Saint Lawrence Seaway
| Saint Lawrence Seaway | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specifications | |
| Length | 370 miles (600 km) |
| Maximum boat length | 740 ft 0 in (225.6 m) |
| Maximum boat beam | 78 ft 0 in (23.8 m) |
| Locks | 15 |
| Maximum height above sea level | 570 ft (170 m) |
| Status | Open |
| History | |
| Construction began | 1954 |
| Date of first use | April 25 |
| Date completed | 1959 |
| Geography | |
| Start point | Port Colborne, Ontario |
| End point | Montreal, Quebec |



The Saint Lawrence Seaway (French: la Voie Maritime du Saint-Laurent) is a system of locks, canals and channels in Canada and the United States that permit ocean-going vessels to travel from the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes of North America, as far inland as the western end of Lake Superior. The Seaway is named for the Saint Lawrence River, which flows from Lake Ontario to the Atlantic Ocean. Legally, the Seaway extends from Montreal, Quebec, to Lake Erie and includes the Welland Canal.
This section upstream of the Seaway is not a continuous canal; rather, it consists of several stretches of navigable channels within the river, a number of locks, and canals along the banks of the St. Lawrence River to bypass several rapids and dams. A number of the locks are managed by the St. Lawrence Seaway Management Corporation in Canada, and others in the United States by the Saint Lawrence Seaway Development Corporation; the two bodies together advertise the Seaway as part of "Highway H2O".[1] The section of the river from Montreal to the Atlantic is within Canadian jurisdiction and is regulated by the offices of Transport Canada in the Port of Quebec.
History
The Saint Lawrence Seaway was preceded by a number of other canals. In 1871, locks on the Saint Lawrence allowed transit of vessels 186 ft (57 m) long, 44 ft 6 in (13.56 m) wide, and 9 ft (2.7 m) deep. The First Welland Canal, constructed from 1824–1829, had a minimum lock size of 110 ft (34 m) long, 22 ft (6.7 m) wide, and 8 ft (2.4 m) deep, but it was generally too small to allow passage of larger ocean-going ships. The Welland Canal's minimum lock size was increased to 150 ft (46 m) long, 26.5 ft (8.1 m) wide, and 9 ft (2.7 m) deep for the Second Welland Canal; to 270 ft (82 m) long, 45 ft (14 m) wide, and 14 ft (4.3 m) deep with the Third Welland Canal; and to 766 ft (233 m) long, 80 ft (24 m) wide, and 30 ft (9.1 m) deep for the current (Fourth) Welland Canal.[2]
The first proposals for a bi-national comprehensive deep waterway along the Saint Lawrence were made in the 1890s. In the following decades, developers proposed a hydropower project as inseparable from the seaway; the various governments and seaway supporters believed that the deeper water to be created by the hydro project was necessary to make the seaway channels feasible for ocean-going ships. United States proposals for development up to and including the First World War met with little interest from the Canadian federal government. But the two national governments submitted Saint Lawrence plans to a group for study. By the early 1920s, both The Wooten-Bowden Report and the International Joint Commission recommended the project.
Although the Liberal Prime Minister William Lyon Mackenzie King was reluctant to proceed, in part because of opposition to the project in Quebec, in 1932 he and the United States representative signed a treaty of intent. This treaty was submitted to the United States Senate in November 1932 and hearings continued until a vote was taken on March 14, 1934. The majority voted in favor of the treaty, but it failed to gain the necessary two-thirds vote for ratification. Subsequent attempts between the governments in the 1930s to forge an agreement came to naught due to opposition by the Ontario government of Mitchell Hepburn, and that of Quebec. In 1936, John C. Beukema, head of the Great Lakes Harbors Association and a member of the Great Lakes Tidewater Commission, was among a delegation of eight from the Great Lakes states to meet at the White House with U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt to get his support of the Seaway concept.
