Magic lantern

The magic lantern, also known by its Latin name lanterna magica, is an early type of image projector employing pictures on sheets of glass (originally painted, but later also printed or as photographic plates), a lens, and a bright light source. It was mostly developed in the 17th century and commonly used for entertainment purposes. It was increasingly applied to educational purposes during the 19th century and was in wide use until the mid-20th century, when a smaller-format version for photographs on film, marketed and commonly known as a slide projector, superseded it.
Technology
Apparatus

The magic lantern used a concave mirror in back of a light source to direct as much of the light as possible through a small rectangular sheet of glass—a "lantern slide"—on which was the image to be projected, and onward into a lens at the front of the apparatus. The lens was adjusted to optimally focus the plane of the slide at the distance of the projection screen, which could be simply a white wall, and it therefore formed an enlarged image of the slide on the screen.[1] Some lanterns, including those of Christiaan Huygens and Jan van Musschenbroek, used 3 lenses.
Slides
Originally the pictures were hand painted on glass slides. Initially figures were rendered with black paint but soon transparent colors were also used. Sometimes the painting was done on oiled paper. Usually black paint was used as a background to block superfluous light, so the figures could be projected without distracting borders or frames. Many slides were finished with a layer of transparent lacquer, but in a later period cover glasses were also used to protect the painted layer.[2] Most hand-made slides were mounted in wood frames with a round or square opening for the picture.[3]
After 1820 the manufacturing of hand colored printed slides started, often making use of decalcomania transfers.[4] Many manufactured slides were produced on strips of glass with several pictures on them and rimmed with a strip of glued paper.
The first photographic lantern slides, called "Hyalotypes", were invented by the German-born brothers Ernst Wilhelm (William) and Friedrich (Frederick) Langenheim in 1848 in Philadelphia and patented in 1850.[5][6][7]
Light sources
Apart from sunlight, the only light sources available at the time of invention in the 17th century were candles and oil lamps, which were very inefficient and produced very dim projected images. The invention of the Argand lamp in the 1790s helped to make the images brighter. The invention of limelight in the 1820s made them very much brighter. The invention of the intensely bright electric arc lamp in the 1860s eliminated the need for combustible gases or hazardous chemicals, and eventually the incandescent electric lamp further improved safety and convenience, although not brightness.[8]
Invention
Several types of projection systems existed before the invention of the magic lantern. For these precursors:
The magic lantern can be seen as a further development of the Camera Obscura. This is a natural phenomenon that occurs when an image of a scene at the other side of a screen (or for instance a wall) is projected through a small hole in that screen as an inverted image (left to right and upside down) on a surface opposite to the opening. It was known at least since the 5th century BCE and experimented with in darkened rooms at least since circa 1000 CE. The use of a lens in the hole has been traced back to circa 1550. The portable camera obscura box with a lens was developed in the 17th century. Dutch inventor Cornelis Drebbel is thought to have sold one to Dutch poet, composer and diplomat Constantijn Huygens in 1622,[9] while the oldest known clear description of a box-type camera is in German Jesuit scientist Gaspar Schott's 1657 book Magia universalis naturæ et artis.
In the 17th century there was an immense interest in optics. The telescope and microscope were invented (in 1608 and the 1620s respectively) and apart from being useful to some scientists, such instruments were especially popular as entertaining curiosities with people who could afford them.[10] The magic lantern would prove to be a perfect successor.
Prominent Dutch scientist Christiaan Huygens, is nowadays widely accepted as the true inventor of the magic lantern. He knew Athanasius Kircher's 1646 edition of Ars Magna Lucis et Umbrae which described a primitive projection system with a focusing lens and text or pictures painted on a concave mirror reflecting sunlight. Christiaan's father Constantijn had been acquainted with Cornelis Drebbel who used some unidentified optical techniques to transform himself and summon wonderful appearances in magical performances. Constantijn Huygens wrote very enthusiastically about a camera obscura device that he got from Drebbel in 1622.

