Laws against Holocaust denial
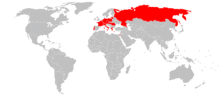
Holocaust denial, the denial of the systematic genocidal killing of millions of people of various ethnic groups in Europe by Nazi Germany in the 1930s and 1940s, is illegal in 16 European countries. Many countries also have broader laws that criminalize genocide denial. Of the countries that ban Holocaust denial, some, such as Austria, Germany, Hungary, and Romania, were among the perpetrators of the Holocaust, and many of these also ban other elements associated with Nazism, such as the expression of Nazi symbols.
In several nations such as the United Kingdom and the United States, laws against Holocaust denial have come up in legal discussion and have been proposed, but the measures have been rejected. Organizations representing groups that have been victimized during the Holocaust have generally been split about such laws. In the United States, the First Amendment to the country's constitution establishes freedom of expression and protects virtually all speech (including "hate speech").
Overview and commentary
Scholars have pointed out that countries that specifically ban Holocaust denial generally have legal systems that limit speech in other ways, such as banning "hate speech". According to D. D. Guttenplan, this is a split between the "common law countries of the United States, Ireland and many British Commonwealth countries from the civil law countries of continental Europe and Scotland. In civil law countries the law is generally more proscriptive. Also, under the civil law regime, the judge acts more as an inquisitor, gathering and presenting evidence as well as interpreting it".[1] Michael Whine argues that Holocaust denial can inspire violence against Jews; he states, "Jews' experience in the post-World War II era suggests that their rights are best protected in open and tolerant democracies that actively prosecute all forms of racial and religious hatred".[2]
János Kis[3] and in particular András Schiffer[4] feel the work of Holocaust deniers should be protected by a universal right to free speech. An identical argument was used[5] by the Hungarian Constitutional Court (Alkotmánybíróság) led by László Sólyom when it struck down a law against Holocaust denial in 1992.
The argument that laws punishing Holocaust denial are incompatible with the European Convention on Human Rights and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights have been rejected by institutions of the Council of Europe (the European Commission of Human Rights,[6] the European Court of Human Rights[7]) and also by the United Nations Human Rights Committee.[8]
Historians who oppose such laws include Raul Hilberg,[9] Richard J. Evans, and Pierre Vidal-Naquet. Other prominent opponents of the laws are Timothy Garton Ash,[10] Christopher Hitchens, Peter Singer,[11] and Noam Chomsky.[12] An uproar resulted when Serge Thion used one of Chomsky's essays without explicit permission as a foreword to a book of Holocaust denial essays (see Faurisson affair). These laws have also been criticized on the grounds that education is more effective than legislation at combating Holocaust denial and that the laws will make martyrs out of those imprisoned for their violation.[13]
By country
Australia
While Australia lacks a specific law against Holocaust denial, Holocaust denial is prosecuted in Australia under various laws against "hate speech" and "racial vilification".[15][16] Gerald Fredrick Töben and his Adelaide Institute are the best-known case of someone being prosecuted in Australia for Holocaust denial.[17]
Austria
In Austria, the Verbotsgesetz 1947 provided the legal framework for the process of denazification in Austria and suppression of any potential revival of Nazism. In 1992, it was amended to prohibit the denial or gross minimisation of the Holocaust.
National Socialism Prohibition Law (1947, amendments of 1992)§ 3g. He who operates in a manner characterized other than that in § § 3a – 3f will be punished (revitalising of the NSDAP or identification with), with imprisonment from one to up to ten years, and in cases of particularly dangerous suspects or activity, be punished with up to twenty years' imprisonment.[18]
§ 3h. As an amendment to § 3 g., whoever denies, grossly plays down, approves or tries to excuse the National Socialist genocide or other National Socialist crimes against humanity in a print publication, in broadcast or other media.[19]
Belgium
In Belgium, Holocaust denial was made illegal in 1995.
Negationism Law (1995, amendments of 1999)Article 1 Whoever, in the circumstances given in article 444 of the Penal Code denies, grossly minimises, attempts to justify, or approves the genocide committed by the German National Socialist Regime during the Second World War shall be punished by a prison sentence of eight days to one year, and by a fine of twenty six francs to five thousand francs. For the application of the previous paragraph, the term genocide is meant in the sense of article 2 of the International Treaty of 9 December 1948 on preventing and combating genocide. In the event of repetitions, the guilty party may in addition have his civic rights suspended in accordance with article 33 of the Penal Code.
Art.2 In the event of a conviction on account of a violation under this Act, it may be ordered that the judgement, in its entity or an excerpt of it, is published in one of more newspapers, and is displayed, to the charge of the guilty party.
Art.3. Chapter VII of the First Book of the Penal Code and Article 85 of the same Code are also applicable to this Act.
Art. 4. The Centre for Equal Opportunities and Opposition to Racism, as well as any association that at the time of the facts had a legal personality for at least five years, and which, on the grounds of its statutes, has the objective of defending moral interests and the honour of the resistance or the deported, may act in law in all legal disputes arising from the application of this Act.[20]
Bosnia and Herzegovina
In May 2007 Ekrem Ajanovic, a Bosniak MP in the Bosnian Parliament proposed a legislation on criminalizing the denial of Holocaust, genocide and crimes against humanity. This was the first time that somebody in Bosnia and Herzegovina's Parliament proposed such a legislation. Bosnian Serb MPs voted against this legislation and proposed that such an issue should be resolved within the Criminal Code of Bosnia and Herzegovina.[21] Following this, on 6 May 2009 Bosniak MPs Adem Huskic, Ekrem Ajanovic and Remzija Kadric proposed to the BH parliament a change to the Criminal Code of Bosnia and Herzegovina where Holocaust, genocide and crimes against humanity denial would be criminalized.[22] Bosnian Serb MPs have repeatedly been against such a legislation claiming that the law "would cause disagreement and even animosity" according to SNSD member Lazar Prodanovic.[23]
Czech Republic
In the Czech Republic, Holocaust denial and denial of communist-perpetrated atrocities is illegal.