Beukema and Saint Lawrence Seaway proponents were convinced that such a nautical link would lead to development of the communities and economies of the Great Lakes region by enabling ocean-going ships. In this period, grain exports to Europe were highly important to the national economy, along with other commodities. The negotiations on the treaty resumed in 1938 and by January 1940, substantial agreement was reached between Canada and the United States. By 1941, President Roosevelt and Prime Minister Mackenzie King made an executive agreement to build the joint hydro and navigation works, but this failed to receive the assent of the U.S. Congress. Proposals for the seaway were met with resistance; primary opposition came from interests representing existing harbors on the Atlantic and Gulf coasts and internal waterways, and from the railroads associations. The railroads carried freight and goods between the coastal ports and the Great Lakes cities.
After 1945, proposals to introduce tolls to the Seaway were not sufficient to gain support by the U.S. Congress for the project. Growing impatient, and with Ontario desperate for the power to be generated by hydro-electricity, Canada began to consider "going it alone". This seized the imagination of Canadians, engendering a groundswell of Saint Lawrence nationalism. Canadian Prime Minister Louis St. Laurent advised U.S. President Harry S. Truman on September 28, 1951 that Canada was unwilling to wait for the United States and would build a seaway alone; the Canadian Parliament authorized the founding of the Saint Lawrence Seaway Authority on December 21 of that year. Fueled by this support, Saint Laurent's administration decided over the course of 1951 and 1952 to construct the waterway alone, combined with the Moses-Saunders Power Dam. (This became the joint responsibility of Ontario and New York: as a hydro-power dam would change the water levels, it required bilateral cooperation.)
The International Joint Commission issued an order of approval for joint construction of the dam in October 1952. U.S. Senate debate on the bill began on January 12, 1953, and the bill emerged from the House of Representatives Committee of Public Works on February 22, 1954. It received approval by the Senate and the House by May 1954. The first positive action to enlarge the seaway was taken on May 13, 1954 when U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower signed the Wiley-Dondero Seaway Act[3] to authorize joint construction and to establish the Saint Lawrence Seaway Development Corporation as the US authority. The need for cheap haulage of Quebec - Labrador iron ore was one of the arguments that finally swung the balance in favor of the seaway. Ground-breaking ceremonies took place in Massena, New York, on August 10, 1954. That year John C. Beukema was appointed by Eisenhower to the five-member St. Lawrence Seaway Advisory Board.
In May 1957, the Connecting Channels Project was begun by the United States Army Corps of Engineers. By 1959, Beukema was on board the U.S. Coast Guard cutter Maple for the first trip through the U.S. locks that opened up the Great Lakes to ocean-going ships. On April 25, 1959,[4] large, deep-draft, ocean vessels began streaming to the heart of the North American continent through the seaway, a project which had been supported by every administration from Woodrow Wilson through Eisenhower.
In the United States, Dr. N.R. Danelian (who was the director of the 13-volume Saint Lawrence Seaway Survey in the U.S. Department of Navigation (1932–1963)), worked with the U.S. Secretary of State on Canadian-United States issues regarding the Seaway, persevering through 15 years to gain passage by Congress of the Seaway Act. He later became President of the Great Lakes St. Lawrence Association to promote Seaway development to benefit the American Heartland. The Seaway was heavily promoted by the Eisenhower administration, who were concerned with the its locus of control.[5]
The seaway opened in 1959 and cost C$470 million, $336.2 million of which was paid by the Canadian government.[6] Queen Elizabeth II and American President Dwight D. Eisenhower formally opened the Seaway with a short cruise aboard the royal yacht HMY Britannia after addressing crowds in Saint-Lambert, Quebec. 22,000 workers were employed at one time or another on the project, a 2,300-mile-long superhighway for ocean freighters.[5] Port of Milwaukee director Harry C. Brockel forecast just before the Seaway opened in 1959 that "The St. Lawrence Seaway will be the greatest single development of this century in its effects on Milwaukee's future growth and prosperity." Lester Olsen, president of the Milwaukee Association of Commerce, said, "The magnitude and potential of the St. Lawrence Seaway and the power project stir the imagination of the world."[5]
The seaway's opening is often credited with making the Erie Canal obsolete, and causing the severe economic decline of several cities along the canal in Upstate New York. By the turn of the 20th century, the Erie Canal had already been largely supplanted by the railroads, which had been constructed across New York and could carry freight more quickly and cheaply. The economic decline of Upstate New York was precipitated by numerous factors, only some of which had to do with the St. Lawrence Seaway.