The oldest known document concerning the magic lantern is a page on which Christiaan Huygens made ten small sketches of a skeleton taking off its skull, above which he wrote "for representations by means of convex glasses with the lamp" (translated from French). As this page was found between documents dated in 1659, it is believed to also have been made in 1659.[11] Huygens probably only constructed the lantern to amuse young family members and soon seemed to regret it, as he thought it was too frivolous. In a 1662 letter to his brother Lodewijk he claimed he thought of it as some old "bagatelle" and seemed convinced that it would harm the family's reputation if people found out the lantern came from him. Christiaan had reluctantly sent a lantern to their father, but when he realized that Constantijn intended to show the lantern to the court of King Louis XIV of France at the Louvre, Christiaan asked Lodewijk to sabotage the lantern.[12]
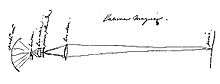
Christiaan initially referred to the magic lantern as "la lampe" and "la lanterne", but in the last years of his life he used the then common term "laterna magica" in some notes. In 1694 he drew the principle of a "laterna magica" with two lenses.[13]

Thomas Rasmussen Walgensten (circa 1627-1681), a mathematician from Gotland, studied at the university of Leyden in 1657-58 and was acquainted with Christiaan Huygens. It is unclear if one was inspired by the other or if they even may have collaborated on the development of the magic lantern. At least from 1664 until 1670 Walgensten was giving magic lantern shows in Paris, Lyon, Rome and Copenhagen,[10] and he "sold such lanterns to different Italian princes in such an amount that they now are almost everyday items in Rome" according to Athanasius Kircher in 1671.[14] In 1670 Walgensten projected an image of Death at the court of King Frederick III of Denmark. This scared some courtiers, but the king dismissed their cowardice and requested to repeat the figure three times. The king died a few days later. After Walgensten died, his widow sold his lanterns to the Danish Royal collection, but they have not been preserved.[10] Walgensten is credited with coining the term "Laterna Magica".[15]

There are probably many gaps in the magic lantern's recorded history. A separate early magic lantern tradition seems to have been developed in southern Germany and includes lanterns with horizontal cylindrical bodies, while Walgensten's lantern and probably Huygens' both had vertical bodies. This tradition can be traced back to 1671 with the arrival of instrument maker Johann Franz Griendel in the city of Nürnberg, which Johann Zahn identified as one of the centers of magic lantern production in 1686. Griendel was indicated as the inventor of the magic lantern by Johann Christoph Kohlhans in a 1677 publication.[16] It has been suggested that this tradition is older and that instrument maker Johann Wiesel (1583-1662) from Augsburg may have been making magic lanterns earlier on and possibly inspired Griendel and even Huygens.[17]
Further history
Although Christiaan Huygens was very critical about his magic lantern, he most likely familiarized several people with the device. In a 1664 letter to Huygens[18], Parisian engineer Pierre Petit asked some specifications because he was trying to construct a magic lantern after seeing one of "the dane" (probably Walgensten). Huygens was also in touch with London optical instrument-maker Richard Reeve.[10] Reeve was soon selling magic lanterns. He demonstrated one in his shop on 17 May 1663 to Balthasar de Monconys[19] and sold one to Samuel Pepys in August 1666.[20][21].


One of Christiaan Huygens' contacts imagined how Athanasius Kircher would use the magic lantern: "If he would know about the invention of the Lantern he would surely frighten the cardinals with specters."[22] Kircher would eventually learn about the existence of the magic lantern via Thomas Walgensten and introduced it as "Lucerna Magica" in the widespread 1671 second edition of his book Ars Magna Lucis et Umbrae.[23] Kircher claimed that Thomas Walgensten reworked his ideas from the previous edition of this book into a better lantern. Kircher described this improved lantern, but it was illustrated in a confusing manner:[24] the pictures seem technically incorrect with both the projected image and the transparencies (H) shown upright (while the text states that they should be drawn in an inverted position), the hollow mirror is too high in one picture and absent in the other, and the lens (I) seems to be placed at the wrong side of the slide. Experiments with a construction as illustrated in Kircher's book proved that it could work as a point light-source projection system.[25] The projected image in one of the illustrations shows a person in purgatory or hellfire and the other depicts Death with a scythe and an hourglass. According to legend Kircher secretly used the lantern at night to project the image of Death on windows of apostates to scare them back into church.[26] Kircher did suggest in his book that an audience would be more astonished by the sudden appearance of images if the lantern would be hidden in a separate room, so the audience would be ignorant of the cause of their appearance.[24]

The earliest reports and illustrations of lantern projections suggest that they were all intended to scare the audience. Pierre Petit, who probably saw a show by Walgensten, called the apparatus "lanterne de peur" (lantern of fear) in a 1664 letter to Huygens.[18] Surviving lantern plates and descriptions from the next decades prove that the new medium was not just used for horror shows, but that all kinds of subjects were projected.