Law Against Support and Dissemination of Movements Oppressing Human Rights and Freedoms (2001)§ 260 (1) The person who supports or spreads movements oppressing human rights and freedoms or declares national, race, religious or class hatred or hatred against other group of persons will be punished by prison from 1 to 5 years. (2) The person will be imprisoned from 3 to 8 years if: a) he/she commits the crime mentioned in paragraph (1) in print, film, radio, television or other similarly effective manner, b) he/she commits the crime as a member of an organized group c) he/she commits the crime in a state of national emergency or state of war.
§ 261 The person who publicly declares sympathies with such a movement mentioned in § 260, will be punished by prison from 6 months to 3 years.
§ 261a The person who publicly denies, puts in doubt, approves or tries to justify Nazi or communist genocide or other crimes of Nazis or communists will be punished by prison of 6 months to 3 years.[24]
France
In France, the Gayssot Act, voted for on July 13, 1990, makes it illegal to question the existence of crimes that fall in the category of crimes against humanity as defined in the London Charter of 1945, on the basis of which Nazi leaders were convicted by the International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg in 1945–46. When the act was challenged by Robert Faurisson, the Human Rights Committee upheld it as a necessary means to counter possible antisemitism.[25] Similarly, the applications of Pierre Marais and Roger Garaudy were rejected by the European Court of Human Rights, in 1996 and 2003.[26]
In 2012, the Constitutional Council of France ruled that to extend the Gayssot Act to the Armenian Genocide denial was unconstitutional because it violated the freedom of speech.[27][28] The Gayssot Act itself, however, was found consistent with the Constitution four years later.[29]
LAW No 90-615 to repress acts of racism, anti-semitism and xenophobia (1990)MODIFICATIONS OF THE LAW OF JULY 29, 1881 ON THE FREEDOM OF THE PRESS Art 8. – Article 24 of the Law on the Freedom of the Press of 29 July 1881 is supplemented by the following provisions: In the event of judgment for one of the facts envisaged by the preceding subparagraph, the court will be able moreover to order: Except when the responsibility for the author of the infringement is retained on the base for article 42 and the first subparagraph for article 43 for this law or the first three subparagraphs for article 93-3 for the law No 82-652 for July 29, 1982 on the audio-visual communication, the deprivation of the rights enumerated to the 2o and 3o of article 42 of the penal code for imprisonment of five years maximum;
Art 9. – As an amendment to Article 24 of the law of July 29, 1881 on the freedom of the press, article 24 (a) is as follows written: <<Art. 24 (a). - those who have disputed the existence of one or more crimes against humanity such as they are defined by Article 6 of the statute of the international tribunal military annexed in the agreement of London of August 8, 1945 and which were a carried out either by the members of an organization declared criminal pursuant to Article 9 of the aforementioned statute, or by a person found guilty such crimes by a French or international jurisdiction shall be punished by one month to one year's imprisonment or a fine.
Art 13. – It is inserted, after article 48-1 of the law of July 29, 1881 on the freedom of the press, article 48-2 thus written: <<Art. 48-2. - publication or publicly expressed opinion encouraging those to whom it is addressed to pass a favourable moral judgment on one or more crimes against humanity and tending to justify these crimes (including collaboration) or vindicate their perpetrators shall be punished by one to five years' imprisonment or a fine.[30]
Germany
§ 130 Incitement to hatred
In Germany, Volksverhetzung ("incitement of the people")[31][32] is a concept in German criminal law that bans incitement to hatred against segments of the population. It often applies to (though not limited to) trials relating to Holocaust denial in Germany. In addition, Strafgesetzbuch § 86a outlaws various symbols of "unconstitutional organisations", such as the Swastika and the SS runes.
§ 130 Incitement to hatred (1985, Revised 1992, 2002, 2005, 2015)[33][34](1) Whosoever, in a manner capable of disturbing the public peace:
- incites hatred against a national, racial, religious group or a group defined by their ethnic origins, against segments of the population or individuals because of their belonging to one of the aforementioned groups or segments of the population or calls for violent or arbitrary measures against them; or
- assaults the human dignity of others by insulting, maliciously maligning an aforementioned group, segments of the population or individuals because of their belonging to one of the aforementioned groups or segments of the population, or defaming segments of the population,
shall be liable to imprisonment from three months to five years.[33][34]
(...)
