Ubu Roi
| Ubu Roi | |
|---|---|
 1st ed. cover | |
| Written by | Alfred Jarry |
| Date premiered | December 10, 1896 |
| Place premiered | Paris |
| Original language | French |
| Series |
Ubu Cocu Ubu Enchaîné |
Ubu Roi (Ubu the King or King Ubu) is a play by Alfred Jarry. It was first performed in Paris at the Théâtre de l'Œuvre, causing a riotous response in the audience as it opened and closed on December 10, 1896.[1][2] It is considered a wild, bizarre and comic play, significant for the way it overturns cultural rules, norms, and conventions. For those who were in the audience on that night to witness the response, including William Butler Yeats, it seemed an event of revolutionary importance. It is now seen by some to have opened the door for what became known as modernism in the twentieth century.[3] It is a precursor to Dada, Surrealism and the Theatre of the Absurd. It is the first of three stylised burlesques in which Jarry satirises power, greed, and their evil practices — in particular the propensity of the complacent bourgeoisie to abuse the authority engendered by success.
The title is sometimes translated as King Turd; however, the word "Ubu" is actually merely a nonsense word that evolved from the French pronunciation of the name "Herbert",[4] which was the name of one of Jarry's teachers who was the satirical target and inspirer of the first versions of the play.[5]
Jarry made some suggestions regarding how his play should be performed. He wanted King Ubu to wear a cardboard horse's head in certain scenes, "as in the old English theatre", for he intended to "write a guignol". He thought a "suitably costumed person would enter, as in puppet shows, to put up signs indicating the locations of the various scenes". He also wanted costumes with as little specific local colour reference or historical accuracy as possible.[6]
Ubu Roi was followed by Ubu Cocu (Ubu Cuckolded) and Ubu Enchaîné (Ubu in Chains), neither of which was performed during Jarry's 34-year life.[7] One of his later works, a novel/essay on "'pataphysics", is offered as an explanation behind the ideas that underpin Ubu Roi. 'Pataphysics is, as Jarry explains, "the science of the realm beyond metaphysics". 'Pataphysics is a pseudo-science Jarry created to critique members of the academy. It studies the laws that "govern exceptions and will explain the universe supplementary to this one". It is the "science of imaginary solutions".[8]
Synopsis

The story may at first glance seem merely frivolous — the obscene nonsense of schoolboys. It is a parody of Shakespeare's Macbeth with bits of Hamlet and King Lear tossed in. But with Jarry's rich imagination at work, the material began to express something deeper, an inner consciousness in a way that is similar to the Symbolists, a group Jarry had befriended. In fact, many critics consider Jarry a Symbolist author.[1][9]
As the play begins, Ubu leads a revolution, and kills the King of Poland and most of the royal family. The Queen of Poland then dies. The ghost of the dead king calls for revenge, prompting Ubu to begin killing the population and taking their money. Ubu's henchman gets thrown into prison; he then escapes to Russia, where he gets the Tsar to declare war on Ubu. As Ubu heads out to confront the invading Russians, his wife tries to steal money that Ubu has stashed in the palace. She is driven away by Bougrelas, the crown prince, who is leading a revolt of the people against Ubu. She runs away to her husband, Ubu, who has, in the meantime, defeated the Russians, and who has also been attacked by a bear. Ubu's wife pretends to be the angel Gabriel, in order to try to scare Ubu into forgiving her for her attempt to steal from him. They fight, and she is rescued by the entrance of Bougrelas, who is after Ubu. Ubu knocks down the attackers with the body of the dead bear, after which he and his wife flee to France, which ends the play.
The action contains motifs found in the plays of Shakespeare: a king's murder and a scheming wife from Macbeth, the ghost from Hamlet, Fortinbras' revolt from Hamlet, the reneging of Buckingham's reward from Richard III, and the pursuing bear from The Winter's Tale. It also includes other cultural references, for example, to Sophocles' Oedipus Rex (Œdipe Roi in French) in the play's title. Ubu Roi is seen to have been preceded in the spirit of outrageousness, and comic grotesquery by the great French Renaissance author François Rabelais's Gargantua and Pantagruel novels.[10][11]
The language of the play is a unique mix of slang from the playground, code-words, puns and near-gutter vocabulary, set to strange speech patterns.[12]
Development
"The beginnings of the original Ubu", wrote Jane Taylor, "have attained the status of legend within French theatre culture".[7] In 1888, when he became a student at the Lycée in Rennes at the age of fifteen, Jarry encountered a brief farcical sketch, Les Polonais, written by his friend Henri Morin, and Henri's brother Charles. This farce was part of a campaign by the students to ridicule their physics teacher, Félix-Frederic Hébert (1832-1917).[13] Les Polonais depicted their teacher as the King of an imaginary Poland,[2] and was one of many plays created around Père Hébé, the character that, in Jarry's hands, would eventually evolved into King Ubu. Les Polonais was performed as a marionette play by the students at their homes in what they called the "Theatre des Phynances", named in honor of Père Hébert's lust for "phynance" (finance), or money. This prototype for Ubu Roi is long-lost, so the true and complete details of the authorship of Ubu Roi may never be known. It is clear, however, that Jarry considerably revised and expanded the play.