By the 1730s the use of magic lanterns started to become more widespread when travelling showmen, conjurers and storytellers added them to their repertoire. The travelling lanternists were often called Savoyards (they supposedly came from the Savoy region in France) and became a common sight in many European cities.[10]
In France in the 1770s François Dominique Séraphin used magic lanterns to perform his "Ombres Chinoises" (Chinese shadows), a form of shadow play.
Magic lanterns had also become a staple of science lecturing and museum events since Scottish lecturer Henry Moyes’s tour of America in 1785–86, when he recommended that all college laboratories procure one. French writer and educator Stéphanie Félicité, comtesse de Genlis popularized the use of magic lanterns as an educational tool in the late 1700s when using projected images of plants to teach botany. Her educational methods were published in America in English translation during the early 1820s.[27] A type of lantern was constructed by Moses Holden between 1814–15 for illustrating his astronomical lectures.[28]
In 1821 Philip Carpenter's London company, that would become Carpenter and Westley after his death, started manufacturing a sturdy but lightweight and transportable "Phantasmagoria lantern" with an Argand style lamp, which produced high quality projections and was suitable for use in classrooms. Carpenter also developed a "secret" copper plate printing/burning process to mass-produce glass lantern slides with printed outlines, which were then easily and quickly hand painted ready for sale.[29] These "copper-plate sliders" contained three or four very detailed 4" circular images mounted in thin hardwood frames. The first known set The Elements of Zoology became available in 1823, showing over 200 images in 56 frames of zoological figures, classified according to the system of the Swedish scientist Carl Linnaeus. The same year many other slides appeared in the company's catalogue: "The Kings and Queens of England" (9 sliders taken from David Hume’s History of England), "Astronomical Diagrams and Constellations" (9 sliders taken from Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel’s textbooks), "Views and Buildings", Ancient and Modern Costume (62 sliders from various sources).[30] Fifteen sliders of the category "Humorous" provided some entertainment, but the focus on education was obvious and very successful.
The mass production of slides also meant that the magic lantern now became affordable to the common men, opening a market for smaller lanterns with smaller glass sliders which instead of wooden frames usually had colorful strips of paper glued around their edges.
Although the popularity of magic lanterns waned after the introduction of movies in the 1890s, they remained a common medium until slide projectors came into widespread use during the 1950s.
Moving images

The magic lantern was not only a direct ancestor of the motion picture projector as a means for visual storytelling, but it could itself be used to project moving images.
Some suggestion of movement could be achieved by alternating between pictures of different phases of a motion, but most magic lantern "animations" used two glass slides projected together - one with the stationary part of the picture and the other with the part that could be set in motion by hand or by a simple mechanism.
Motion in animated slides was mostly limited to either two phases of a movement or transformation, or a more gradual singular movement (e.g. a train passing through a landscape). These limitations made subjects with repetitive movements popular, like the sails on a windmill turning around or children on a seesaw. Movements could be repeated over and over and could be performed at different speeds.
A common technique that is comparable to the effect of a panning camera makes use of a long slide that is simply pulled slowly through the lantern and usually shows a landscape, sometimes with several phases of a story within the continuous backdrop.
Movement of projected images was also possible by moving the magic lantern itself. This became a staple technique in phantasmagoria shows in the late 18th century, often with the lantern sliding on rails or riding on small wheels and hidden from the view of the audience behind the projection screen.