(3) Whosoever publicly or in a meeting approves of, denies or downplays an act committed under the rule of National Socialism of the kind indicated in section 6 (1) of the Code of International Criminal Law, in a manner capable of disturbing the public peace shall be liable to imprisonment not exceeding five years or a fine.[33][34]
(4) Whosoever publicly or in a meeting disturbs the public peace in a manner that violates the dignity of the victims by approving of, glorifying, or justifying National Socialist rule of arbitrary force shall be liable to imprisonment not exceeding three years or a fine.[33][34]
The definition of section 6 of the Code of Crimes against International Law referenced in the above § 130 is as follows:
§ 6 Genocide(1) Whoever with the intent of destroying as such, in whole or in part, a national, racial, religious or ethnic group:
- kills a member of the group,
- causes serious bodily or mental harm to a member of the group, especially of the kind referred to in section 226 of the Criminal Code,
- inflicts on the group conditions of life calculated to bring about their physical destruction in whole or in part,
- imposes measures intended to prevent births within the group,
- forcibly transfers a child of the group to another group, shall be punished with imprisonment for life. (...)[35]
Other sections
The following sections of the German criminal code are also relevant:
§ 189 Disparagement of the Memory of Deceased Persons (1985, amendments of 1992)Whoever disparages the memory of a deceased person shall be punished with imprisonment for not more than two years or a fine.[36]
§ 194 Application for Criminal Prosecution(1) An insult shall be prosecuted only upon complaint. If the act was committed through dissemination of writings (Section 11 subsection (3)) or making them publicly accessible in a meeting or through a presentation by radio, then a complaint is not required if the aggrieved party was persecuted as a member of a group under the National Socialist or another rule by force and decree, this group is a part of the population and the insult is connected with this persecution. The act may not, however, be prosecuted ex officio if the aggrieved party objects. When the aggrieved party deceases, the rights of complaint and of objection devolve on the relatives indicated in Section 77 subsection (2). The objection may not be withdrawn.
(2) If the memory of a deceased person has been disparaged, then the relatives indicated in Section 77 subsection (2), are entitled to file a complaint. If the act was committed through dissemination of writings (Section 11 subsection (3)) or making them publicly accessible in a meeting or through a presentation by radio, then a complaint is not required if the deceased person lost his life as a victim of the National Socialist or another rule by force and decree and the disparagement is connected therewith. The act may not, however, be prosecuted ex officio if a person entitled to file a complaint objects. The objection may not be withdrawn. (...)[37]
Greece
In September 2014 with a legislative vote 54 to 99, Greece made Holocaust denial a criminal offence.[38]
Hungary
The Parliament of Hungary declared the denial or trivialization of the Holocaust a crime punishable by up to three years' imprisonment on February 23, 2010.[39] The law was signed by the President of the Republic in March 2010.[40] On June 8, 2010, the newly elected Fidesz-dominated parliament changed the formulation of the law to "punish those, who deny the genocides committed by national socialist or communist systems, or deny other facts of deeds against humanity".[41] The word "Holocaust" is no longer in the law.
In 2011, the first man was charged with Holocaust denial in Budapest. The Court sentenced the man to 18 months in prison, suspended for three years, and probation. He also had to visit either Budapest's memorial museum, Auschwitz or Yad Vashem in Jerusalem. He chose his local Holocaust Memorial Center and had to make three visits in total and record his observations.[42]
In January 2015, the court ordered far-right on-line newspaper Kuruc.info to delete its article denying the Holocaust published in July 2013, which was the first ruling in Hungary of its kind.[43] The Association for Civil Liberties (TASZ) offered free legal aid to the website as a protest against restrictions on freedom of speech,[44] but the site refused citing the liberal views of the association, and also refused to delete the article.[45]
Israel
In Israel, a law to criminalize Holocaust denial was passed by the Knesset on July 8, 1986.
Denial of Holocaust (Prohibition) Law, 5746-1986Definitions 1. In this Law, "crime against the Jewish people" and "crime against humanity" have the same respective meanings as in the "Nazis and Nazi Collaborators Law, 5710-1950.
Prohibition of Denial of Holocaust 2. A person who, in writing or by word of mouth, publishes any statement denying or diminishing the proportions of acts committed in the period of the Nazi regime, which are crimes against the Jewish people or crimes against humanity, with intent to defend the perpetrators of those acts or to express sympathy or identification with them, shall be liable to imprisonment for a term of five years.
Prohibition of publication of expression for sympathy for Nazi crimes 3. A person who, in writing or by word of mouth, publishes any statement expressing praise or sympathy for or identification with acts done in the period of the Nazi regime, which are crimes against the Jewish people or crimes against humanity, shall be liable to imprisonment for a term of five years.
Permitted publication 4. The publication of a correct and fair report of a publication prohibited by this Law shall not be regarded as an offence thereunder so long as it is not made with intent to express sympathy or identification with the perpetrators of crimes against the Jewish people or against humanity.
Filing of charge 5. An indictment for offences under this Law shall only be filed by or with the consent of the Attorney-General.[46]
Italy
In January 2007, Italy's Cabinet unanimously approved a law making Holocaust denial a crime with a possible four-year prison sentence.[47]
Liechtenstein
Although not specifically outlining national socialist crimes, item five of section 283 of Liechtenstein's criminal code prohibits the denial of genocide.
§ 283 Race discriminationWhoever publicly denies, coarsely trivialises, or tries to justify genocide or other crimes against humanity via word, writing, pictures, electronically transmitted signs, gestures, violent acts or by other means shall be punished with imprisonment for up to two years.[48]
Lithuania
In Lithuania, approval and denial of Nazi or Soviet crimes is prohibited.
