Recurrent laryngeal nerve
| Recurrent laryngeal nerve | |
|---|---|
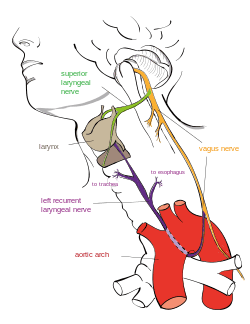 Course of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve | |
 | |
| Details | |
| From | vagus nerve |
| Innervates |
larynx posterior cricoarytenoid lateral cricoarytenoid arytenoid thyroarytenoid aryepiglottis esophagus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus laryngeus recurrens |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | n_05/12566073 |
| TA | A14.2.01.166 |
| FMA | 6246 |
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) is a branch of the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recurrent laryngeal nerves, right and left, in the human body. The right and left nerves are not symmetrical, with the left nerve looping under the aortic arch, and the right nerve looping under the right subclavian artery then traveling upwards. They both travel alongside of the trachea. Additionally, the nerves are one of few nerves that follow a recurrent course, moving in the opposite direction to the nerve they branch from, a fact from which they gain their name.
The recurrent laryngeal nerves supply sensation to the larynx below the vocal cords, gives cardiac branches to the deep cardiac plexus, and branches to the trachea, esophagus and the inferior constrictor muscles. The posterior cricoarytenoid muscles, the only muscles that can open the vocal cords, are innervated by this nerve.
The recurrent laryngeal nerves are the nerves of the sixth pharyngeal arch. The existence of the recurrent laryngeal nerve was first documented by the physician Galen.
Structure
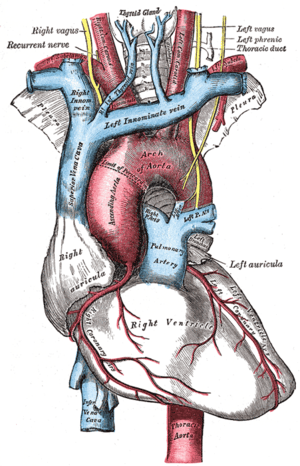
The recurrent laryngeal nerves branch from the vagus nerve, relative to which they get their names; the term "recurrent" from Latin: re- (back) and currere (to run),[1] indicates they run in the opposite direction to the vagus nerves from which they branch.[2] The vagus nerves run down into the thorax, and the recurrent laryngeal nerves run up to the larynx.[3]:930–931
The vagus nerves, from which the recurrent laryngeal nerves branch, exit the skull at the jugular foramen and travel within the carotid sheath alongside the carotid arteries through the neck. The recurrent laryngeal nerves branch off the vagus, the left at the aortic arch, and the right at the right subclavian artery. The left RLN passes in front of the arch, and then wraps underneath and behind it. After branching, the nerves typically ascend in a groove at the junction of the trachea and esophagus.[4]:1346–1347 They then pass behind the posterior, middle part of the outer lobes of the thyroid gland and enter the larynx underneath the inferior constrictor muscle,[3]:918 passing into the larynx just posterior to the cricothyroid joint.[5] The terminal branch is called the inferior laryngeal nerve.[6]:19
Unlike the other nerves supplying the larynx, the right and left RLNs lack bilateral symmetry.[7] The left RLN is longer than the right, because it crosses under the arch of the aorta at the ligamentum arteriosum.[4]:1346–1347
Nucleus
The somatic motor fibers that innervate the laryngeal and pharyngeal muscles are located in the nucleus ambiguus and emerge from the medulla in the cranial root of the accessory nerve. Fibers cross over to and join the vagus nerve in the jugular foramen.[8]:86–88 Sensory cell bodies are located in the inferior jugular ganglion,[9] and the fibers terminate in the solitary nucleus.[8]:86–88 Parasympathetic fibers to segments of the trachea and esophagus in the neck originate in the dorsal nucleus of the vagus nerve.[9]
Development
During human and all vertebrate development, a series of pharyngeal arch pairs form in the developing embryo. These project forward from the back of the embryo towards the front of the face and neck. Each arch develops its own artery, nerve that controls a distinct muscle group, and skeletal tissue. The arches are numbered from 1 to 6, with 1 being the arch closest to the head of the embryo, and the fifth arch only existing transiently.[10]:318–323
Arches 4 and 6 produce the laryngeal cartilages. The nerve of the sixth arch becomes the recurrent laryngeal nerve. The nerve of the fourth arch gives rise to the superior laryngeal nerve. The arteries of the fourth arch, which project between the nerves of the fourth and sixth arches, become the left-sided arch of the aorta and the right subclavian artery. The arteries of the sixth arch persists as the ductus arteriosus on the left, and is obliterated on the right.[10]:318–323
After birth, the ductus arteriosus regresses to form the ligamentum arteriosum. During growth, these arteries descend into their ultimate positions in the chest, creating the elongated recurrent paths.[10]:318–323