History
Christiaan Huygens' 1659 sketches (see above) suggest he intended to animate the skeleton to have it take off its head and place it back on its neck. This can be seen as an indication that the very first magic lantern demonstrations may already have included projections of simple animations.[31]
In 1675 German polymath and philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz proposed a kind of world exhibition that would show all kinds of new inventions and spectacles. In a handwritten document he supposed it should open and close with magic lantern shows, including subjects "which can be dismembered, to represent quite extraordinary and grotesque movements, which men would not be capable of making" (translated from French).[32][33]
Several reports of early magic lantern screenings possibly described moving pictures, but are not clear enough to conclude whether the viewers saw animated slides or motion depicted in still images.[31]
In 1698 German engraver and publisher Johann Christoph Weigel described several lantern slides with mechanisms that made glass parts move over one fixed glass slide, for instance by the means of a silk thread or grooves in which the mobile part slides.[34]
By 1709 a German optician and glass grinder named Themme (or Temme) made moving lantern slides, including a carriage with rotating wheels, a cupid with a spinning wheel, a shooting gun and falling bombs. Wheels were cut from the glass plate with a diamond and rotated by a thread that was spun around small brass wheels attached to the wheels. A paper slip mask would be quickly pulled away to reveal the red fiery discharge and the bullet from a shooting gun. Zacharias Conrad von Uffenbach visited Themme's shop and liked the effects, but was disappointed about the very simple mechanisms. Nonetheless he bought seven moving slides, as well as twelve slides with four pictures each, which he thought were delicately painted.[35]
Several types of mechanical slides were described and illustrated in Dutch professor of mathematics, physics, philosophy, medicine, and astronomy Pieter van Musschenbroek's second edition (1739) of Beginsels Der Natuurkunde.[36] Pieter was the brother of Jan van Musschenbroek, the maker of an outstanding magic lantern with excellent lenses and a diaphragm (see illustration above).[31]
In 1770 Edmé-Gilles Guyot described a method of using two slides for the depiction of a storm at sea, with waves on one slide and ships and a few clouds on another. Lanternists could project the illusion of mild waves turning into a wild sea tossing the ships around by increasing the movement of the separate slides. Guyot also detailed how projection on smoke could be used to create the illusion of ghosts hovering in the air, which would become a technique commonly used in phantasmagoria.[31]
Various types of mechanical slides

Various types of mechanisms were commonly used to add movement to the projected image:
- slipping slides: a movable glass plate with one or more figures (or any part of a picture for which movement was desired) was slipped over a stationary one, directly by hand or with a small drawbar (see: Fig. 7 on the illustration by Petrus van Musschenbroek: a tightrope walker sliding across the rope). A common example showed a creature that could move the pupils in its eyes, as if it was looking in all directions. A long piece of glass could show a procession of figures, or a train with several wagons. Quite convincing illusions of moving waves on a seas or lake have also been achieved with this method.[37]
- slipping slides with masking: black paint on portions of the moving plate would mask parts of the underlying image - with a black background - on the stationary glass. This made it possible to hide and then reveal the previous position of a part, for instance a limb, to suggest repetitious movement. The suggested movement would be rather jerky and usually operated quickly. Masking in slides was also often used to create change rather than movement (see: Fig. 6 on the illustration by Petrus van Musschenbroek: a man, his wig and his hat): for instance a person's head could be replaced with that of an animal. More gradual and natural movement was also possible; for instance to make a nose grow very long by slowly moving a masking glass.
- lever slides: the moving part was operated by a lever. These could show a more natural movement than slipping slides and were mostly used for repetitive movements, for instance a woodcutter raising and lowering his axe, or a girl on a swing.[37] (see: Fig. 5 on the illustration by Petrus van Musschenbroek: a drinking man raising and lowering his glass + Fig. 8: a lady curtsying)
- pulley slides: a pulley rotates the moving part and could for instance be used to turn the sails on a windmill[38] (see: fig. 4 on illustration by Van Musschenbroek)
- rack and pinion slides: turning the handle of a rackwork would rotate or lift the moving part and could for instance be used to turn the sails on a windmill or for having a hot air balloon take off and descend. A more complex astronomical rackwork slide showed the then known eight planets and their satellites orbiting around the sun.[37]
- fantoccini slides: jointed figures set in motion by levers, thin rods, or cams and worm wheels. A popular version had a somersaulting monkey with arms attached to mechanism that made it tumble with dangling feet. Named after the Italian word for animated puppets, like marionettes or jumping jacks. Two different British patents for slides with moving jointed figures were granted in 1891.[39]
