Kasaragod district
| Kasargod district | |
|---|---|
 Location in Kerala, India | |
| Coordinates: 12°30′N 75°00′E / 12.5°N 75°ECoordinates: 12°30′N 75°00′E / 12.5°N 75°E | |
| Country |
|
| State | Kerala |
| District | Kasargod |
| Region | Tulunadu |
| Area | |
| • City | 1,992 km2 (769 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • City | 1,307,375 |
| • Density | 660/km2 (1,700/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,642,892 |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Malayalam, Tulu |
| Time zone | IST (UTC+5:30) |
| PIN | 671 xxx |
| Telephone code | 0499 |
| ISO 3166 code | IN-KL |
| Vehicle registration | KL-14 KL-60 |
| Website |
kasargod |
Kasaragod District is one of the 14 districts in the state of Kerala, India. Kasaragod became part of Kannur district following the reorganisation of states and formation of Kerala in November 1, 1956.[1] Kasaragod was declared as a district on 24 May 1984.
Overview
To its south lies Kannur District, to the South east is Kodagu district(Coorg) and to the north Dakshina Kannada district. All along its east it is walled by the Western Ghats while along the west the Laccadive Sea borders it.
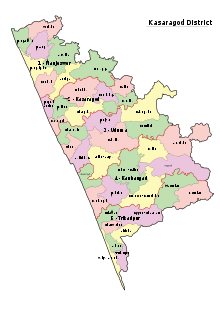
The district, covering an area of around 1992 km2, has a population (2011 census) of 1,307,375 and has four taluks, namely, Kasaragod and Hosdurg (Kanhangad), Vellarikundu and Manjeshwaram Taluk. Major towns in Kasaragod district are Nileshwar, Kanhangad, Kasaragod, Uppala, Kumbla, cheruvathur and Trikaripur. It has three municipalities (Nileshwar Kasaragod, and Kanhangad and thirty-eight grama panchayats.[2]
History
Kasaragod was known to the Arabs by the name Harkwillia.[3] Many Arab travelers who visited Kerala between the 9th and the 14th centuries visited Kasaragod, which was an important trade centre then. Duarte Borbosa, the Portuguese traveler who visited Kumbla, near Kasaragod in 1514, recorded rice being exported for coir to Maldives.[3]
Kasaragod was part of the kumbala Kingdom in which there were 64 Tulu and Malayalam villages.[3] When the Vijayanagara empire attacked Kasaragod, it was still under the Kolathiri Raja who had Nileshwaram as one of his capitals. During the decline of the Vijayanagara empire, the administration of this area was vested with Ikkeri Nayakas.[3] At the onset of collapse of the Vijayanagara empire, Venkappa Nayaka declared independence to Ikkery. Kumbla, Chandragiri and Bekal are considered to be the chain of forts constructed or renovated by Shivappa Nayaka.[3]
Francis Buccanan, the family doctor of Arthur Wellesley, visited Kasargod in 1800.[3] In his travelogue, he recorded information on places like Athiraparambu, Kavvai, Nileshwaram, Bekal, Chandragiri and Manjeshwaram.[3] In 1763, Hyder Ali conquered Bedanoor (Bidnur), the capital of the Ikkery Naiks. His son Tippu Sultan conquered much of Malabar. As per the Sreerangapattanam Treaty of 1792, Tippu surrendered Malabar, except Kanara to the British. The British got Kanara only after the death of Tippu Sultan.[3] it is said that Kinavoor Molom (Sree Dharma Shashtha Temple)is belonging to Karinthalam (one among 64 Brahmin Villages in old Kerala).
Before the formation of Kerala, Kasaragod was a part of erstwhile South Canara district of Madras Presidency. Kasaragod became part of Kannur district following the reorganisation of states and formation of Kerala in November 1, 1956.[4] Kasaragod was declared as a district on 24 May 1984.