Variation
In roughly 1 out of every 100–200 people, the right inferior laryngeal nerve is nonrecurrent, branching off the vagus nerve around the level of the cricoid cartilage. Typically, such a configuration is accompanied by variation in the arrangement of the major arteries in the chest; most commonly, the right subclavian artery arises from the left side of the aorta and crosses behind the esophagus. A left nonrecurrent inferior laryngeal nerve is even more uncommon, requiring the aortic arch be on the right side, accompanied by an arterial variant which prevents the nerve from being drawn into the chest by the left subclavian.[11]:10, 48
In about four people out of five, there is a connecting branch between the inferior laryngeal nerve, a branch of the RLN, and the internal laryngeal nerve, a branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. This is commonly called the anastomosis of Galen (Latin: ansa galeni), even though anastomosis usually refers to a blood vessel,[12][13]:35 and is one of several documented anastomoses between the two nerves.[14]
As the recurrent nerve hooks around the subclavian artery or aorta, it gives off several branches. There is suspected variability in the configuration of these branches to the cardiac plexus, trachea, esophagus and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle.[15]
Function
The recurrent laryngeal nerves control all intrinsic muscles of the larynx except for the cricothyroid muscle.[15][lower-alpha 1] These muscles act to open, close, and adjust the tension of the vocal cords, and include the posterior cricoarytenoid muscles, the only muscle to open the vocal cords.[16]:10–11 The nerves supply muscles on the same side of the body, with the exception of the interarytenoid muscle, which is innervated from both sides.[15]
The nerves also carry sensory information from the mucous membranes of the larynx below the lower surface of the vocal fold,[17]:847–9 as well as sensory, secretory and motor fibres to the cervical segments of the esophagus and the trachea.[8]:142–144
Clinical significance
Injury
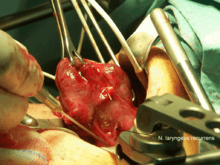
The recurrent laryngeal nerves may be injured as a result of trauma, during surgery, as a result of tumour spread, or due to other means.[16]:12 Injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerves can result in a weakened voice (hoarseness) or loss of voice (aphonia) and cause problems in the respiratory tract.[16]:11–12 Injury to the nerve may paralyze the posterior cricoarytenoid muscle on the same side. This is the sole muscle responsible for opening the vocal cords, and paralysis may cause difficulty breathing (dyspnea) during physical activity.[18] Injury to both the right and left nerve may result in more serious damage, such as the inability to speak. Additional problems may emerge during healing, as nerve fibres that re-anastamose may result in vocal cord motion impairment, uncoordinated movements of the vocal cord.[16]:12–13
Surgery
The nerve receives close attention from surgeons since during neck surgery, especially thyroid and parathyroid surgery, the nerve is at risk for injury.[4] Nerve damage can be assessed by laryngoscopy, during which a stroboscopic light confirms the absence of movement in the affected side of the vocal cords. The right recurrent laryngeal nerve is more susceptible to damage during thyroid surgery because it is close to the bifurcation of the right inferior thyroid artery, variably passing in front of, behind, or between the branches.[17]:820–1 The nerve is permanently damaged in 0.3–3% of thyroid surgery, and transiently in 3–8% of surgeries, and is one of the leading causes of medicolegal issues for surgeons.[19]
Tumors
The RLN may be compressed by tumors. Studies have shown that 2–18% of lung cancer patients develop hoarseness because of recurrent laryngeal nerve compression, usually left-sided.[20] This is associated with worse outcomes, and when found as a presenting symptom, often indicates inoperable tumors. The nerve may be severed intentionally during lung cancer surgery in order to fully remove a tumor.[21]:330
Other disease
In Ortner's syndrome or cardiovocal syndrome, a rare cause of left recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy, expansion of structures within the heart or major blood vessels impinges upon the nerve, causing symptoms of unilateral nerve injury.[22]
Other animals