- a snow effect slide can add snow to another slide (preferably of a winter scene) by moving a flexible loop of material pierced with tiny holes in front of one of the lenses of a double or triple lantern.[40]
Mechanical slides with abstract special effects include:

- the Chromatrope: a slide that produces dazzling colorful geometrical patterns by rotating two painted glass discs in opposite directions, originally with a double pulley mechanism but later usually with a rackwork mechanism.[37][41] It was possibly invented around 1844 by English glass painter and showman Henry Langdon Childe[42][43] and soon added to the program of the Royal Polytechnic Institution.[44][45]
- the Eidotrope: counter-rotating discs of perforated metal or card (or wire gauze or lace), producing swirling Moiré patterns of bright white dots. It was invented by English scientist Charles Wheatstone in 1866.[46][47]
- the Kaleidotrope: a slide with a single perforated metal or cardboard disc suspended on a spiral spring. The holes can be tinted with colored pieces of gelatin. When struck the disc's vibration and rotation sends the colored dots of light swirling around in all sorts of shapes and patterns. The device was demonstrated at the Royal Polytechnic Institution around 1870 and dubbed "Kaleidotrope" when commercial versions were marketed.[48]
- the Cycloidotrope (circa 1865): a slide which had an adjustable stylus bar drawing geometric patterns on sooty glass when hand cranked during projection. The patterns are similar to that produced with a Spirograph.[40]
- a Newton colour wheel slide which, when spinning fast enough, blends seven colours into a white circle[40]
Dissolving views

The effect of a gradual transition from one image to another, known as a dissolve in modern filmmaking, became the basis of a popular type of magic lantern show in England in the 19th century. Typical dissolving views showed landscapes dissolving from day to night or from summer to winter. This was achieved by aligning the projection of two matching images and slowly diminishing the first image while introducing the second image.[37] The subject and the effect of magic lantern dissolving views is similar to the popular Diorama theatre paintings which originated in Paris in 1822. The terms "dissolving views", "dioramic views", or simply "diorama" were often used interchangeably in 19th century magic lantern broadsides.[49]
The effect was reportedly invented by phantasmagoria pioneer Paul de Philipsthal while in Ireland in 1803 or 1804. He thought of using two lanterns to make the spirit of Samuel appear out of a mist in his representation of the Witch of Endor. While working out the desired effect, he got the idea of using the technique with landscapes. A 1812 newspaper about a London performance indicates that De Philipsthal presented what was possibly a relatively early incarnation of a dissolving views show, describing it as a "a series of landscapes (in imitation of moonlight), which insensibly change to various scenes producing a very magical effect.”[50][51]
Another possible inventor is Henry Langdon Childe, who purportedly once worked for De Philipsthal.[51] He is said to have invented the dissolving views in 1807 and to have improved and completed the technique in 1818.[52] The oldest known use of the term "dissolving views" occurs on playbills for Childe's shows at the Adelphi Theatre in London in 1837.[49] Childe further popularized the dissolving views at the Royal Polytechnic Institution in the early 1840s.[50]
Despite the later reports about the early invention and apart from De Philipsthal's 1812 performance, no reports of dissolving view shows before the 1820s are known and in some cases confusion with the Diorama or similar media is possible. In 1826 Scottish magician and ventriloquist M. Henry's introduced what he referred to as "Beautiful Dissolvent Scenes", "imperceptibly changing views", "dissolvent views" and "Magic Views" which were created "by Machinery invented by M. Henry". In 1827 Henry Langdon Childe presented "Scenic Views, showing the various effects of light and shade" with a series of subjects that would become classics for the dissolving views. In December 1827 De Philipsthal returned with a show that included "various splendid views (...) transforming themselves imperceptibly (as if it were by Magic) from one form into another".[51][49]
Biunial lanterns, with two projecting optical sets in one apparatus, were produced to more easily project dissolving views. Probably the first biunial lantern, dubbed the "Biscenascope" was made by the optician Mr. Clarke and presented at the Royal Adelaide Gallery in London on December 5, 1840.[50] Later on triple lanterns enabled additional effects, for instance the effect of snow falling while a green landscape dissolves into a snowy winter version.
A mechanical device could be fitted on the magic lantern, which locked up a diaphragm on the first slide slowly whilst a diaphragm on a second slide was opened simultaneously.[51]
Philip Carpenter's copper-plate printing process, introduced in 1823, may have made it much easier to create duplicate slides with printed outlines that could then be colored differently to create dissolving view slides.[51] However, all early dissolving view slides seem to have been hand-painted.[49]
Experiments
There have been many different experiments involving sorts of movement with the magic lantern. These include:
- galvanometer slide: a flattened coil with a magnetized needle moving from side to side when a battery is connected.