While his schoolmates lost interest in the Ubu legends when they left school, Jarry continued adding to and reworking the material for the rest of his short life. His plays are controversial for their scant respect to royalty, religion and society, their vulgarity and scatology,[14][15] their brutality and low comedy, and their perceived utter lack of literary finish.[16]
Ubu
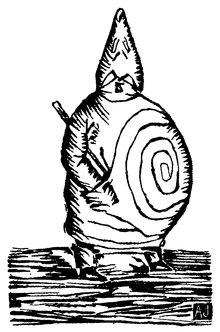
According to Jane Taylor, "the central character is notorious for his infantile engagement with his world. Ubu inhabits a domain of greedy self-gratification".[7] Jarry's metaphor for the modern man, he is an antihero — fat, ugly, vulgar, gluttonous, grandiose, dishonest, stupid, jejune, voracious, greedy, cruel, cowardly and evil — who grew out of schoolboy legends about the imaginary life of a hated teacher who had been at one point a slave on a Turkish galley, at another frozen in ice in Norway and at one more the King of Poland. Ubu Roi follows and explores his political, martial and felonious exploits.
"There is", wrote Taylor, "a particular kind of pleasure for an audience watching these infantile attacks. Part of the satisfaction arises from the fact that in the burlesque mode which Jarry invents, there is no place for consequence. While Ubu may be relentless in his political aspirations, and brutal in his personal relations, he apparently has no measurable effect upon those who inhabit the farcical world which he creates around himself. He thus acts out our most childish rages and desires, in which we seek to gratify ourselves at all cost".[7] The derived adjective "ubuesque" is recurrent in French and francophone political debate.
Première
Both Ubu Cocu and Ubu Roi have a convoluted history, going through decades of rewriting and, in the case of the former, never arriving, despite Jarry's exertions, at a definitive version.[17] By the time Jarry wanted Ubu Roi published and staged, the Morins had lost their interest in schoolboy japes, and Henri gave Jarry permission to do whatever he wanted with them. Charles, however, later tried to claim credit, but it had never been a secret that he had had some involvement with the earliest version.
The first word of the play ("merdre", the French word for "shit", with an extra "r") may have been part of the reason for the response to the play in Paris. At the end of the performance a riot broke out, an incident which has since become "a stock element of Jarry biographia".[7] After this, Ubu Roi was outlawed from the stage, and Jarry moved it to a puppet theatre.
Jarry said to the audience in a curtain speech just before that first performance in Paris: "You are free to see in M. Ubu however many allusions you care to, or else a simple puppet — a school boy's caricature of one of his professors who personified for him all the ugliness in the world".[14]
The poet William Butler Yeats, who joined in the shouting on that first night, later described his experience and had this comment regarding the event: "After Stéphane Mallarmé, after Paul Verlaine, after Gustave Moreau, after Puvis de Chavannes, after our own verse, after all our subtle colour and nervous rhythm, after the faint mixed tints of Conder, what more is possible? After us the Savage God".[18]
Adaptations
Ubu Roi was translated to Czech by Jiří Voskovec and Jan Werich as Král Ubu, and premiered in 1928 at Osvobozené divadlo. The play was banned in Czechoslovakia after the 1968 Soviet invasion.
The play was the basis for Jan Lenica's animated film Ubu et la Grande Gidouille (1976).
In Lithuania (then part of the USSR) the play was adapted as "Karalius Ūbas" by director Jonas Vaitkus in 1983.
The play has been adapted for an opera with libretto by Michael Finnissy and Andrew Toovey with music by Andrew Toovey. Production by the Banff Centre Theatre, Canada in collaboration with Music Theatre Wales (May 1992). Directed by Keith Turnbull.
A musical adaptation, "Ubu Rock," book by Andrei Belgrader and Shelly Berc, music and lyrics by Rusty Magee, premiered at the American Repertory Theatre in 1995 and was remounted at ART the following year.
