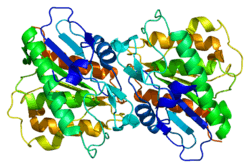
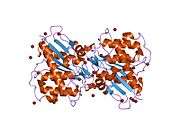
LYPLA1
Acyl-protein thioesterase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the LYPLA1 gene.[3][4]
Lysophospholipases are enzymes that act on biological membranes to regulate the multifunctional lysophospholipids. The protein encoded by this gene hydrolyzes lysophosphatidylcholine in both monomeric and micellar forms. The use of alternate polyadenylation sites has been found for this gene. There are alternatively spliced transcript variants described for this gene but the full length nature is not known yet.[4]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Wang A, Yang HC, Friedman P, Johnson CA, Dennis EA (Apr 1999). "A specific human lysophospholipase: cDNA cloning, tissue distribution and kinetic characterization". Biochim Biophys Acta. 1437 (2): 157–69. PMID 10064899. doi:10.1016/s1388-1981(99)00012-8.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: LYPLA1 lysophospholipase I".
Further reading
- Wang A, Dennis EA (1999). "Mammalian lysophospholipases.". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1439 (1): 1–16. PMID 10395961. doi:10.1016/s1388-1981(99)00063-3.
- Bohn E, Gerke V, Kresse H, et al. (1992). "Annexin II inhibits calcium-dependent phospholipase A1 and lysophospholipase but not triacyl glycerol lipase activities of rat liver hepatic lipase.". FEBS Lett. 296 (3): 237–40. PMID 1531641. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(92)80294-Q.
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY, et al. (1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction.". Anal. Biochem. 236 (1): 107–13. PMID 8619474. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138.
- Yu W, Andersson B, Worley KC, et al. (1997). "Large-scale concatenation cDNA sequencing.". Genome Res. 7 (4): 353–8. PMC 139146
 . PMID 9110174. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353.
. PMID 9110174. doi:10.1101/gr.7.4.353. - Wang A, Johnson CA, Jones Y, et al. (2000). "Subcellular localization and PKC-dependent regulation of the human lysophospholipase A/acyl-protein thioesterase in WISH cells.". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1484 (2-3): 207–14. PMID 10760470. doi:10.1016/s1388-1981(00)00020-2.
- Zhang QH, Ye M, Wu XY, et al. (2001). "Cloning and functional analysis of cDNAs with open reading frames for 300 previously undefined genes expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells.". Genome Res. 10 (10): 1546–60. PMC 310934
 . PMID 11042152. doi:10.1101/gr.140200.
. PMID 11042152. doi:10.1101/gr.140200. - Devedjiev Y, Dauter Z, Kuznetsov SR, et al. (2001). "Crystal structure of the human acyl protein thioesterase I from a single X-ray data set to 1.5 A.". Structure. 8 (11): 1137–46. PMID 11080636. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(00)00529-3.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899.
. PMID 12477932. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. - Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC).". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504.
. PMID 15489334. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. - Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network.". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. PMID 16189514. doi:10.1038/nature04209.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.