Under the Canada Marine Act (1998), the Canadian portions of the Seaway were set up with a non-profit corporate structure; this legislation also introduced changes to the federal Ports.[7]
Great Lakes and Seaway shipping generates $3.4 billion in business revenue annually in the US. In 2002, ships moved 222 million tons of cargo per year. Overseas shipments, mostly of inbound steel and outbound grain, accounted for 15.4 million tons, 6.9% of the total cargo moved.[5] In 2004, Seaway grain exports accounted for about 3.6% of the US' overseas grain shipments, according to the U.S. Grains Council. In a typical year, Seaway steel imports account for around 6% of the U.S. annual total. The toll revenue obtained from ocean vessels is about 25-30% of cargo revenue.[5] The Port of Duluth shipped just over 2.5 million metric tons of grain, which is less than the port typically moved in the decade before the Seaway opened Lake Superior to deep-draft oceangoing vessels in 1959.[5]
International changes have affected shipping through the Seaway. Europe is no longer a major grain importer; big US export shipments are now going to South America, Asia and Africa. These destinations make Gulf and West Coast ports more critical to 21st-century grain exports. Referring to the Seaway project, a retired Iowa State University economics professor who specialized in transportation issues said, "It probably did make sense, at about the time it (the Seaway) was constructed and conceived, but since then everything has changed."[5]
Certain Seaway users have been concerned about the low water levels of the Great Lakes that have occurred since 2010.[8]
Expansion proposal
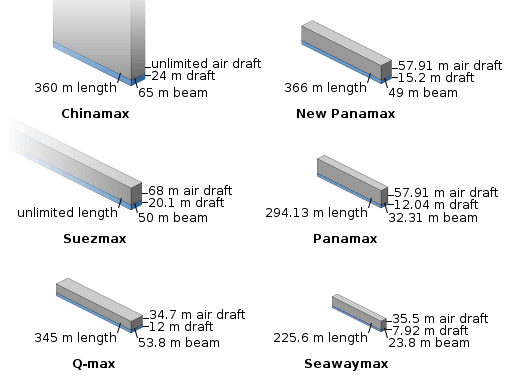
The Panama Canal was completed in 1914 and also serves ocean-going traffic. In the 1950s, Seaway designers chose not to build the locks to match the size of ships permitted by the 1914 locks at the Panama Canal (965 by 106 feet (294 by 32 m), known as the Panamax limit). Instead, the Seaway locks were built to match the smaller locks of Welland Canal, which opened in 1932. The Seaway locks permit passage of a ship 740 feet (230 m) long by 78 feet (24 m) feet wide (the Seawaymax limit).[5] The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers did a study to expand the St. Lawrence Seaway, but the plan was scrapped in 2011 because of tight budgets.[9][10]
The Seaway locks are planned for expansion in 2030. The expansion would allow container ships to travel into the Great Lakes. The maximum height clearance would be 150 feet (46 m), because of the hight clearence limitations of the Mackinac Bridge, Ambassador Bridge, Blue Water Bridge, and the Gordie Howe International Bridge (to be completed in 2019-20). The maximum water draft would be 35 feet (11 m) or 36 feet (11 m), compared to 27 feet (8.2 m) now. The Port of Montreal, at the eastern end of the St. Lawrence Seaway, allows 36-foot (11 m) drafts in the estuary.
The proposed New Seawaymax locks would be 1,000 by 110 feet (305 by 34 m) and would allow Panamax-size ships to access the Great Lakes. Only two limits would hinder the largest Panamax ships from entering the Seaway: Ships could be no higher than 150 feet (46 m) above the water line (air draft) and could have a water draft of no more than 37 feet (11 m). The New Seawaymax locks would permit a ship 45 feet (14 m) longer and 4 feet (1.2 m) wider than the Panamax ships permitted by the Panama Canal's 1914 locks.