170(2) Publicly condoning international crimes, crimes of the USSR or Nazi Germany against the Republic of Lithuania and her inhabitants, denial or belittling of such crimes.[49]
Luxembourg
In Luxembourg, Article 457-3 of the Criminal Code, Act of 19 July 1997 outlaws Holocaust denial and denial of other genocides.[50] The punishment is imprisonment for between 8 days and 6 months and/or a fine.[50] The offence of "negationism and revisionism" applies to:
...anyone who has contested, minimised, justified or denied the existence of war crimes or crimes against humanity as defined in the statutes of the International Military Tribunal of 8 August 1945 or the existence of a genocide as defined by the Act of 8 August 1985. A complaint must be lodged by the person against whom the offence was committed (victim or association) in order for proceedings to be brought, Article 450 of the Criminal Code, Act of 19 July 1997.[50]
Netherlands
While Holocaust denial is not explicitly illegal in the Netherlands, the courts consider it a form of spreading hatred and therefore an offence.[51] According to the Dutch public prosecution office, offensive remarks are only punishable by Dutch law if they equate to discrimination against a particular group.[52] The relevant laws of the Dutch penal code are as follows:
Article 137c
- He who in public, either verbally or in writing or image, deliberately offends a group of people because of their race, their religion or beliefs, their hetero- or homosexual orientation or their physical, psychological or mental handicap, shall be punished with imprisonment not exceeding one year or a fine of the third category. [...][53]
Article 137d
- He who in public, either verbally or in writing or image, incites hatred or discrimination against people or incites acts of violence towards people or property of people because of their race, their religion or beliefs, their gender, their hetero- or homosexual orientation or their physical, psychological or mental handicap, shall be punished with imprisonment not exceeding one year or a fine of the third category. [...][54]
Poland
In Poland, Holocaust denial and the denial of communist crimes is punishable by law.
Act of 18 December 1998 on the Institute of National Remembrance – Commission for the Prosecution of Crimes against the Polish Nation (Dz.U. 1998 nr 155 poz. 1016)Article 55
He who publicly and contrary to facts contradicts the crimes mentioned in Article 1, clause 1 shall be subject to a fine or a penalty of deprivation of liberty of up to three years. The judgment shall be made publicly known.Article 1
This Act shall govern:
1. the registration, collection, access, management and use of the documents of the organs of state security created and collected between 22 July 1944 and 31 December 1989, and the documents of the organs of security of the Third Reich and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics concerning:
- a) crimes perpetrated against persons of Polish nationality and Polish citizens of other ethnicity, nationalities in the period between 1 September 1939 and 31 December 1989:
- - Nazi crimes,
- - communist crimes,
- - other crimes constituting crimes against peace, crimes against humanity or war crimes
- b) other politically motivated repressive measures committed by functionaries of Polish prosecution bodies or the judiciary or persons acting upon their orders, and disclosed in the content of the rulings given pursuant to the Act of 23 February 1991 on the Acknowledgement as Null and Void Decisions Delivered on Persons Repressed for Activities for the Benefit of the Independent Polish State (Journal of Laws of 1993 No. 34, item 149, of 1995 No. 36, item 159, No. 28, item 143, and of 1998 No. 97, item 604),
2. the rules of procedure as regards the prosecution of crimes specified in point 1 letter a),
3. the protection of the personal data of grieved parties, and
4. the conduct of activities as regards public education.[55]
Portugal
Although denial of the Holocaust is not expressly illegal in Portugal, Portuguese law prohibits denial of war crimes if used to incite to discrimination.
Article 240: Racial, religious, or sexual discrimination[…]
2 — Whoever in a public meeting, in writing intended for dissemination, or by any means of mass media or computer system whose purpose is to disseminate:
- […]
- b) defames or slanders an individual or group of individuals because of race, colour, ethnic or national origin, or religion, particularly through the denial of war crimes or those against peace and humanity;
- […]
with intent to incite to racial, religious or sexual discrimination or to encourage it, shall be punished with imprisonment from six months to five years.[56]
Romania
In Romania, Emergency Ordinance No. 31 of March 13, 2002 prohibits Holocaust denial. It was ratified on May 6, 2006. The law also prohibits racist, fascist, xenophobic symbols, uniforms and gestures: proliferation of which is punishable with imprisonment from between six months to five years.
Emergency Ordinance No. 31 of March 13, 2002[...]
Article 3. – (1) Establishing a fascist, racist or xenophobic organisation is punishable by imprisonment from 5 to 15 years and the loss of certain rights.
[...]
Article 4. – (1) The dissemination, sale or manufacture of symbols either fascist, racist or xenophobic, and possession of such symbols is punished with imprisonment from 6 months to 5 years and the loss of certain rights.
[...]
Article 5. – Promoting the culture of persons guilty of committing a crime against peace and humanity or promoting fascist, racist or xenophobic ideology, through propaganda, committed by any means, in public, is punishable by imprisonment from 6 months to 5 years and the loss of certain rights.
Article 6. – Denial of the Holocaust in public, or to the effects thereof is punishable by imprisonment from 6 months to 5 years and the loss of certain rights.[57]
Russia
In May 2014, Russia's President Vladimir Putin signed a law making the denial of Nazi crimes and "wittingly spreading false information about the activity of the USSR during the years of World War Two" or portraying Nazis as heroes a criminal offence.[58][59]
Slovakia
In Slovakia, Holocaust denial has been a crime since 2001 (law 485/2001), and the penal law (300/2005) specifies in §422d that "who publicly denies, denies, approves or tries to justify the Holocaust, crimes of regimes based on fascist ideology, crimes of regimes based on communist ideology or crimes of other similar movements that use violence, the threat of violence or the threat of other serious harm with the aim of suppressing the fundamental rights and freedoms of persons shall be punished by imprisonment of six months to three years".