Geography
The district is the northernmost district of the State of Kerala. Kasaragod is located at 12°30′N 75°00′E / 12.5°N 75.0°E.[5] It has an average elevation of 19 metres (62 feet).
Climate
| Climate data for Kasaragod | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 33.1 (91.6) |
33.3 (91.9) |
33.9 (93) |
34.3 (93.7) |
33.4 (92.1) |
29.8 (85.6) |
28.7 (83.7) |
28.8 (83.8) |
30.1 (86.2) |
31.2 (88.2) |
32.7 (90.9) |
33.1 (91.6) |
31.87 (89.36) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 21.1 (70) |
21.9 (71.4) |
23.7 (74.7) |
24.9 (76.8) |
24.9 (76.8) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23.2 (73.8) |
23.2 (73.8) |
22.7 (72.9) |
21.3 (70.3) |
23.03 (73.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 0.8 (0.031) |
0 (0) |
17.3 (0.681) |
32.7 (1.287) |
182.9 (7.201) |
1,010.5 (39.783) |
1,002.8 (39.48) |
663.6 (26.126) |
246.5 (9.705) |
222.6 (8.764) |
69 (2.72) |
12.4 (0.488) |
3,461.1 (136.266) |
| Source: Meo Weather | |||||||||||||
Demographics
According to the 2011 census Kasaragod district has a population of 1,307,375,[6] roughly equal to the nation of Mauritius[7] or the US state of New Hampshire.[8] This gives it a ranking of 375th in India (out of a total of 640).[6] The district has a population density of 654 inhabitants per square kilometre (1,690/sq mi) .[6] Its population growth rate over the decade 2001–2011 was 8.18%.[6] Kasaragod has a sex ratio of 1079 females for every 1000 males,[6] and a literacy rate of 89.85%.[6]
Health
Kasaragod district is one of the worst HIV infected areas in Kerala. 970 HIV cases were registered in Kasaragod district. Ten AIDS related deaths were reported in the Kasaragod district within a short period of two months in 2016. In terms of general healthcare, kasaragod is comparable to any other district in Kerala.[9]
Languages
Kasargod district is one of the rare districts in India which houses as many as 7 different languages (excluding dialects and tribal languages), with each spoken by a substantial number of people. [10]
The Malayalam spoken here has influences from Tulu and Kannada.[11][12]
Administration
Parliament Constituency
- Kasaragod
Assembly Constituencies
See also
- Kasaragod North
- Kasaragod Taluk
- Kasaragod East
- List of educational institutions in Kasaragod District
References
- ↑ "Kasaragod - After District Formation". Kasaragod District. Retrieved 2009-03-11.
- ↑ There are 38 Grama Panchayats in Kasaragod District (kasaragod.nic.in).
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Kasaragod History". Government of Kerala. Archived from the original on September 25, 2008. Retrieved 2009-03-11.
- ↑ "Kasaragod - After District Formation". Kasaragod District. Retrieved 2009-03-11.
- ↑ Falling Rain Genomics, Inc - Kasaragod
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "District Census 2011". Census2011.co.in. 2011. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
- ↑ US Directorate of Intelligence. "Country Comparison:Population". Retrieved 2011-10-01.
Mauritius 1,303,717 July 2011 est.
- ↑ "2010 Resident Population Data". U. S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
New Hampshire 1,316,470
- ↑ http://english.mathrubhumi.com/health/health-news/10-hiv-deaths-reported-in-kasargod-dist-within-2-months-english-news-1.1315218
- ↑ Kumar Suresh Singh (1998). India's communities. 6. Anthropological Survey of India. p. 1549.
- ↑ A Sreedhara Menon (1 January 2007). A Survey Of Kerala History. DC Books. pp. 14–15. ISBN 978-81-264-1578-6.
- ↑ "Introduction to Kasaragod district".
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kasaragod district. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Kasaragod District. |
- Official District Website
- List of tourism places in Kasaragod