The play was adapted as Jane Taylor's Ubu and the Truth Commission (1998), a play critical of the South African Truth and Reconciliation Commission, which was formed in response to the atrocities committed during Apartheid.
The play was also adapted for the Czech film Král Ubu, directed by F. A. Brabec in 1996. The film received three Czech Lion Awards.
In Poland the play was adapted for the film Ubu Król 2003 by Piotr Szulkin, highlighting the grotesque nature of political life in Poland immediately after the fall of communism.
Inspired by the black comedy of corruption within Ubu Roi, the Puerto Rican absurdist narrative United States of Banana by Giannina Braschi dramatizes, with over-the-top grotesque flourishes known to 'pataphysics, the fall of the American Empire and the liberation of Puerto Rico.[19]
The play was translated by David Ball in the Norton Anthology of Drama (2010), and performed at the University of Virginia the same year. Sherry CM Lindquist's adaptation was performed in Chicago, at The Public Theater in New York City, at the International Festival Of Puppet Theater and at the Edison Theater, St. Louis, Missouri, by Hystopolis Productions, Chicago, from 1996 to 1997.
The play was adapted and directed by Dash Kruck as part of Vena Cava Production's 2013 Mainstage Season. Performed in Brisbane, Australia, the adaptation made cultural political references to Queensland's Premier Campbell Newman, even including him in the show's promotional poster.[20]
In 2014, Toronto's One Little Goat Theatre Company produced Ubu Mayor: A Harmful Bit of Fun, combining the merde-filled sensibilities of Ubu Roi with the internationally renowned antics, absurdities and obscenities of Toronto's mayor Rob Ford and his brother Doug.
Ubu Roi was translated into Serbian in 1964 by Ljubomir Draškić and performed at Atelje 212 theatre in Belgrade for the next 20 years when Zoran Radmilović who played Pere Ubu, died. The play was so successful at the box-office that it was adapted into a movie in 1973.
In 2016, the play was adapted by Jared Strange into UBU ROY: An American Tale, an updated version of the original play through the lens of the 2016 United States presidential election. The show opened November 3, 2016 in Lubbock, Texas as the Lubbock Community Theatre's first play in their "LCT After Dark" season.[21][22]
References in popular culture
Alfred Jarry is one of the few real figures to appear among the many literary characters in Les Faux-Monnayeurs (The Counterfeiters), by André Gide. In Part III, Chapter 8, Jarry attends a literary banquet, where the fictional Comte de Passavant introduces him as the author of Ubu Roi, saying that they (the literary set) "lui confèrent du génie, parce que le public vient de siffler sa pièce. C'est tout de même ce qu'on a donné le plus curieux au théâtre depuis longtemps".[23] They "have dubbed him a genius because the public have just damned his play. All the same, it's the most interesting thing that's been put on the stage for a long time".[24]
Joan Miró used Ubu Roi as a subject of his 50 1940 lithographs called the Barcelona Series. These pictures could be Ubu Roi but they also satirise General Franco and his generals after he had won the Spanish Civil War.[25]
In her book Linda McCartney's Sixties: Portrait of an Era, Linda McCartney mentions that Paul had become interested in avant-garde theatre and immersed himself in the writings of Jarry. This is how McCartney discovered the word "'pataphysical", which he used in the lyrics of his song "Maxwell's Silver Hammer".[26]
The Walter Jon Williams novel Angel Station is based on the plot.
The American experimental rock group Pere Ubu is named after the main character. Their 2009 album Long Live Père Ubu! is an adaptation of Jarry's play.[27]
Dead Can Dance's frontman Brendan Perry makes a reference to Père Ubu in the song "The Bogus Man" (on his second solo album Ark) with the line "Hail, Father Ubu, here comes the Grand Guignol".
The figure of Ubu Roi, particularly as depicted by Jarry in his woodcut, appears to have inspired the character Oogie Boogie in Tim Burton's animated film The Nightmare Before Christmas.[28]
Television producer Gary David Goldberg named his dog Ubu and his production company Ubu Productions after Ubu Roi.
