Wheel train
In horology, a wheel train (or just train) is the gear train of a mechanical watch or clock.[1] Although the term is used for other types of gear trains, the long history of mechanical timepieces has created a traditional terminology for their gear trains which is not used in other applications of gears.
Watch movements are very standardized, and the wheel trains of most watches have the same parts. The wheel trains of clocks are a little more varied, with different numbers of wheels depending on the type of clock and how many hours the clock runs between windings (the "going").[2] However, the wheel trains of clocks and watches share the same terminology, and are similar enough that they can be described together. The large gears in timepieces are generally called wheels, the smaller gears they mesh with (large to small, large to small) are called pinions, and the shafts that the wheels and pinions are mounted on are called arbors.[3] The wheels are mounted between the plates of the movement, with the pivots rotating in holes in the plates. The pivot holes have semicircular depressions around them, called oil cups, to hold the oil in contact with the shaft by capillary action. There are several wheel trains in a typical clock or watch.
Going train
The going train is the main gear train of the timepiece. It consists of the wheels that transmit the force of the timepiece's power source, the mainspring or weight, to the escapement to drive the pendulum or balance wheel.[4] The going train has two functions. First, it scales up the speed of rotation of the mainspring or weight pulley. This allows the use of a very strong, slow turning mainspring or heavy weight that will run the timepiece for days or weeks. Second, its gear ratios divide the rotation of the escape wheel into convenient time units of seconds, minutes, and hours, to turn the timepiece's hands. The going train wheels are the only ones under load in a timepiece, since they bear the constant torque of the mainspring which is applied to the escapement, so these wheels are the only ones that receive significant wear.[5] In watches and some high quality clocks their arbors have jewel bearings. The going train in a modern clock or watch consists of:
- First or Great wheel - is attached and ratcheted to the main spring, or cable, barrel. The ratchet allows the main spring or cable barrel to be wound without turning the wheel. In horology jargon the pawl of the ratchet is called "the click". The first wheel turns the pinion of the Center wheel.
- Center or second wheel - which turns once per hour. Its pinion is turned by the teeth on the mainspring barrel in watches and spring driven clocks, and by the weight pulley in weight driven clocks. Its arbor projects through a hole in the face and drives, via a friction coupling, the cannon pinion, which carries the minute hand. It also drives the pinion of the third wheel. In wrist watches with centre seconds, that is with the seconds hand pivoted coaxially with the minute and hour hands, this wheel is positioned off centre to allow the fourth wheel to be placed at the centre of the movement. In this arrangement the wheel is called the second wheel, because it is still the second wheel in the train but no longer at the centre of the movement.
- Third wheel - which drives the pinion of the fourth wheel. (this is called the third wheel because the mainspring barrel is the first wheel and the center wheel is the second wheel in the gear train)
- Fourth wheel - In clocks and watches with the second hand in a subdial on the face, this turns once per minute, and the shaft projects through the face and holds the second hand. The fourth wheel also turns the escape wheel pinion. Many clocks don't need this wheel, because of their slower moving escapements, and in these the third wheel drives the escape wheel directly.
- Escape wheel - This wheel is released one tooth at a time by the escapement, with each swing of the pendulum or balance wheel. The escape wheel keeps the pendulum or balance swinging by giving it a small push each time it moves forward.
Motion work
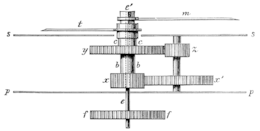
The motion work is the small 12-to-1 reduction gear train that turns the timepiece's hour hand from the minute hand.[6][7] It is attached to the going train by the friction coupling of the cannon pinion, so the minute and hour hands can be turned independently to set the timepiece. It is often located on the outside of the movement's front plate, just under the dial. It consists of:
- Cannon pinion - a pinion with a hollow shaft that fits friction tight over the center wheel shaft, projects through the face, and holds the minute hand. While the timepiece is not being set, this is turned by the center wheel, and drives the minute wheel. While being set it is turned by the setting mechanism, in modern clocks a setting knob on the back of the clock. In watches during setting this is turned by the minute wheel, which is turned by the keyless work. In older clocks the setting was done by opening the face and manually pushing the minute hand, which rotated the cannon pinion directly.
- Minute wheel - Its pinion drives the hour wheel. During setting, this is driven by the intermediate wheel in the keyless work and it turns both the cannon pinion and the hour wheel, moving the hands.
- Hour wheel - which fits over the shaft of the cannon pinion, and whose shaft holds the hour hand. The hour wheel rotates once for every 12 rotations of the cannon pinion.
Keyless work
Used in watches, the keyless work are the gears that wind the mainspring when the crown is turned, and when the crown is pulled out allow the hands to be set.[8] The term originated because, before the modern form of keyless work was invented by the French watchmaker Adrien Philippe in 1843, watches were wound and set by inserting a separate key into holes in the back and turning it.[9] The core of the keyless mechanism is a gear on the watch's winding stem, the clutch (or castle wheel in Britain), with two sets of axial gear teeth on it, which slides in and out. When the stem is pushed in, a lever slides the clutch out, and the outer set of teeth engages a small wheel train which turns the mainspring arbor, winding the mainspring. When the stem is pulled out, the clutch slides in, and the inner teeth engage another wheel, which turns the hour wheel in the motion work, turning the watch's hands.
Striking train
In striking clocks, the striking train is a gear train that moves a hammer to strike the hours on a gong. It is usually driven by a separate but identical power source to the going train. In antique clocks, to save costs, it was often identical to the going train, and mounted parallel to it on the left side when facing the front of the clock.[10]
Footnotes
- ↑ "Mechanical clock: p.3 The wheelwork". Encyclopædia Britannica online. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc. 2008. Retrieved 2008-07-06.
- ↑ Milham, Willis I. (1945). Time and Timekeepers. New York: MacMillan. p. 178. ISBN 0-7808-0008-7.
- ↑ Britannica 2008
- ↑ Odets, Walt (2004). "The Wheel Train". Illustrated Glossary of Watch Parts. TimeZone Watch School. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
- ↑ Hahn, Ed. "Are more jewels better?". Sec. 1.1.5 Mechanical Watch FAQ v.1.0. TimeZone.com. Retrieved 2008-07-02.
- ↑ Milham 1945, p.113-114
- ↑ Odets, Walt (2004). "The Motion Works". Illustrated Glossary of Watch Parts. TimeZone Watch School. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
- ↑ Odets, Walt (2004). "The Keyless Works". Illustrated Glossary of Watch Parts. TimeZone Watch School. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
- ↑ Odets, Walt (2004). "The Keyless Works of a Watch". The Horologium. TimeZone.com. Retrieved 2008-07-05.
- ↑ Milham 1945, p.198