Klotski

Klotski (from Polish klocki—wooden blocks) is a sliding block puzzle. The name may refer to a specific layout of ten blocks, or in a more global sense to refer to a whole group of similar sliding-block puzzles where the aim is to move a specific block to some predefined location.
Rules
Like other sliding-block puzzles, several different-sized block pieces are placed inside a box, which is generally in 4×5 size. Among the blocks, there is a special one (usually the largest) which must be moved to a special area designated by the game board. The player is not allowed to remove blocks, and may only slide blocks horizontally and vertically. Common goals are to solve the puzzle with a minimum number of moves or in a minimum amount of time.
Naming

The earliest known reference of the name Klotski originates from the computer version for Windows 3.1 by ZH Computing in 1991, which was also included in Microsoft Windows Entertainment Pack. The sliding puzzle had already been trademarked and sold under different names for decades, including Psychoteaze[1] Square Root,[2] Intreeg,[3] and Ego Buster. There was no known widely used name for the category of sliding puzzles described before Klotski appeared.
History
- Henry Walton filed U.S. Patent 516,035 on 1893-03-14 for a sliding puzzle resembling 15-puzzle. According to Edward Hordern, this is the first even known sliding puzzle with rectangular blocks.
- Frank E. Moss filed U.S. Patent 668,386 on 1900-06-08 for a sliding puzzle which again, resembles 15-puzzle. This is currently one of the first known occurrence of sliding puzzle with non-equal blocks.
- Lewis W. Hardy obtained copyright for a game named Pennant Puzzle in 1909, manufactured by OK Novelty Co., Chicago.[4] The aim of this puzzle is completely identical to Klotski, just default blocks and arrangement are different. He also filed U.S. Patent 1,017,752 on 1907-12-14, which is about a sliding-block puzzle similar to Pennant Puzzle, but with a slightly different combination of blocks and a different goal—not only the largest block must be moved to a specific location, but all of the other blocks must achieve a specific configuration as well. The patent was granted on 1912-02-20.
- John Harold Fleming obtained a patent in 1934 in England.[5] He applied for it on 1932-12-07 and it was granted on 1934-06-07. The puzzle concerned has the same blocks and almost identical placement as forget-me-not, only that the unique horizontal 2×1 block is placed at the bottom instead of beneath the 2×2 block. The patent included a 79-step solution.
- It is said that the game was already known in Japan around the 10th year of the Shōwa period, i.e. around 1935.
- First account of occurrence of Klotski in China is in Shaanxi Province; prof. Lín Dé Kuān of Northwestern Polytechnical University saw children in a village playing Klotski made with pieces of paper in 1938.[6]
- One of the earliest books about standard Klotski was written by the Chinese professor Jiāng Cháng Yīng of Northwestern Polytechnical University in 1949,in his book 科学消遣. (translation: Science Pastime) This book has been republished as 科学思维锻炼与消遣. 1997. ISBN 7-5612-0971-1. (translation: Scientific mindset training and pastime)
It is still unknown which one is the original, or (in turn) if it has evolved from some other sliding-block puzzle, say, the 15 puzzle, which enjoyed immense popularity in western countries during the late 19th century. There are many confusing and conflicting claims, and several countries claim to be the ultimate origin of this game.
Solving
The minimum number of moves for the original puzzle is 81, which is verified by computer to be the absolute minimum for the default starting layout, if you consider sliding a piece two positions in the same direction to be a single move.
The first published 81-step solution is by Martin Gardner, in the February 1964 issue of Scientific American. In the article he discussed the following puzzles (with Edward Hordern classification code in parentheses): Pennant Puzzle (C19), L'Âne Rouge (C27d), Line Up the Quinties (C4), Ma's Puzzle (D1) and a form of Stotts' Baby Tiger Puzzle (F10).
For earliest published solutions (not optimal solution), currently known is from Chinese educator Xǔ Chún Fǎng, in his book 數學漫談. (translation: Mathematics Tidbits; Kāi Mínɡ Shū Diàn, March 1952) His solution involves 100 steps.
Variation
There are several variations of this game, some with names specific to the culture of certain countries, some with different arrangement of blocks.
It is still unknown whether these variations affected each other and how.
Block name variation
The following variations basically have the same layout and block arrangement, varying only in name (human, animal, or others), usually with some sort of story behind the names. It is completely unknown whether they share the same origin, though this is highly possible as they are identical to each other.
Huarong Dao
Huarong Dao (alternatively named Huarong Path or Huarong Trail, Chinese name: 華容道) is the Chinese variation, based on a fictitious story in the historical novel Romance of the Three Kingdoms about the warlord Cao Cao retreating through Huarong Trail (in present-day Jianli County, Jingzhou, Hubei) after his defeat at the Battle of Red Cliffs in the winter of 208/209 CE during the late Eastern Han Dynasty. He encountered an enemy general, Guan Yu, who was guarding the path and waiting for him. Guan Yu spared Cao Cao and allowed the latter to pass through Huarong Trail on account of the generous treatment he received from Cao in the past. The largest block in the game is named "Cao Cao".
Daughter in the box