Spain
Genocide denial was illegal in Spain until the Constitutional Court of Spain ruled that the words "deny or" were unconstitutional in its judgement of November 7, 2007.[60] As a result, Holocaust denial is legal in Spain, although justifying the Holocaust or any other genocide is an offence punishable by imprisonment in accordance with the constitution.[61]
PENAL CODE- BOOK II, TITLE XXIV Crimes against the International Community
Chapter II: Crimes of genocide – Article 6071.1. Those who, with the intention to total or partially destroy a national, ethnic, racial or religious group, perpetrate the following acts, will be punished:
- 1) With the prison sentence of fifteen to twenty years, if they killed to some of its members.
- If the fact two or more aggravating circumstances concurred in, the greater punishment in degree will prevail.
- 2) With the prison of fifteen to twenty years, if they sexually attacked to some of members [of the group] or produced some of the injuries anticipated in article 149.
- 3) With prison sentence of eight to fifteen years, if they subjected the group or anyone of its individuals to conditions of existence that put their lives in danger or seriously disturbed their health, or when they produced some to them of the injuries anticipated in article 150.
- 4) With the same punishment, if they carried out [unavoidable] displacements of the group or their members, they adopted any measurement that tend to prevent their sort of life or reproduction, or transferred by force individuals from a group to another one.
- 5) With imprisonment of four to eight years, if they produced any other injury different from the ones indicated in numbers 2) and 3) of this section.
2. The diffusion by any means of ideas or doctrines that
deny orjustify the crimes in the previous section of this article, or tries the rehabilitation of regimes or institutions which they protect generating practices of such, will be punished with a prison sentence of one to two years.[62]
Switzerland
Holocaust denial is not expressly illegal in Switzerland, but the denial of genocide and other crimes against humanity is an imprisonable offence.
Art. 261bis 1Racial discrimination
Whoever publicly, by word, writing, image, gesture, acts of violence or any other manner, demeans or discriminates against an individual or a group of individuals because of their race, their ethnicity or their religion in a way which undermines human dignity, or on those bases, denies, coarsely minimizes or seeks to justify a genocide or other crimes against humanity [...] shall be punished with up to three years' imprisonment or a fine.[63]
European Union
The European Union's Executive Commission proposed a European Union-wide anti-racism xenophobia law in 2001, which included the criminalization of Holocaust denial. On July 15, 1996, the Council of the European Union adopted the Joint action/96/443/JHA concerning action to combat racism and xenophobia.[64][65] During the German presidency there was an attempt to extend this ban.[66] Full implementation was blocked by the United Kingdom and the Nordic countries because of the need to balance the restrictions on voicing racist opinions against the freedom of expression.[67] As a result, a compromise has been reached within the EU and while the EU has not prohibited Holocaust denial outright, a maximum term of three years in jail is optionally available to all member nations for "denying or grossly trivialising crimes of genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes".[68][69]
The EU extradition policy regarding Holocaust denial was tested in the UK during the 2008 failed extradition case brought against the suspected Holocaust denier Frederick Toben[70] by the German government. As there is no specific crime of Holocaust denial in the UK, the German government had applied for Toben's extradition for racial and xenophobic crimes. Toben's extradition was refused by the Westminster Magistrates' Court, and the German government withdrew its appeal to the High Court.
European Union Framework Decision for Combating Racism and Xenophobia (2007)The text establishes that the following intentional conduct will be punishable in all EU Member States:
- - Publicly inciting to violence or hatred, even by dissemination or distribution of tracts, pictures or other material, directed against a group of persons or a member of such a group defined by reference to race, colour, religion, descent or national or ethnic origin.
- - Publicly condoning, denying or grossly trivialising
- - crimes of genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes as defined in the Statute of the International Criminal Court (Articles 6, 7 and 8) directed against a group of persons or a member of such a group defined by reference to race, colour, religion, descent or national or ethnic origin, and
- - crimes defined by the Tribunal of Nuremberg (Article 6 of the Charter of the International Military Tribunal, London Agreement of 1945) directed against a group of persons or a member of such a group defined by reference to race, colour, religion, descent or national or ethnic origin.
Member States may choose to punish only conduct which is either carried out in a manner likely to disturb public order or which is threatening, abusive or insulting.
The reference to religion is intended to cover, at least, conduct which is a pretext for directing acts against a group of persons or a member of such a group defined by reference to race, colour, descent, or national or ethnic origin.
