Lake Erie Basin
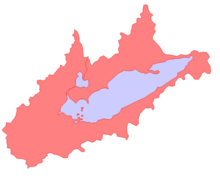

Lake Erie Basin consists of Lake Erie and surrounding watersheds, which are typically named after the river, creek, or stream that provides drainage into the lake. The watersheds are located in the states of Indiana, Michigan, New York, Ohio, and Pennsylvania in the United States, and in the Province of Ontario in Canada. The basin is part of the Great Lakes Basin and Saint Lawrence River Watershed, which feeds into the Atlantic Ocean. 80% of the lake's water flows in from the Detroit River, with only 9% coming from all of the remaining watersheds combined. (The remainder (11%) is derived from direct precipitation into the lake.) A littoral zone serves as the interface between land and lake, being that portion of the basin where the lake is less than 15 feet (4.6 m) in depth.[1]
History

The Lake Erie Basin was formed at the end of the Wisconsin glaciation. The basin was part of Glacial Lake Maumee until an eastern drainage opened at Niagara, at which point the Maumee River Watershed reversed its flow eastward. The Great Black Swamp is thought to be a remnant of the glacial lake.
Geography
Indiana
Michigan

Michigan's drainage basin consists of 5,808 square miles (15,040 km2).
- Belle Watershed (Lapeer, Macomb, Oakland, and St. Clair counties)
- Black Watershed
- Clinton Watershed (Lapeer, Macomb, Oakland, and St. Clair counties)
- Detroit Watershed (see also Ontario)
- Huron Watershed (Livingston, Monroe, Oakland, Washtenaw, and Wayne counties)
- Huron River
- Portage River
- Pine Watershed
- Raisin Watershed
- Maumee Watershed (see Ohio)
- Tiffin River becomes Bean Creek in northern Ohio and Michigan
New York

New York's drainage basin covers 2,300 square miles (6,000 km2).
- Buffalo River Watershed (Erie, Genesse, and Wyoming counties)
- Cattaraugus Creek Watershed (Cattaraugus, Chautauqua, Erie, and Wyoming counties)
- Chautauqua Creek - Lake Erie Watershed (Chautauqua County) (see also Pennsylvania)
- Beaver Creek
- Chautauqua Creek
- Crooked Brook
- Hyde Creek
- Scott Creek
- Silver Creek
- Twentymile Creek
- Walnut Creek
Ohio

- Ashtabula-Chagrin Watershed (Ashtabula, Cuyahoga, Geauga, Lake, and Portage counties) (see also Pennsylvania)
- Auglaize Watershed (Allen, Auglaize, Defiance, Mercer, Paulding, Putnam, and Van Wert counties)
- Black-Rocky Watershed (Ashland, Cuyahoga, Huron, Lorain, and Medina counties)
- Blanchard Watershed (Allen, Hancock, Hardin, Putnam, and Wyandot counties)
- Cedar-Portage Watershed (Hancock, Lucas, Ottawa, Sandusky, and Wood counties)
- Cedar Creek
- Crane Creek
- Packer Creek
- Portage River
- Rusha Creek
- Toussaint River
- Turtle Creek
- Chautauqua-Conneaut Watershed (Ashtabula County) (see also Pennsylvania)
- Cuyahoga Watershed (Cuyahoga, Geauga, Portage, and Summit counties)
- Grand Watershed (Ashtabula, Geauga, Lake, Portage, and Trumbull counties)
- Huron-Vermilion Watershed (Ashland, Crawford, Erie, Huron, Lorain, Richland, and Seneca counties)
- Maumee Watershed (Defiance, Fulton, Hancock, Henry, Lucas, Putnam, Williams, and Wood counties) (see Michigan)
- Bad Creek
- Beaver Creek
- Brush Creek
- Maumee River
- Swan Creek
- Tenmile Creek
- Tiffin River becomes Bean Creek in northern Ohio and Michigan
- Turkeyfoot Creek
- Ottawa-Stony Watershed (Fulton and Lucas counties) (see also Michigan)
- Sandusky Watershed (Crawford, Erie, Hardin, Huron, Marion, Ottawa, Richland, Sandusky, Seneca, and Wyandot counties)
Pennsylvania
- Ashtabula-Chagrin Watershed (Erie County) (see also Ohio)
- Chautauqua-Conneaut Watershed (Crawford and Erie counties) (see also Ohio)
- Conneaut Creek
- Turkey Creek
- Lake Erie Watershed (Crawford and Erie counties)
Ontario

- Detroit River Watershed (see also Michigan)

- Grand River Watershed is the largest drainage in southern Ontario at 2,600 sq mi (7,000 km²)
- Lynn River Watershed
Economy
Agricultural, industrial, and residential land use are the primary nonpoint sources of pollution in the Lake Erie Basin. National and state environmental agencies, as well as interstate and binational cooperative efforts, focus on water quality, especially since the freshwater lake is used extensively for drinking water, recreation, and the fishing industry. Habitat and flow alteration cause siltation and sedimentation issues which can require dredging. Fertilizer runoff from farms and residences and unplanned releases from sewage treatment plants promote eutrophication through nutrient and organic enrichment, bacterial contamination, and the appearance of ammonium hydroxide. Industrial land use adds metals that flow into the basin and cause sediment contamination.[2]
See also
- Great Lakes
- Waterways that feed the Lake Erie Basin
References
External links
Overall
- Lakenet map of North American watersheds
- Lakenet profile of Lake Erie Basin
- Lakewide Management Plan (LaMP)
- Lake Erie Basin integrated habitat and mapping project of the Great Lakes Commission
- USGS Water Quality in the Lake Erie / Lake Saint Clair Drainages - MI, OH, IN, NY and PA 1996-1998 (Circular 1203)
Indiana
- See Map of Ohio's Principal Streams and Drainage Areas, including a small but important extension of waterway mapping across Ohio's Lake Erie Basin borders into the states of Indiana, Michigan, and Pennsylvania
Michigan
- Michigan and the Lake Erie Basin
- See Map of Ohio's Principal Streams and Drainage Areas, including a small but important extension of waterway mapping across Ohio's Lake Erie Basin borders into the states of Indiana, Michigan, and Pennsylvania
New York
- Lake Erie Basin (pp 235-279 of the Comprehensive Wildlife Conservation Strategy for New York)
- Lake Erie/Chautauqua Creek Watershed Waterbody Inventory
Ohio
- Map of Ohio's Lake Erie watersheds
- Map of Ohio's Principal Streams and Drainage Areas, including a small but important extension of waterway mapping across Ohio's Lake Erie Basin borders into the states of Indiana, Michigan, and Pennsylvania
- Chagrin River Watershed Partners
- Report on Toussaint River and Rusha Creek watersheds includes detailed map on page 4
Pennsylvania
- Pennsylvania's watersheds
- Interactive map of Pennsylvania's watersheds
- Pennsylvania Lake Erie NEMO Project on land use and water quality
- Pennsylvania Lake Erie Drainage Basin map
- Pennsylvania Lake Erie Basin Subwatersheds map
- See Map of Ohio's Principal Streams and Drainage Areas, including a small but important extension of waterway mapping across Ohio's Lake Erie Basin borders into the states of Indiana, Michigan, and Pennsylvania
- Samuel Bates' History of Erie County, Pennsylvania, 1884, Chapter IV Streams, Lakes, Bays, Bridges and Culverts
- Mill Creek Flood of August 3, 1915
Ontario
Coordinates: 42°N 82°W / 42°N 82°W