- projection of moving frog legs, with the nerves and muscles of severed frog legs connected to electric wires.
- hour-glass projection: the projection of a flattened hourglass showed the sand flowing upwards. Extreme magnification made the effect extra impressive, with the grains of sand forming a wave-like pattern.
- cohesion figure projection of liquids: different oils and fats create all kinds of moving patterns when manipulated between clear glass plates or a narrow glass box.
Several of these experiments were publicly demonstrated at the London Polytechnic Institution.[53]
Choreutoscope and phenakistiscope-type systems
Versions of the magic lantern were used to project transparent variations of the phénakisticope. These were adapted with a mechanism that spins the disc and a shutter system. Duboscq produced some in the 1850s and Thomas Ross patented a version called "Wheel of life" in 1869 and 1870.[54]
The Choreutoscope was invented around 1866 by the Greenwich engineer J.Beale and demonstrated at the Royal Polytechnic. It projected six pictures from a long slide and used a hand-cranked mechanism for intermittent movement of the slide and synchronized shutter action. The mechanism became a key to the development of the movie camera and projector. The Choreutoscope was used at the first professional public demonstration of the Kinetoscope to explain its principles.[55]
An "Optical Instrument" was patented in the U.S. in 1869 by O.B. Brown, using a phenakistiscope-like disc with a technique very close to the later cinematograph; with Maltese Cross motion; a star-wheel and pin being used for intermittent motion, and a two-sector shutter.[56]
Life in the lantern - Bio-Phantoscope
John Arthur Roebuck Rudge built a lantern for William Friese-Greene with a mechanism to project a sequence of seven photographic slides. It was reportedly made in 1872, but also 1875 and a more likely date of 1882 have been given. The surviving slides show a man removing his head with his hands and raising the loose head. The photographed body belonged to Rudge and Friese-Greene posed for the head. The slides probably provided the very first trick photography sequence projection. Friese-Greene's demonstrated the machine in his shop, until the police ordered him to remove it when it attracted too large a crowd.[57]
Phantasmagoria

Phantasmagoria was a form of horror theater that used one or more magic lanterns to project frightening images, especially of ghosts. Showmen used rear projection, mobile or portable projectors and all kinds of effects to produce convincing necromantic experiences. It was very popular in Europe from the late 18th century to well into the 19th century.
It is thought that optical devices like concave mirrors and the camera obscura have been used since antiquity to fool spectators into believing they saw real gods and spirits,[51] but it was the magician "physicist" Phylidor who created what must have been the first true phantasmagoria show. He probably used mobile magic lanterns with the recently invented Argand lamp[58] to create his successful Schröpferischen, und Cagliostoischen Geister-Erscheinungen (Schröpfer-esque and Cagiostro-esque Ghost Apparitions)[59] in Vienna from 1790 to 1792. Phylidor stated that his show of perfected apparitions revealed how charlatans like Johann Georg Schröpfer and Cagliostro had fooled their audiences. As "Paul Filidort" he presented his Phantasmagorie in Paris From December 1792 to July 1793,[60][61] probably using the term for the first time. As "Paul de Philipsthal" he performed Phantasmagoria shows in Britain since 1801 with great success.
One of many showmen who were inspired by Phylidor, Etienne-Gaspard Robert became very famous with his own Fantasmagorie show in Paris from 1798 to 1803 (later performing throughout Europe and returning to Paris for a triumphant comeback in Paris in 1814). He patented a mobile "Fantascope" lantern in 1798.[51]
Royal Polytechnic Institution shows
Since its opening in 1838 The Royal Polytechnic Institution in London became a very popular and influential venue with all kinds of magic lantern shows as an important part of its program. At the main theatre, with 500 seats, lanternists would make good use of a battery of six large lanterns running on tracked tables to project the finely detailed images of extra large slides on the 648 square feet screen. The magic lantern was used to illustrate lectures, concerts, pantomimes and other forms of theatre. Popular magic lantern presentations included Henry Langon Childe's dissolving views, his chromatrope, phantasmagoria and mechanical slides.[51][62]
Today
Some enthusiasts claim that the brilliant quality of color in lantern slides is unsurpassed by successive projection media. The magic lantern and lantern slides are still popular with collectors and can be found in many museums. However, of the original lanterns from the first 150 years after its invention only 28 are known to still exist (as of 2009).[16] Museums usually prefer not to use their slides for projections, but often provide video representations of the slides.