Member States will ensure that these conducts are punishable by criminal penalties of a maximum of at least between 1 and 3 years of imprisonment.[71]
Prosecutions and convictions
Laws against Holocaust denial have been enforced in most jurisdictions that have them. Convictions and sentencings include:
| Date | Name | Country where the sentence was pronounced | Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| September 1987, June 1999, April 2016 | Jean-Marie Le Pen | France, Germany | fines of €183,000 (1987), €6,000 (1999)[72] and €30,000 (2016)[73] |
| Feb. 27, 1998 | Roger Garaudy | France | 6 months' imprisonment (suspended), ₣240,000 (€37,500) fine[74] |
| Jul. 21, 1998 | Jürgen Graf | Switzerland | 15 months' imprisonment (fled Switzerland to avoid sentence)[75] |
| Jul. 21, 1998 | Gerhard Förster | Switzerland | 12 months' imprisonment, disgorgement[76] |
| April 8, 1999 | Fredrick Töben | Australia | 7 months' imprisonment Mannheim, Germany – retrial – 2011 indefinitely stayed by judge Dr Meinerzhagen. October 1 – November 19, 2008, London, extradition to Mannheim, Germany, on European Arrest Warrant issued by Germany, failed. August 15 – November 12, 2009, Adelaide, Australia – for contempt of court because he refused to stop questioning the Holocaust's 3 basics: 6 million, systematic state extermination, gas chambers as murder weapon. |
| May 27, 1999 | Jean Plantin | France | 6 months' imprisonment (suspended), fine, damages[77] |
| Apr. 11, 2000 | Gaston-Armand Amaudruz | Switzerland | 1 year's imprisonment, damages[78] |
| Feb. 20, 2006 | David Irving | Austria | 3 years' imprisonment.[79] Released and deported after serving 13 months. |
| Mar. 15, 2006 | Germar Rudolf | Germany | 2½ years' imprisonment[80] |
| Oct. 3, 2006 | Robert Faurisson | France | €7,500 fine, 3 months' probation[81] |
| Feb. 15, 2007 | Ernst Zündel | Germany | 5 years' imprisonment[82] |
| Nov. 8, 2007 | Vincent Reynouard | France | 1 year's imprisonment and a fine of 10,000 euros[83] |
| Jan. 14, 2008 | Wolfgang Fröhlich | Austria | 6 years' imprisonment (third offence)[84] |
| Jan. 15, 2008 | Sylvia Stolz | Germany | 3½ years' imprisonment[85] |
| Mar. 11, 2009 | Horst Mahler | Germany | 5 years' imprisonment[86] |
| Oct. 23, 2009 | Dirk Zimmerman | Germany | 9 months' imprisonment[87] |
| Oct. 27, 2009 | Richard Williamson | Germany | €12,000 fine[88] (later overturned) |
| Jan. 31, 2013 | Gyorgy Nagy | Hungary | 18-month suspended jail sentence[89] |
| Feb. 11, 2015 | Vincent Reynouard | France | 2 years' imprisonment[90] |
| Nov. 12, 2015 | Ursula Haverbeck | Germany | 10 months' imprisonment[91] |
See also
References
- ↑ D D Guttenplan, Should Freedom of Speech Stop at Holocaust Denial? Archived January 15, 2008, at the Wayback Machine., Index of Free Expression, 2005.
- ↑ Whine, Michael (Spring 2008), Expanding Holocaust Denial and Legislation Against It, Jewish Political Studies Review
- ↑ János Kis: Szólássabadság és náci beszéd, Népszabadság, March 30, 1996.
- ↑ Fogadatlan prókátorok – A gárdaítélet félreértelmezéseiről, Magyar Narancs, July 23, 2009
- ↑ "Alkotmánybíróság - Kezdőlap" (PDF). Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- ↑ X. v. Federal Republic of Germany (European Commission of Human Rights 16 July 1982).
- ↑ Lehideux and Isorni v. France, 1998-VII, no. 92; application number 24662/94, case number 55/1997/839/1045 (European Court of Human Rights 23 September 1998).
- ↑ Faurisson v France, 2 BHRC UN Doc. CCPR/C/58/D/550/1993, 1 (United Nations Human Rights Committee 1996).
- ↑ "Is There a New Anti-Semitism? A Conversation with Raul Hilberg". Logos. 6 (1–2). Winter–Spring 2007. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
I have come to the conclusion, not once but several times, that, as far as I am concerned, I do not agree with legislation that makes it illegal to utter pronouncements claiming that there was no Holocaust. I do not want to muzzle any of this because it is a sign of weakness not of strength when you try to shut somebody up.
- ↑ Garton Ash, Timothy (19 October 2006). "This is the moment for Europe to dismantle taboos, not erect them". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ Singer, Peter (1 March 2006). "David Irving has a right to free speech, too". JPost.com. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
- ↑ Chomsky, Noam (28 February 1981). "His Right to Say It". The Nation. Retrieved 30 July 2012.
[I]t is elementary that freedom of expression (including academic freedom) is not to be restricted to views of which one approves, and that it is precisely in the case of views that are almost universally despised and condemned that this right must be most vigorously defended.
- ↑ Adam Lebor (March 25, 2010), A bad law against Holocaust denial, Jewish Chronicle
- ↑ Chomsky, Noam. "His Right to Say It". The Noam Chomsky Website. Retrieved 16 February 2015.
- ↑ Ben Collins. "George Brandis: Holocaust Denial Would Not Become Legal Under My New Laws". Business Insider Australia. Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- ↑ "Racial Discrimination Act changes would allow Holocaust denial, says Shane Rattenbury". The Age. Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- ↑ "Letter to HREOC, Oct 1998". Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- ↑ "Verbotsgesetz 1945 in der Fassung des NSG 1947" (in German). Austrian Research Centre for Post-War Trials. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ "Verfassungsgesetz vom 8. Mai 1945 über das Verbot der NSDAP (Verbotsgesetz 1947) in der Fassung der Verbotsgesetznovelle 1992" (in German). Austrian Research Centre for Post-War Trials. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ "23 MARS 1995. – Loi tendant à réprimer la négation, la minimisation, la justification ou l'approbation du génocide commis par le régime national-socialiste allemand pendant la seconde guerre mondiale." (in French). juridat.be. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ PORICANJE GENOCIDA PROGLASITI KRIVIČNIM DJELOM, Prof. dr. Fikret Karcic, Preporod, 5.7.2007 Archived September 19, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "24sata.info - Stranka za BiH: Krivičnim zakonom BiH obuhvatiti genocid i holokaust". Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- ↑ Dzidic, Denis (27 January 2009). "Bosnia's Etnic Tensions Delay Holocaust Denial Law". Balkan Investigative Reporting Network. Archived from the original on 2009-09-16. Retrieved 2016-06-28.