Locks in the Saint Lawrence River


There are seven locks in the Saint Lawrence River portion of the Seaway. From downstream to upstream they are:[11]
- St. Lambert Lock—Saint Lambert, QC
- Côte Ste. Catherine Lock—Sainte-Catherine, QC
- Beauharnois Locks (two locks)—Melocheville, QC at 45°18′12.6″N 73°55′36.5″W / 45.303500°N 73.926806°W and 45°19′0.1″N 73°55′6.6″W / 45.316694°N 73.918500°W
- Snell Lock—Massena, NY
- Eisenhower Lock—Massena, NY
- Iroquois Lock—Iroquois, ON at 44°49′48″N 75°18′46.8″W / 44.83000°N 75.313000°W
Water Level Elevations
Lake Ontario 243 feet above sea level.
Drop through Iroqois Lock is 1 foot.
Lake St. Lawrence 242 feet above sea level.
Drop through Eisenhower Lock is 38 feet.
Wiley-Dondero Canal 204 feet above sea level.
Drop through Snell Lock is 45 feet.
Lake St. Francis 159 feet above sea level.
Drop through Upper Beauharnois Lock is 41 feet.
Beauharnois Canal 118 feet above sea level.
Drop through Lower Beauharnois Lock is 41 feet.
Lake St. Louis 77 feet above sea level.
Drop through Cote Ste Catherine Lock is 30 feet.
Laprairie Basin 47 feet above sea level.
Drop through St. Lambert Lock is 15 feet.
Drop through Lachine Rapids is a few feet.
Montreal Harbour 30 feet approximately above sea level.
Locks in the Welland Canal
There are eight locks on the Welland Canal. From the north to the south, there is the Lake Ontario level control lock at Port Weller, followed by Lock 2 and then Lock 3, a site with a visitors' information centre and museum in St. Catharines, Ontario. There are four locks in Thorold, Ontario, including twin flight locks 4, 5 and 6, with Lock 7 leading up to the main channel. The Lake Erie level control lock sits in Port Colborne, Ontario.

Lock, channel dimensions and additional statistical data
The size of vessels that can traverse the seaway is limited by the size of locks. Locks on the St. Lawrence and on the Welland Canal are 766 ft (233.5 m) long, 80 ft (24.4 m) wide, and 30 ft (9.14 m) deep. The maximum allowed vessel size is slightly smaller: 740 ft (225.6 m) long, 78 ft (23.8 m) wide, and 26.5 ft (8.1 m) deep. Many vessels designed for use on the Great Lakes following the opening of the seaway were built to the maximum size permissible by the locks, known informally as Seawaymax or Seaway-Max. Large vessels of the lake freighter fleet are built on the lakes and cannot travel downstream beyond the Welland Canal. On the remaining Great Lakes, these ships are constrained only by the largest lock on the Great Lakes Waterway, the Poe Lock at the Soo Locks (at Sault Ste. Marie), which is 1,200 ft (365.8 m) long, 110 ft (33.5 m) wide and 32 ft (9.8 m) deep.
A vessel's draft is another obstacle to passage on the seaway, particularly in connecting waterways such as the St. Lawrence River. The depth in the channels of the seaway is 41 ft (12.5 m) (Panamax-depth) downstream of Quebec City, 35 ft (10.7 m) between Quebec City and Deschaillons, 37 ft (11.3 m) to Montreal, and 27 ft (8.2 m) upstream of Montreal. Channel depths and limited lock sizes mean that only 10% of current ocean-going ships, which have been built much larger than in the 1950s, can traverse the entire seaway. Proposals to expand the seaway, dating from as early as the 1960s, have been rejected since the late 20th century as too costly. In addition, researchers, policymakers and the public are much more aware of the environmental issues that have accompanied Seaway development and are reluctant to open the Great Lakes to more invasions of damaging species, as well as associated issues along the canals and river. Questions have been raised as to whether such infrastructure costs could ever be recovered. Lower water levels in the Great Lakes have also posed problems for some vessels in recent years, and pose greater issues to communities, industries and agriculture in the region.