A collaborative research project of several European universities called A Million Pictures started in June 2015 and will last until May 2018. It addresses the sustainable preservation of the massive, untapped heritage resource of the tens of thousands of lantern slides in the collections of libraries and museums across Europe.[63]
Genuine public lantern shows are relatively rare; several regular performers state to be the only one of their kind in their part of the world. These include Pierre Albanese and glass harmonica player Thomas Bloch live Magic Lantern/Phantasmagoria shows since 2008 in Europe[64] and The American Magic-Lantern Theater.[65] The Magic Lantern Society maintains a list of active lanternists, which contains more than 20 performers in the U.K. and circa eight performers in other parts of the world (Europe, U.S., Canada, Australia and New Zealand).[66]
Dutch theatre group Lichtbende produces contemporary magical light spectacles and workshops with magic lanterns.[67]
See also
- List of lantern slide collections
- Slide projector
- Projector (disambiguation) for a directory of projector types
- Phantasmagoria
- Zoopraxiscope
- Film
References
- ↑ Pfragner, Julius. "An Optician Looks for Work". The Motion Picture: From Magic Lantern to Sound. Great Britain: Bailey Brothers and Swinfen Ltd. 9-21. Print.
- ↑ "All about lantern slides (1)".
- ↑ "All about magic lantern slides (2)".
- ↑ "All about lantern slides (1)".
- ↑ U.S. Patent US7784 A: Improvement in photographic pictures on glass.
- ↑ Timby, Kim (2016). Glass Transparencies: Marketing Photography’s Luminosity and Precision.
- ↑ "Historic Camera: William and Frederick Langenheim".
- ↑ Waddington, Damer. "Introduction". Panoramas, Magic Lanterns and Cinemas. Channel Islands, NJ: Tocan Books. xiii-xv. Print.
- ↑ Snyder, Laura J. (2015). "Eye of the Beholder".
- 1 2 3 4 5 Rossell, Deac (2002). "The Magic Lantern".
- ↑ Huygens, Christiaan. "Pour des representations par le moyen de verres convexes à la lampe" (in French).
- ↑ Huygens, Christiaan (19 April 1662). "letter to Lodewijk Huygens" (in French).
- ↑ Huygens, Christiaan (1694). "Aanhangsel II bij het eerste Complement van de Dioptrica" (in Dutch).
- ↑ "mageng.html".
- ↑ http://www.magiclantern.org.uk/history/history04.php
- 1 2 Rossell, Deac (2009), "Early Magic Lantern Illustrations: What Can They Tell Us About Magic Lantern History?" (PDF), The Magic Lantern Gazette
- ↑ Rossell, Deac (2004). The Origins of the Magic Lantern in Germany.
- 1 2 Petit, Pierre (28 November 1664). "letter to Christiaan Huygens".
- ↑ http://picturegoing.com/?p=4885
- ↑ http://www.pepysdiary.com/diary/1666/08/19/
- ↑ http://www.pepysdiary.com/diary/1666/08/22/
- ↑ letter from Pierre Guisony to Christiaan Huygens (in French). 25 March 1660.
- ↑ Kircher, Athanasius (1671). Ars Magna Lucis et Umbrae (in Latin). pp. 767=769. Retrieved 19 August 2010.
- 1 2 Kircher, Athanasius; Rendel, Mats. "About the Construction of The Magic Lantern, or The Sorcerers Lamp".
- ↑ "The mystery of the wrongly placed lenses (luikerwaal.com)".
- ↑ "The miracle of the magic lantern".
- ↑ http://www.mitpressjournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1162/TNEQ_a_00418
- ↑ "Holden, Moses (DNB00) - Wikisource, the free online library". en.m.wikisource.org. Retrieved 17 September 2015.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 October 2011. Retrieved 2011-08-01.
- ↑ Philip Carpenter, 1823, A Companion to the Magic Lantern: Part II.
- 1 2 3 4 Rossell, Deac (2005). The Magic Lantern and Moving Images before 1800.