Cast
|
|
Notes
- 1 2 Hill, Phillip G. Our Dramatic Heritage. Vol. 6. Fairleigh Dickenson, 1995, p. 30. ISBN 0838634214
- 1 2 Ford, Mark (May 10, 2012), "The King of Charisma", The New York Review of Books. 59 (8): 63–64
- ↑ Ball, David. "UBU-ing a Theatre-Translation: Defense and Illustration". Metamorphoses, a Journal of Literary Translation. Spring and Fall. 2006
- ↑ Fell, JIll. Alfred Jarry, an Imagination in Revolt. Rosemont Publishing & Printing Corp. page 142
- ↑ Jarry, Alfred. Ubu Roi. Dover (2003)
- ↑ Benedikt, Michael and Wellwarth. Modern French Theatre. Dutton. 1966. pp. x-xi
- 1 2 3 4 5 Taylor, Jane. "Ubu and the Truth Commission". University of Cape Town Press. 2007. ISBN 978 19197 13168 p. iii
- ↑ Hill, Phillip G. Our Dramatic Heritage. Vol. 6. Fairleigh Dickenson, 1995, p. 31. ISBN 0838634214
- ↑ Innes, Christopher. Avant-Garde Theatre: 1892 1992. Routledge. 1993, p. 24. ISBN 0-415-06517-8
- ↑ Faustroll, Dr. Pataphysica 2: Pataphysica E Alchimia, Volume 2. iUniverse (2004). ISBN 9780595337453
- ↑ Offord, M.H. Francophone Literatures: A Literary and Linguistic Companion. Psychology Press (2001). ISBN 9780415198400 page 123
- ↑ Jarry, Alfred. The Ubu Plays. Nick Hearn Books, Ltd. 1997. Introduction.
- ↑ Pindar, Ian. "Merrrrdrrrre! Alfred Jarry and Pere Ubu". Times Literary Supplement. 17 April 2013.
- 1 2 Jarry, Alfred. Ubu Roi. Dover. 2003
- ↑ Ubu carries as his weapons a pshittasword and a pshittashook, while his sceptre takes the traditional form of a commode scrubber; at one point, he thrusts his conscience down said commode. His peers, meanwhile, bear such names as MacNure, Pissweet and Pissale. In addition, the first word of Ubu Roi is "merdre", deliberately close to "merde", meaning "excrement".
- ↑ Ubu Roi has a loose narrative thread, a large number of characters who appear for only a short scene and a mashup of high literature and slang, much of it invented.
- ↑ The third play was the only one wholly written by the adult Jarry.
- ↑ Benedikt, Michael and Wellwarth. Modern French Theatre. Dutton. 1966.
- ↑ World Literature Today, What to Read Now: Mixed-Genre Literature, Giannina Braschi
- ↑ Vena Cava Productions presents UBU ROI. Wherevent (2013-07-22). Retrieved on 2014-05-25.
- ↑ Kelly, Aden. "LCT After Dark debuts Thursday". Retrieved 2016-11-03.
- ↑ Falkenberg, Emily (2016-11-01). "Looking to Find Humor in this Election? Lubbock Community Theatre Has You Covered". EVERYTHINGLUBBOCK. Retrieved 2016-11-03.
- ↑ Les Faux-Monnayeurs, André Gide. edition Folio Plus Classiques. p.319
- ↑ The Counterfeiters, André Gide, translated by Dorothy Bussy. Vintage Books. p.289
- ↑ Searle, Adrian (11 April 2011). "Joan Miró: A fine line". The Guardian. Retrieved 28 September 2011.
- ↑ McCartney, Linda. Linda McCartney's Sixties: Portrait of an Era. Bullfinch Press. Page 153. 1992
- ↑ "Long Live Père Ubu!"
- ↑ Atomic Caravan Blog
Bibliography
- Jarry, Alfred. Ubu Roi. Translated by Barbara Wright and illustrated by Franciszka Themerson. Gaberbocchus Press. 1951
- Jarry, Alfred. Ubu Roi. Translated by David Ball as Ubu the King. [Norton Anthology of Drama, 2010.]
- Jarry, Alfred. Ubu Roi. Translated by Beverly Keith and Gershon Legman. Dover, 2003.
- Innes, Christopher. Avant-Garde Theatre 1892-1992. London and New York: Routledge, 1993. 0415065186.
- Taylor, Jane. Ubu and the Truth Commission. Cape Town: University of Cape Town Press, 2007.
- Pile, Stephen, The Return of Heroic Failures, Harmondsworth, Penguin Books, 1988.
- Fell, Jill: Alfred Jarry: An Inagination in Revolt. Fairleigh Dickinson University Press. 2005
- Brotchie, Alastair. Alfred Jarry, a Pataphysical Life. MIT Press. 2013. ISBN 978 0 262 01619 3
External links
| French Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Ubu Roi |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ubu Roi. |
- UBU-ing a Theatre-Translation: Defense and Illustration by David Ball (with his translation of the first act). Metamorphoses, Spring 2001 (9.1).
- Ubu Roi at Project Gutenberg in the original French
- Article about Polish adaptations of Ubu