While the seaway is currently (2010) mostly used for shipping bulk cargo, the possibility of its use for large-scale container shipping is under consideration as well. If the expansion project goes ahead, feeder ships would take containers from the port of Oswego on Lake Ontario in upstate New York to Melford International Terminal in Nova Scotia for transfer to larger ocean-going ships.[12]
A useful website hosts measurements of wind, water levels and water temperatures.[13] A real-time interactive map of Seaway Locks, Vessels and Ports is available at.[14] The NOAA-funded Great Lakes Water Level Dashboard compiles statistics on water depth at various points along the Seaway.[15]
Ecology
To create a navigable channel through the Long Sault rapids and to allow hydroelectric stations to be established immediately upriver from Cornwall, Ontario and Massena, New York, Lake St. Lawrence was created behind a dam. It required the condemnation and acquisition by the government of all the properties of six villages and three hamlets in Ontario; these are now collectively known as "The Lost Villages".[16] The area was flooded on July 1, 1958, creating the lake. There was also inundation on the New York side of the border and the village of Louisville Landing was submerged. A notable adverse environmental effect of the operation of the Seaway has been the introduction of numerous invasive species of aquatic animals into the Great Lakes Basin. The zebra mussel has been most damaging in the Great Lakes and through its invasion of related rivers, waterways and city water facilities.
The Seaway, along with the Saint Lawrence River it passes through also provides opportunities for outdoor recreation, such as boating, camping, fishing, and scuba diving. Unfortunately invasive species and artificial water level controls imposed by the Seaway have had a negative impact on recreational fishing.[17] Of note, The Old Power House near Lock 23 (near Morrisburg, Ontario) became an attractive site for scuba divers. The submerged stone building has become covered with barnacles and is home to an abundance of underwater life.[18]
The Seaway passes through the Saint Lawrence River, which provides a number of divable shipwrecks within recreational scuba limits (shallower than 130 ft (40 m)) The region also offers technical diving with some wrecks lying at 240 ft (73 m). Surprisingly, the water temperature can be as warm as 75 °F (24 °C) during the mid to late summer months. The first 10 ft (3 m) of Lake Ontario is warmed and enters the St. Lawrence river as the fast-moving water body has no thermocline circulation.
On July 12, 2010, Richelieu (owned by Canada Steamship Lines) ran aground after losing power near the Côte-Sainte-Catherine lock. The grounding punctured a fuel tank, spilling an estimated 200 tonnes of diesel fuel, covering approximately 500 m2. The Seaway and the lock were shut down to help contain the spill.[19]
International trade and tourism
The seaway is important for American and Canadian international trade. The seaway handles 40 to 50 million annual tons of cargo. About 50% of the cargo carried travels to and from international ports in Europe, the Middle East and Africa. The rest comprises coastal trade, or short sea shipping, between various American and Canadian ports.[20] Among international shippers are found:
- Polsteam maintains a fleet of dry-bulk only vessels that transit every two weeks from the Dutch town of IJmuiden to Duluth, Minnesota
- Fednav Group, private[21] international dry-bulk only ocean transportation group, with routes between the Port of Antwerp and Sorel, Quebec even in wintertime[22]
- World Shipping Inc., a privately owned[23] and truly global logistics operation[24]
- Canfornav, a subsidiary of Canfor[25] which does dry-bulk only and registers most of its vessels in Cyprus
- American Steamship Company, a subsidiary of the General American Transportation Corporation (GATX)[26]
- Rand Logistics, which was formed from the acquisition of Lower Lakes Towing Ltd,[27] and does not ship containers
- McKeil Marine, headquartered in Hamilton, provides service to Arctic ports[28]
- Groupe Desgagnes,[29] owner of the MV Camilla Desgagnés, an arctic steamer
- The Port of Montreal is the site of operations of
- Maersk Line, a unit of the A.P. Moller-Maersk Group
- Mediterranean Shipping Company
- Compagnie Maritime d'Affrètement / Compagnie Generale Maritime, a French transshipper
- Hapag-Lloyd acquired the Port of Montreal docks of, along with the rest of, CP Ships in 2005
- Orient Overseas Container Line, a Hong Kong-based multinational
- Arrimage Quebec has stevedoring operations in Baie-Comeau, Becancour, Chicago, Cote-Sainte-Catherine, Gaspe, Gros-Cacouna, Hamilton, Matane, Oshawa, Pointe-au-Pic, Port Colborne, Portneuf, Quebec, Rimouski, Saguenay, Sept-Iles, Sorel-Tracy, St. Catharines, and other ports in the Maritime provinces of Canada.[30]
The Saint Lawrence seaway (along with ports in Quebec) is the main route for Ontario grain exports to overseas markets.[31] Its fees are publicly known, and were limited in 2013 to an increase of 3%.[32] A trained Pilot is required for any foreign trade vessel,[33] and the employment of these skilled personnel follows the law of supply and demand. A set of rules and regulations are available to help transit.[34]
Commercial vessel transit information is hosted on the U.S. Saint Lawrence Seaway Development Corporation website.