The Daughter in the Box (Japanese name: hakoiri musume) wood puzzle depicts an "innocent young girl, who knows nothing of the world" trapped in a building. The largest piece is named "daughter", and other blocks are given names of other family members (like father, mother and so on).
Another Japanese variation uses the names of shogi pieces.
L'âne rouge
In France it is well known as L'âne rouge. It features a red donkey (the largest piece) trying to escape a maze of fences and pens to get to its carrots.[7] However, there is no known and documented record of its first existence in France.
Khun Chang Khun Phaen
This is a variation from Thailand. Khun Phaen is a famous character in Thai legend, and the game is named after the epic poem Khun Chang Khun Phaen, in which the character is imprisoned. The game depicts Khun Phaen breaking out of the prison by overcoming its nine sentries.[8]
There is a slight difference between Khun Chang Khun Phaen and the standard layout – the two middle 1×1 blocks are moved to bottom. Other than that, all other blocks are the same. The origin of this variation is unknown.
Block arrangement variation
In this context, the "basic" arrangement is assumed to be a 4×5 area laid out as follows:-
- In the left-hand column, two 1×2 blocks with a 1×1 block beneath.
- In the right-hand column, two 1×2 blocks with a 1×1 block beneath.
- In the middle two columns, a 2×2 block at the top, with a horizontal 2×1 block beneath it, two 1×1 blocks beneath that, leaving a 2×1 empty space at the bottom.
This is used globally as the "basic" game of Klotski. It is coded C27d in Hordern classification of sliding puzzle games.
Pennant Puzzle
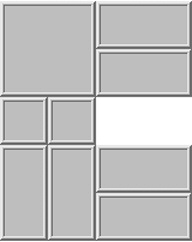
Coded as C19 in Hordern classification, it is first copyrighted in 1909 by Lewis. W. Hardy in United States. Standard Trailer Co. has it copyrighted under the name Dad's Puzzler in 1926 (also in US). Its arrangement is different:
- The default location of all blocks are different from Klotski. For example, the largest square block is in upper left corner.
- It is in 4×5 area, with one 2×2, two 1×2, four 2×1, two 1×1 pieces.
- The exit of block is not at the bottom middle, but bottom left.
Other than these, the game rules are the same as Klotski. The minimum number of moves to solve the puzzle is 59.
Ma's Puzzle
Ma's Puzzle is copyrighted by Standard Trailer Co. at 1927. It was the first sliding puzzle to use non-rectangular shape. Its goal is to join its 2 L-shaped pieces together, either anywhere or top right corner of the board.
Computerized version
The first known graphical version of Klotski was created for Windows by ZH Computing in 1991. It was later in the same year included in the third Microsoft Windows Entertainment Pack. Many versions of Klotski followed, either freely available or commercially available. For example, one is included in the GNOME desktop environment. Some include blocks which have special effects.
Notes and references
- ↑ Catalog of Copyright Entries. Third Series: 1969: January-June - Library of Congress. Copyright Office - Google 圖書. Books.google.com.hk. Retrieved 2013-04-18.
- ↑ "3 0 + Y e a r s A g o". Home.comcast.net. 1928-03-27. Retrieved 2013-04-18.
- ↑ "Rob's Puzzle Page - Sliding Block Puzzles". Home.comcast.net. 1915-03-16. Retrieved 2013-04-18.
- ↑ http://www.eldar.org/~problemi/singmast/material.html Enlisted in Sources in Recreational Mathematics - An Annotated Bibliography. (8th Preliminary ed.). Jan 1998.
- ↑ http://www.wikipatents.com/GB-Patent-411515/an-improved-puzzle-and-means-therefor patent number 411515
- ↑ Wú Hè Líng (2004). 七巧板、九连环和华容道. ISBN 9787030139856. (translation: Tangram, Baguenaudier and Klotski)
- ↑ "3 0 + Y e a r s A g o". Home.comcast.net. 1928-03-27. Retrieved 2013-04-18.
- ↑ "Mathematics Enrichment :: Khun Phaen Escapes to Freedom". nrich.maths.org. Retrieved 2013-04-18.
See also
External links
- easy-to-follow gif animation. Animation of the 'Forget-me-not' (L'Âne Rouge) solution.
- Solving Dad's Puzzle
- Klotski by ZH Computing
- Play Huarong Dao online