- ↑ Rossell, Deac (2002). Leibniz and the Lantern.
- ↑ Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (1675). Drôle de Pensée, touchant une nouvelle sorte de représentations. Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ↑ Mannoni; Campagnoni; Robinson (1995). Light and Movement.
- ↑ Von Uffenbach (1753). Merkwürdige Reisen durch Niedersachsen, Holland und Engelland - Erster Theil (in German). pp. 62–63.
- ↑ Van Musschenbroek, Pieter (1739). Beginsels Der Natuurkunde.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Luikerwaal - Mechanical Slides".
- ↑ "Magic lantern - collection of moving magic lantern slides part 1.". Luikerwaal.
- ↑ "Luikerwaal - Fantoccini Slides".
- 1 2 3 "Luikerwaal - Mechanical special effects slides".
- ↑ "de Luikerwaal - Chromatropes".
- ↑ "the saleroom.com - lot 266".
- ↑ "dickbalzer.com - Polytechnic size".
- ↑ The Athenæum. 1845-01-04.
- ↑ The Royal Polytechnic Institution - Catalogue for 1845.
- ↑ Timbs, John (1867). The Year-book of Facts in Science and Art.
- ↑ Wheatstone, Charles (1850–1875). Extracts from the papers of Sir Charles Wheatstone (PDF).
- ↑ The Magic Lantern - Vol. 1. No. 2. October 1874.
- 1 2 3 4 Huhtamo, Erkki. "Ghost Notes: Reading Mervyn Heard’s Phantasmagoria. The Secret Life of the Magic Lantern" (PDF). The Magic Lantern Gazette. 18 (4).
- 1 2 3 The Mirror of Literature, Amusement, And Instruction. 1842. p. 98.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Heard, Mervyn. PHANTASMAGORIA: The Secret History of the Magic Lantern. The Projection Box, 2006
- ↑ The Art-journal, New Series, Volume XIII. 1874.
- ↑ Hepworth, T.C. (1888). The book of the lantern. pp. 171–203.
- ↑ Herbert, Stephen. "Projection Phenakistoscope 1". www.stephenherbert.co.uk. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- ↑ Rossell, Deac (1998). Living Pictures: The Origins of the Movies.
- ↑ U.S. Patent No. 93,594. 10 August 1869.
- ↑ http://www.cinematheque.fr/fr/catalogues/appareils/collection/lanterne-de-projectionap-94-33.html
- ↑ Grau, Oliver. Remember the Phantasmagoria! chapter from MediaArtHistories, MIT Press/Leonardo Books, 2007, p. 144
- ↑ Phylidor Schröpferischen, und Cagliostoischen Geister-Erscheinungen flyer 1790
- ↑ Rossell, Deac (2001). The_19_Century_German_Origins_of_the_Phantasmagoria_Show.
- ↑ Affiches, annonces et avis divers. 1793-07-23
- ↑ The Magazine of Science, and Schools of Art - Vol. IV. 1843. p. 410.
- ↑ "A Million Pictures (website)".
- ↑ http://www.thomasbloch.net/en_performances.html
- ↑ http://www.magiclanternshows.com/introducing.htm
- ↑ "Active Lanternists: The Magic Lantern Society".
- ↑ "Lichtbende - Magic Lantern".
External links
| Look up magic lantern in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Magic lanterns. |
- luikerwaal.com Magic Lantern site 'de Luikerwaal'. Comprehensive information on the use and history of the Magic Lantern
- magic-lantern.eu website with more than 8000 lantern slides online
- Cinema and its Ancestors: The Magic of Motion Video interview with Tom Gunning
- A live Magic Lantern performance with accompaniment of crystal instruments is proposed here – feat. Pierre Albanese and Thomas Bloch
- Live Magic Lantern Shows The American Magic Lantern Theater
- Magic Lantern – A School of Cinema Film Institute Chennai
- University of Tasmania Library Lantern Slide Collection
- LUCERNA - The Magic Lantern Web Ressource
- The Magic Lantern Society An introduction to lantern history featuring images of lanterns, slides, and lantern accessories
- Joseph Boggs Beale collection of magic lantern illustrations, Margaret Herrick Library, Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences
- Images of Lantern Slides from the National Museum of Australia
- The Magic Lantern Society, United Kingdom
- The Lantern Slide Collection at the New-York Historical Society