H.-C.; Song, H.-K.; Cho, J., "Who Will Drive Electric Vehicles, Olivine or Spinel?", Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, volume 4, pages 1621-1633. doi:10.1039/c0ee00559b
- ↑ Ozawa, Ryan. "New Energy Storage Startup to Take Hawaii Homes Off-Grid". Hawaii Blog. Retrieved 2015-07-09.
- ↑ Kim, Jongsoon. "Thermal Stability of Fe-Mn Binary Olivine Cathodes for Li Rechargeable Batteries.". The Royal Society of Chemistry. Retrieved 19 Oct 2012.
- ↑ Wang, J.; Sun, X., "Olivine Lifepo4: The Remaining Challenges for Future Energy Storage", Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, volume 8, pages 1110-1138. doi:10.1039/C4EE04016C
- ↑ "LiFePO
4: A Novel Cathode Material for Rechargeable Batteries", A.K. Padhi, K.S. Nanjundaswamy, J.B. Goodenough, Electrochemical Society Meeting Abstracts, 96-1, May, 1996, pp 73 - ↑ “Phospho-olivines as Positive-Electrode Materials for Rechargeable Lithium Batteries” A. K. Padhi, K. S. Nanjundaswamy, and J. B. Goodenough, J. Electrochem. Soc., Volume 144, Issue 4, pp. 1188-1194 (April 1997)
- ↑ Nature Materials, 2008, 7, 707-711.
- ↑ Jugovic, D.; Uskokovic, D., "A Review of Recent Developments in the Synthesis Procedures of Lithium Iron Phosphate Powders", J. Power Sources 2009, volume 190, 538-544. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.01.074
- 1 2 Love, Corey T.; Korovina, Anna; Patridge, Christopher J.; Swider-Lyons; Karen E.; Twigg, Mark E.; Ramaker, David E. (2013). "Review of LiFePO4 phase transition mechanisms and new observations from X-ray absorption spectroscopy". Journal of the Electrochemical Society. 160: A3153–A3161. doi:10.1149/2.023305jes.
- ↑ Malik, R.; Abdellahi, A.; Ceder, G., "A Critical Review of the Li Insertion Mechanisms in LiFePO4 Electrodes", J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, volume 160, pages A3179-A3197. doi:10.1149/2.029305jes
- ↑ http://www.clariant.com.br/C12576850036A6E9/8650B24BC3A7BAF3C12579C2003552DA/$FILE/20120314_BASF_enters_into_a_sublicense_agreement_with_LiFePO4C_Licensing_AG.pdf
- ↑ http://www.greencarcongress.com/2008/12/epo-revokes-uni.html
- ↑ http://techon.nikkeibp.co.jp/english/NEWS_EN/20081007/159256/
- ↑ J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 7046-7051.
- ↑ J. Electrochem. Soc, 2005, 152, A191-A196.
- ↑ J. Power Sources, 2004, 137, 93–99.
- ↑ J. Power Sources, 2006, 153, 274–280.
- ↑ J. Electrochem. Soc, 2008, 155, A211-A216.
- ↑ Electrochem Commun, 2008, 10, 165–169.
- ↑ Electrochem and Solid-State Lett, 2002, 5, A47-A50.
- ↑ Materials Letters, 2005, 59, 2361–2365.
- ↑ J. Power Sources, 2004, 133, 272–276.
- ↑ Hamid, N., Wennig, S., Hardt, S., Heinzel, A., Schulz, C., & Wiggers, H. (2012). High-capacity cathodes for lithium-ion batteries from nanostructured LiFePO
4 synthesized by highly-flexible and scalable flame spray pyrolysis. Journal of Power Sources, 216, 76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.05.047