Since 1997, international cruise liners have been known to transit the Seaway. The Hapag-Lloyd Christopher Columbus carried 400 passengers to Duluth, Minnesota that year. Since then, the number of annual Seaway cruising passengers has increased to 14,000.[35]
Every year, more than 2,000 recreational boats, of more than 20 ft and one ton, transit the Seaway.[36] The tolls have been fixed for 2013 at $30 per lock, except for the Welland Canal, where $30 pays for all eight locks between Lake Erie and Lake Ontario.[37] Lockages are scheduled 12 hours a day between the hours of 07:00 and 19:00 from June 15 to September 15.[38]
A list of organisations that serve the Seaway in some fashion, such as Chambers of Commerce and Municipal or Port authorities, is available at the SLSDC website. A 56-page electronic "Great Lakes St. Lawrence Seaway System" Directory is published by Harbor House Publishers.[39]
Map
Map of the North American Great Lakes and the Saint Lawrence Seaway from 1959, depicting the entire length beginning at the Gulf of Saint Lawrence in the east to the western-most terminus at Lake Superior. This map is in the public domain and is available at Wikimedia Commons in several resolutions.

See also
References
Notes
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-11-06. Retrieved 2014-08-15.
- ↑ "Brief History of the Welland Canal and the Welland Recreational Canal" (PDF). Welland Recreational Canal Corporation. Retrieved September 1, 2016.
- ↑ "GreatLakesSeawayNews.com". GreatLakesSeawayNews.com. Retrieved November 25, 2016.
- ↑ Rodrigue, Jean-Paul. "The St. Lawrence Seaway and Regional Development". The Geography of Transport Systems. Hofstra University.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Egan, Dan (October 30, 2005). "Sinking treasure". Jsonline.com. Retrieved November 25, 2016.
- ↑ "History of the Saint Lawrence Seaway" (PDF). Infrastructure Canada. Infrastructure.gc.ca. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 25, 2008. Retrieved March 27, 2010.
- ↑ "Canada Marine Act (1998, c. 10)". Transport Canada.
- ↑ "Great Lakes low water levels could cost $19B by 2050". CBC News. The Canadian Press. June 27, 2014. Retrieved October 11, 2016.
- ↑ US Army Corps of Engineers, "Weighing Costs-Benefits of Expanding the St. Lawrence Seaway", California State University
- ↑ Michelle McQuigge (2011-08-16). "St. Lawrence Seaway Expansion Plans Nixed: Report". Huffingtonpost.ca. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "Seaway System". Greatlakes-seaway.com. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ John Doherty, "Oswego Considered For Major Container Port: Plan calls for $3M facility to create first Great Lakes site handling global container shipments", Syracuse Post-Standard, October 22, 2008.
- ↑ "Great Lakes St. Lawrence Seaway System". Greatlakes-seaway.com. Retrieved November 25, 2016.
- ↑ "Seaway System". Greatlakes-seaway.com. Retrieved November 25, 2016.
- ↑ noaa.gov: "Great Lakes Water Level Dashboard", accessed July 2014.