- ↑ "Punishment for Holocaust Denial Incorporated in Czech Law". Permanent Representation of the Czech Republic to the European Union. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ "Communication No 550/1993 : France. 16/12/96. CCPR/C/58/D/550/1993. (Jurisprudence)". United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ ECHR, Marais c. France, n° 31159/96, 25 June 1996; Garaudy v. France, No 65831/01, 24 June 2003.
- ↑ Libération, La loi contre la négation du génocide arménien est censurée
- ↑ Constitutional Council, Decision no. 2012-647 DC of 28 FEBRUARY 2012
- ↑ Décision n° 2015-512 QPC du 8 janvier 2016
- ↑ "Loi n°90-615 du 13 juillet 1990 tendant à réprimer tout acte raciste, antisémite ou xénophobe" (in French). Légifrance. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ Timmermann, Wibke K (2014). Incitement in International Law. Abingdon, Oxon, England: Routledge. p. 139. ISBN 9781138020801.
- ↑ Shoshan, Nitzan (2008), Reclaiming Germany: Young Right Extremists, the Return of the Nation, and the State of Politics on the Streets of East Berlin, 1, Chicago, Illinois: The University of Chicago, p. 183
- 1 2 3 4 Bohlander, Michael (1998), Bundesministerium der Justiz und für Verbraucherschutz: GERMAN CRIMINAL CODE [Federal Ministry of Justice and Consumer Protection: GERMAN CRIMINAL CODE], Federal Ministry of Justice, Germany, para. 130
- 1 2 3 4 Bundesministerium der Justiz und für Verbraucherschutz: Strafgesetzbuch [Federal Ministry of Justice and Consumer Protection: Criminal Code] (in German), Federal Ministry of Justice, Germany, para. 130
- ↑ "§ 6 Völkermord" (in German). Bundesministerium der Justiz. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ "§ 189 Verunglimpfung des Andenkens Verstorbener" (in German). Bundesministerium der Justiz. Retrieved 2016-06-26.
- ↑ "§ 194 Strafantrag" (in German). Bundesministerium der Justiz. Retrieved 2009-05-29.
- ↑ "Greece Passes Bill Making Holocaust-Denial Illegal, Tougher Anti-Racism Laws". Website. Reuters. 9 September 2014. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ "Hungary criminalises holocaust denial". The Independent. Associated Press. 23 February 2010. Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- ↑ President Sólyom signs Holocaust denial bill, politics.hu
- ↑ Hungary equates Communism to Nazism, rt.com
- ↑ Bennettsmith, Meredith (February 2, 2013). "Hungary Criminalizes Holocaust Denial, Orders Man To Visit Memorial". Huffington Post.
- ↑ "A Kuruc.info cikke az első, amit betiltottak Magyarországon". ORIGO. January 14, 2015.
- ↑ "Jogsegélyt kínál a TASZ a Kuruc.info-nak". ORIGO. January 15, 2015.
- ↑ ""Jogsegélyt ajánl a Kuruc.infónak a TASZ" – nem kérünk belőle". Kuruc.info. January 15, 2015.
- ↑ "Denial of Holocaust -Prohibition- Law- 5746-1986-". Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Retrieved 2009-05-30.
- ↑ "Italy Approves Law Making Holocaust Denial a Crime". Newspaper. Haaretz. 25 January 2007. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ "Liechtensteinisches Landesgesetzblatt" (in German). LLV Government Portal. Retrieved 2009-05-31.
- ↑ "LIETUVOS RESPUBLIKOS BAUDŽIAMASIS KODEKSAS" (in Lithuanian). Retrieved 2012-01-22.
- 1 2 3 "LUXEMBOURG – National Legal Measures". Council of Europe. Retrieved 2009-05-31.
- ↑ "Denying holocaust 'not a crime': VVD". DutchNews.nl. May 27, 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-31.
- ↑ "Dutch Liberal leader: Holocaust Denial should Not be Crime". tripolipost.com. May 29, 2009. Archived from the original on July 17, 2011. Retrieved 2009-05-31.
- ↑ "Wetboek van Strafrecht (Sr), Artikel 137c" (in Dutch). www.wetboek-online.nl. Retrieved 2009-05-31.
- ↑ "Wetboek van Strafrecht (Sr), Artikel 137d" (in Dutch). www.wetboek-online.nl. Retrieved 2009-05-31.
- ↑
- (in English) old Act of 18 December 1998 on the Institute of National Remembrance – Commission for Prosecution of Crimes against the Polish Nation Archived October 20, 2007, at the Wayback Machine.. Institute of National Remembrance. Retrieved May 31, 2009.
- (in Polish) Ustawa z dnia 18 grudnia 1998 r. o Instytucie Pamięci Narodowej – Komisji Ścigania Zbrodni przeciwko Narodowi Polskiemu Archived September 30, 2007, at the Wayback Machine.. Sejm of the Republic of Poland, click tekst ujednolicony to see act. Retrieved May 31, 2009.
- ↑ "Código Penal português (texto oficial)" (PDF) (in Portuguese). Diário da República. September 4, 2007. pp. 57–58. Retrieved 2009-05-31.
- ↑ "ORDONANTA DE URGENTA nr. 31 din 13 martie 2002" (PDF) (in Romanian). Romanian Government Department for Interethnic Relations. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 28, 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-31.
