Leukocoria
| Leukocoria | |
|---|---|
|
| |
| A child with leukocoria due to retinoblastoma in the left eye | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | neurology |
| ICD-9-CM | 360.44 |
| DiseasesDB | 33379 |
| MedlinePlus | 003315 |
Leukocoria (also leukokoria[1] or white pupillary reflex) is an abnormal white reflection from the retina of the eye. Leukocoria resembles eyeshine, but leukocoria can occur in humans and other animals that lack eyeshine because their retina lacks a tapetum lucidum.
Leukocoria is a medical sign for a number of conditions, including Coats disease, congenital cataract, corneal scarring, melanoma of the ciliary body,[2] Norrie disease, ocular toxocariasis, persistence of the tunica vasculosa lentis (PFV/PHPV), retinoblastoma, and retrolental fibroplasia.
Because of the potentially life-threatening nature of retinoblastoma, a cancer, that condition is usually considered in the evaluation of leukocoria. In some rare cases (1%) the leukocoria is caused by Coats' disease (leaking retinal vessels).
Diagnosis
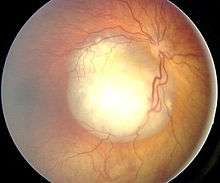
On photographs taken using a flash, instead of the familiar red-eye effect, leukocoria can cause a bright white reflection in an affected eye. Leukocoria may appear also in low indirect light, similar to eyeshine.
Leukocoria can be detected by a routine eye exam (see Ophthalmoscopy). For screening purposes, the red reflex test is used. In this test, when a light is shone briefly through the pupil, an orange red reflection is normal. A white reflection is leukocoria.
Media depictions
- The fictional serial killer known as "The Collector", the main antagonist of the films The Collector (2009) and The Collection (2012), suffers the condition in both eyes.
References
- ↑ thefreedictionary.com
- ↑ Demirci H, Shields CL, Shields JA, Honavar SG, Eagle RC (January 2001). "Leucocoria as the presenting sign of a ciliary body melanoma in a child". The British Journal of Ophthalmology. 85 (1): 115–6. PMC 1723667
 . PMID 11201946.
. PMID 11201946.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Leukocoria. |
- PHPV Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous
- Retinoblastoma MedPix Images