Horses are subject to equine recurrent laryngeal neuropathy, a disease of the axons of the recurrent laryngeal nerves. The cause is not known, although a genetic predisposition is suspected. The length of the nerve is a factor since it is more common in larger horses, and the left side is affected almost exclusively. As the nerve cells die, there is a progressive paralysis of the larynx, causing the airway to collapse. The common presentation is a sound, ranging from a musical whistle to a harsh roar or heaving gasping noise (stertorous), accompanied by worsening performance. The condition is incurable, but surgery can keep the airway open. Experiments with nerve grafts have been tried.[23]:421–426
Although uncommon in dogs, bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve disease may be the cause of wheezing (stridor) when middle-aged dogs inhale.[24]:771
In sauropod dinosaurs, the vertebrates with the longest necks, the total length of the vagus nerve and recurrent laryngeal nerve would have been up to 28 metres (92 ft) long in Supersaurus, but these would not be the longest neurons that ever existed: the neurons reaching the tip of the tail would have exceeded 30 metres (98 ft).[25]
Evidence of evolution
The extreme detour of the recurrent laryngeal nerves, about 4.6 metres (15 ft) in the case of giraffes,[26]:74–75 is cited as evidence of evolution. The nerve's route would have been direct in the fish-like ancestors of modern tetrapods, traveling from the brain, past the heart, to the gills (as it does in modern fish). Over the course of evolution, as the neck extended and the heart became lower in the body, the laryngeal nerve was caught on the wrong side of the heart. Natural selection gradually lengthened the nerve by tiny increments to accommodate, resulting in the circuitous route now observed.[27]:360–362
History
Roman physician Galen demonstrated the nerve course and the clinical syndrome of recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis, noting that pigs with the nerve severed were unable to squeal. Galen named the nerve the recurrent nerve, and described the same effect in two human infants who had undergone surgery for goiter.[16]:7–8[28] In 1838, five years before he would introduce the concept of homology to biology, anatomist Richard Owen reported upon the dissection of three giraffes, including a description of the full course of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve.[29][30] Anatomists Andreas Vesalius and Thomas Willis described the nerve in what is now regarded as an anatomically standard description, and doctor Frank Lahey documented a way for its interoperative identification during thyroid operations.[31]
Notes
References
- ↑ "Recur". Free Dictionary. Merriam-Webster. Retrieved March 1, 2013.
- ↑ "Recurrent". Medical definition and more. Merriam-Webster. Retrieved March 1, 2013.
- 1 2 Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- 1 2 3 F. Charles Brunicardi; F. Brunicardi; Dana Andersen; E. Pollock Raphael; Timothy Billiar; David Dunn; John Hunter; Jeffrey Matthews; Raphael E. Pollock (September 11, 2009). Schwartz's Principles of Surgery (9th ed.). McGraw Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-154769-7.
- ↑ Agur, A. M. R.; Dalley, Arthur F. (2009). Grant's Atlas of Anatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 770. ISBN 978-0-7817-7055-2.
- ↑ Ross, Lawrence M.; Lamperti, Edward D. (2006). Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: Neck and Internal Organs. Thieme. ISBN 978-1-58890-443-0.
- ↑ Aronson, Arnold Elvin (2009). Clinical Voice Disorders. Thieme. p. 74. ISBN 978-1-58890-662-5.
- 1 2 3 Schulte, Erik; Schumacher, Udo; Rude, Jürgen (2007). Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: Head and Neuroanatomy. Thieme. ISBN 978-1-58890-441-6.
- 1 2 Alberstone, Cary D. (2009). Anatomic Basis of Neurologic Diagnosis. Thieme. pp. 260–261. ISBN 978-0-86577-976-1.
- 1 2 3 Larsen, William J. (1993). Human embryology. Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 0-443-08724-5. Retrieved February 26, 2013.
- ↑ Quan-Yang Duh; Orlo H. Clark; Electron Kebebew (October 14, 2009). Atlas of Endocrine Surgical Techniques. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-1-4160-4844-2. Retrieved March 6, 2013.
- ↑ Naidu, L.; Ramsaroop, L.; Partab, P.; Satyapal, K. S. (2012). "Galen's "Anastomosis" revisited". Clinical Anatomy. 25 (6): 722–728. PMID 22162120. doi:10.1002/ca.22011.
- ↑ Langmore, Susan E. (January 2001). Endoscopic Evaluation and Treatment of Swallowing Disorders. Thieme. ISBN 978-0-86577-838-2.
- ↑ Sañudo, Jose-Ramón; Maranillo, Eva; León, Xavier; Mirapeix, Rosa-María; Orús, Cesar; Quer, Miquel (June 1999). "An anatomical study of anastomoses between the laryngeal nerves". The Laryngoscope. 109 (6): 983–987. PMID 10369294. doi:10.1097/00005537-199906000-00026.