- ↑ "The Lost Villages". The Ottawa Citizen. June 28, 2008. Retrieved February 28, 2013.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-05-15. Retrieved 2015-06-06.
- ↑ "History". Morrisburg.ca. 1958-07-01. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ CBC News (July 13, 2010). "Ship's fuel leaks into St. Lawrence Seaway". CBC. Retrieved July 13, 2010.
- ↑ "Introducing the Great Lakes/St. Lawrence Seaway System" (PDF). Saint Lawrence Seaway Management Corporation.
- ↑ "Fednav Limited - Montreal - Ship chartering, Shipping agency, Marine Agencies, Tie-downs, Stevedoring, Boats, Boats repair and maintenance, International commerce, Ship owning, Navigation services, Exportation services, Ice navigation services, Logistic services, Transportation, Transportation of bulk, Oceanic transportation". Occq-Qcco.com. 1974-08-01. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "Liner Shipping: Falline". Fednav.com. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "World Shipping, Inc.: Private Company Information - Bloomberg". Investing.businessweek.com. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "World Shipping, Inc". Worldshipping.com. 2014-06-20. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "About us". Canfornav.com. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "American Steamship Company". Americansteamship.com. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "About Rand". Rand Logistics, Inc. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-01-04. Retrieved 2014-01-02.
- ↑ "Groupe Desgagnés". Desgagnes.com. 2015-12-01. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-02-11. Retrieved 2014-01-04.
- ↑ "Wheat Export". Grain Farmers of Ontario.
- ↑ "Seaway System - Commercial Shipping - Toll Schedule". Greatlakes-seaway.com. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-02-13. Retrieved 2013-12-03.
- ↑ "Seaway System - Commercial Shipping - Transiting the Seaway". Greatlakes-seaway.com. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "Cruising the Great Lakes St. Lawrence Seaway", p. 1, Seaway, US Dept. of Transportation
- ↑ "Seaway System - Recreational Boating". Greatlakes-seaway.com. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "Seaway System - Recreational Boating - Pleasure Craft Tolls". Greatlakes-seaway.com. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "Seaway System - Recreational Boating - Lockage Schedule". Greatlakes-seaway.com. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ↑ "Great Lakes St. Lawrence Seaway Directory". Harborhouse.com. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
Further reading
- Macfarlane, Daniel (2014) Negotiating a River: Canada, the US, and the Creation of the St. Lawrence Seaway. Vancouver: UBC Press.
- Puccia Parham, Claire (2009), The St. Lawrence Seaway and Power Project : an oral history of the greatest construction show on earth, Syracuse University Press, ISBN 978-0-8156-0913-1
- St. Lawrence Seaway Management Corporation (2006) "Seaway Handbook" Cornwall, Ontario, Canada.
- Willoughby, William R. (1961). The St. Lawrence Waterway: A Study in Politics and Diplomacy. Madison, University of Wisconsin Press.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to St Lawrence Seaway. |
- Tommy Trent's ABC's of the Seaway, a brochure for young people
- Great Lakes St Lawrence Seaway System web site
- The St Lawrence Seaway Development Corporation
- "Stairways to the Seas". Popular Mechanics, January 1959, pp. 97–103. Detail article with illustrations of lock system.
- St. Lawrence Seaway April 25, 1959
- Documents and Photographs relating to the St. Lawrence Seaway, Dwight D. Eisenhower Presidential Library
- The Lost Villages Historical Society
- Excerpt from the Illustrated London News, January 11, 1862 describing the Canals of Canada.
- The Great Waterway: a site dedicated to tourism along the waterway from Lake Ontario to Cornwall and the Seaway Valley
- Exchange of Notes, amending 1959 Agreement of Application of Tolls
- CBC Digital Archives — The St Lawrence Seaway: Gateway to the world
- Bibliography on Water Resources and International Law See Great Lakes; St. Lawrence River and Seaway. Peace Palace Library
- Channel Depth and Width and Length
- A film clip "Longines Chronoscope with George A. Dondero" is available at the Internet Archive
- St. Lawrence Waterway Project Report Clippings, 1921 Brock University Library Digital Repository