- ↑ "Holocaust Deniers in Russia Now Face Five Years in Prison Reuters". Website. Reuters. 5 May 2014. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ "Russia moves to criminalize Holocaust denial". News Service. Russia Today. 26 March 2013. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ "Tribunal Constitucional". Constitutional Court of Spain. November 7, 2007. Retrieved 2012-02-19.
- ↑ Uni, Assaf (November 10, 2007). "Spanish court rules out jail sentences for Holocaust denial". Haaretz. Retrieved 2009-06-01.
- ↑ "Código Penal" (in Spanish). juridicas.com. Retrieved 2015-01-08.
- ↑ "SR 311.0 Art. 261bis Rassendiskriminierung (Schweizerisches Strafgesetzbuch)" (in German). Swiss Confederation. Retrieved 2009-06-01.
- ↑ Joint action to combat racism and xenophobia. Europa.eu. July 27, 2005. Retrieved June 2007.
- ↑ 31996F0443. Eur-lex.Europa.eu. July 24, 1996. Retrieved June 2007.
- ↑ "Push for EU Holocaust denial ban", BBC News, January 15, 2007. Retrieved 2009-11-15.
- ↑ "EU diplomats: Ban on Holocaust denial won't curb civil liberties", Haaretz, April 17, 2004. Retrieved 2009-11-15.
- ↑ "EU agrees new racial hatred law", BBC News, April 19, 2007. Retrieved 2009-11-15.
- ↑ Bilefsky, Dan. "EU adopts measure outlawing Holocaust denial", The New York Times, April 19, 2007. Retrieved 2009-11-15.
- ↑ "Suspected-Holocaust-denier-Dr-Gerald-Toben-wins-extradition-fight". The Daily Telegraph. London: telegraph.co.uk. October 29, 2008. Retrieved 2008-04-14.
- ↑ "EU Justice Ministers agree on racism and xenophobia proposal". European Union @ United Nations. April 19, 2007. Archived from the original on July 20, 2011. Retrieved 2009-06-01.
- ↑ "Le Pen Convicted for Racial Hatred", Associated Press, June 2, 1999. Retrieved 2009-11-14.
- ↑ "Le Pen fined over Holocaust remarks". BBC. BBC. Retrieved 6 April 2016.
- ↑ "Writer fined for Holocaust writings", BBC News, February 27, 1998. Retrieved 2009-11-15.
- ↑ Black, Edwin. "Denial of Holocaust nothing new in Iran / Ties to Hitler led to plots against British and Jews", San Francisco Chronicle, January 8, 2006.
- ↑ "Holocaust Revisionists Will Serve Time", The Spokesman-Review (Associated Press), July 21, 1998. Retrieved 2009-11-15.
- ↑ Francillon, Claude. "A Lyon, l'éditeur chômeur Jean Plantin jugé pour contestation de crimes contre l'humanité", Le Monde, September 9, 1999. Retrieved 2009-11-15.
- ↑ "Holocaust revisionist sentenced", BBC News, April 11, 2000. Retrieved 2009-11-15.
- ↑ Traynor, Ian. "Irving jailed for denying Holocaust", The Guardian, February 21, 2006. Retrieved 2009-11-13.
- ↑ "German Holocaust Denier Imprisoned for Inciting Racial Hatred", Deutsche Welle, March 16, 2007. Retrieved 2009-11-14.
- ↑ Stalinsky, Steven. "The Influence of a Man Who Denies the Holocaust" New York Sun, October 12, 2006. Retrieved 2009-11-14.
- ↑ "Holocaust denier in Germany sentenced to five years in prison – Europe – International Herald Tribune", The New York Times, February 15, 2007. Retrieved 2009-11-14
- ↑ Valérie Igounet, Robert Faurisson. Portrait d'un négationniste, Paris, 2012, p.382 (ISBN 978-2207259986)
- ↑ "Austrian Holocaust denier gets six-and-a-half years in prison" Archived January 7, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. European Jewish Press, January 14, 2008. Retrieved 2009-11-15.
- ↑ "German Neo-Nazi Lawyer Sentenced for Denying Holocaust" Deutsche Welle, January 14, 2008. Retrieved 2009-11-15.
- ↑ "Horst Mahler zu hoher Haftstrafe verurteilt" Archived April 14, 2009, at the Wayback Machine., Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung, March 11, 2009. Retrieved 2009-11-14.
- ↑ "Report on the Trial of Dirk Zimmerman (Germany)", Occidental Quarterly, October 25, 2009. Retrieved 2009-11-15.
- ↑ "German court tells holocaust denier he must face trial", Deutsche Welle, November 10, 2009. Retrieved 2009-11-14.
- ↑ "Hungary orders Holocaust denier to visit Auschwitz ", The Jerusalem Post, February 3, 2013. Retrieved 2013-07-06.
- ↑ "Le négationniste Vincent Reynouard de nouveau condamné à la prison ferme", Le Monde, February 11, 2015. Retrieved 2015-02-15.
- ↑ "Amtsgericht Hamburg: 87-jährige Holocaust-Leugnerin zu zehn Monaten Haft verurteilt", Der Spiegel, November 12, 2015. Retrieved 2015-11-12.
External links
- Jonathan Josephs, Holocaust Denial Legislation – A justifiable infringement of freedom of speech? (Université Libre de Bruxelles; Working Papers du Centre Perelman de philosophie du droit, n° 2008/3)
- Voices on Antisemitism Interview with Brigitte Zypries from the U.S. Holocaust Memorial Museum