- 1 2 3 Yau, Amy Y.; Verma, Sunil P. (February 20, 2013). Meyers, Arlen D., ed. Laryngeal Nerve Anatomy. Medscape Reference. Retrieved January 5, 2014
- 1 2 3 4 5 Hydman, Jonas (2008). Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury. Stockholm. ISBN 978-91-7409-123-6.
- 1 2 Moore, Keith L (1992). Clinically Oriented Anatomy (3rd ed.). ISBN 0-683-06133-X
- ↑ Hartl, D. M.; Travagli, Jean-Paul; Leboulleux, Sophie; Baudin, Eric; Brasnu, Daniel F.; Schlumberger, Martin (2005). "Current Concepts in the Management of Unilateral Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Paralysis after Thyroid Surgery". Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 90 (5): 3084–3088. ISSN 0021-972X. doi:10.1210/jc.2004-2533.
- ↑ Hayward, Nathan James; Grodski, Simon; Yeung, Meei; Johnson, William R.; Serpell, Jonathan (January 2013). "Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in thyroid surgery: a review". ANZ Journal of Surgery. 83 (1–2): 15–21. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.2012.06247.x.
- ↑ Spiro, Stephen G. (2007). "Initial Evaluation of the Patient With Lung Cancer: Symptoms, Signs, Laboratory Tests, and Paraneoplastic Syndromes: ACCP Evidenced-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (2nd Edition)". CHEST Journal. 132 (3_suppl): 149S. ISSN 0012-3692. doi:10.1378/chest.07-1358.
- ↑ David P. Carbone; Harvey I. Pass; David H. Johnson; John D. Minna (2010). Principles and Practice of Lung Cancer: The Official Reference Text of the IASLC. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-7365-2. Retrieved August 12, 2013.
- ↑ Heikkinen, Jaakko; Milger, Katrin; Alejandre-Lafont, Enrique; Woitzik, Christian; Litzlbauer, Detlef; Vogt, Julia-Franziska; Klußmann, Jens Peter; Ghofrani, Ardeschir; Krombach, Gabriele A.; Tiede, Henning (2012). "Cardiovocal Syndrome (Ortner's Syndrome) Associated with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension and Giant Pulmonary Artery Aneurysm: Case Report and Review of the Literature". Case Reports in Medicine. 2012: 1–5. ISSN 1687-9627. doi:10.1155/2012/230736.
- ↑ Munroe, Graham; Weese, Scott (March 15, 2011). Equine Clinical Medicine, Surgery and Reproduction. Manson Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84076-608-0. Retrieved March 2, 2013.
- ↑ Slatter, Douglas H. (2003). Textbook of Small Animal Surgery. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-0-7216-8607-3. Retrieved March 2, 2013.
- ↑ Wedel, Mathew J. (June 2012). "A Monument of Inefficiency: The Presumed Course of the Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve in Sauropod Dinosaurs". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 57 (2): 251–256. doi:10.4202/app.2011.0019.
- ↑ Mammal Anatomy: An Illustrated Guide. Marshall Cavendish Corporation. 2010. ISBN 0-7614-7882-5.
- ↑ Dawkins, Richard (2009). "11. History Written All Over Us". The Greatest Show on Earth. New York: Free Press. ISBN 978-1-4165-9478-9. Retrieved November 21, 2009.
- ↑ Gross, Charles G. (May 1998). "Galen and the Squealing Pig". Neuroscientist. 4 (3): 216–221. ISSN 1073-8584. doi:10.1177/107385849800400317.
- ↑ Owen, Richard (1841). "Notes on the dissection of the Nubian giraffe". Transactions of the Zoological Society of London. Zoological Society of London. pp. 217–248. Retrieved February 27, 2013
- ↑ Robert James Berry; Anthony Hallam (1986). The Collins Encyclopedia of Animal Evolution. HarperCollins Publishers Limited. pp. 82–83. ISBN 978-0-00-219818-9. Retrieved February 27, 2013.
- ↑ Ardito, Guglielmo; Revelli, Luca; D'Alatri, Lucia; Lerro, Valentina; Guidi, Maria Lavinia; Ardito, Francesco (February 2004). "Revisited anatomy of the recurrent laryngeal nerves". The American Journal of Surgery. 187 (2): 249–253. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2003.11.001.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 21:04-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (X)
- Dissection of a giraffe displaying the laryngeal nerve (youTube)