Karachay-Cherkessia
| Karachay-Cherkess Republic Карачаево-Черкесская Республика (Russian) Къарачай-Черкес Республика (Karachay-Balkar) Къэрэшей-Шэрджэс Республикэ (Kabardian) Къарашай-Шеркес Республикасы (Nogai) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| — Republic — | |||||
| |||||
|
| |||||
| |||||
|
| |||||
| Political status | |||||
| Country | Russia | ||||
| Federal district | North Caucasian[2] | ||||
| Economic region | North Caucasus[3] | ||||
| Established | July 3, 1991[4] | ||||
| Capital | Cherkessk | ||||
| Government (as of February 2015) | |||||
| • Head[5] | Rashid Temrezov[6] | ||||
| • Legislature | People's Assembly (Parliament)[5] | ||||
| Statistics | |||||
| Area (as of the 2002 Census)[7] | |||||
| • Total | 14,100 km2 (5,400 sq mi) | ||||
| Area rank | 77th | ||||
| Population (2010 Census)[8] | |||||
| • Total | 477,859 | ||||
| • Rank | 73rd | ||||
| • Density[9] | 33.89/km2 (87.8/sq mi) | ||||
| • Urban | 43.4% | ||||
| • Rural | 56.6% | ||||
| Population (January 2014 est.) | |||||
| • Total | 470,059[10] | ||||
| Time zone(s) | MSK (UTC+03:00)[11] | ||||
| ISO 3166-2 | RU-KC | ||||
| License plates | 09 | ||||
| Official languages | Russian;[12] Abaza, Cherkess, Karachay, Nogai[13] | ||||
| Official website | |||||
The Karachay-Cherkess Republic (Russian: Карача́ево-Черке́сская Респу́блика, Karachayevo-Cherkesskaya Respublika; Karachay-Balkar: Къарачай-Черкес Республика, Qaraçay-Çerkes Respublika; Kabardian: Къэрэшей-Шэрджэс Республикэ, Ķêrêšei-Šêrdžês Respublikê), Nogai: Карашай-Шеркеш Республикасы, Qaraşay-Şerkeş Respublikası; also called Karachay-Cherkessia (Karachay-Circassia) (Карача́ево-Черке́сия, Karachayevo-Cherkesiya) and the Karachay-Circassian Republic, is a republic of Russia located in the North Caucasus area of southern European Russia.
Karachay-Cherkessia is a landlocked republic, bordered by Krasnodar Krai to the west and northwest, Stavropol Krai to the northeast, Abkhazia to the west, Kabardino-Balkaria to the southeast and Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti to the south. It covers mostly mountainous terrain. The republic has several distinct ethnic groups, and the government recognizes five official languages.[13] The population in 2010 was just under half a million people.[8]
Geography


The republic is located at the slopes of northwestern Caucasus and borders with Krasnodar Krai in the west and northwest, the Kabardino-Balkar Republic in the southeast, Georgia (including Abkhazia) in the south and west, and with Stavropol Krai in the northeast. It stretches for 140 kilometers (87 mi) from north to south and for 170 kilometers (110 mi) from east to west. Mountains cover 80% of the republic's territory; Mount Elbrus, which at 5,642 meters (18,510 ft) is the highest peak in Caucasus, is located on the republic's border with Kabardino-Balkaria. The republic is rich in water resources. A total of 172 rivers flow through its territory, with the largest one being the Kuban, Bolshoy Zelenchuk, Maly Zelenchuk, Urup, and Laba. There are about 130 mountain lakes of glacial origin and an abundance of mineral springs. Climate is moderate, with short winters and long, warm, humid summers. The average January temperature is −3.2 °C (26.2 °F), and the average July temperature is +20.6 °C (69.1 °F). Average annual precipitation varies from 550 millimeters (22 in) in the plains to 2,500 millimeters (98 in) in the mountains. Natural resources include gold, coal, clays, and more.
History
The Karachay-Cherkess Autonomous Oblast was created 12 January 1922, in the early years of the Soviet Union. It was split into Karachay Autonomous Oblast and Cherkess National Okrug on 26 April 1926. The Cherkess National District was elevated to an autonomous oblast status on 30 April 1928.
In 1943, Karachay Autonomous Oblast was abolished, the Karachay people were accused of collaboration with the Nazis and subsequently deported to the Kazakh and Uzbek republics. Most of the Karchay territory was split between Stavropol Krai and the Georgian SSR. The remaining territory populated by the Cherkessians was known as Cherkess Autonomous Oblast until 9 January 1957 when it was re-established into Karachay-Cherkess Autonomous Oblast[14] in its former borders due to the rehabilitation of the Karachay.
On July 3, 1991, the autonomous oblast was elevated to the status of the Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic of Karachay-Cherkessia (under the jurisdiction of the Russian SFSR). With the dissolution of the Soviet Union, congresses of deputies of various nationalities proclaimed:
- Karachay Soviet Socialist Republic (Карачаевская Советская Социалистическая Республика; Къарачай Совет Социалист Республика) on 18 November 1990 (renamed Karachay Republic [Карачаевская Республика; Къарачай Республика] on October 17, 1991)
- Batalpashinsk Cossack Republic (Баталпашинская Казачья Республика) and Zelenchuk-Urup Cossack Soviet Socialist Republic (Зеленчукско-Урупская Казачья Советская Социалистическая Республика) on August 19, 1991 (united as the Upper Kuban Cossack Republic [Верхне-Кубанская Казачья Республика] on November 30, 1991)
- Cherkess Republic (Республика Черкесия) on October 27, 1991
- Abazin Republic (Абазинская Республика) in November 1991
After demonstrations in December 1991, the Supreme Soviet of Karachay-Cherkessia adopted an appeal for the recognition of the individual republics. Also in December 1991, the words "Autonomous Soviet Socialist" were dropped from the official name of Karachay-Cherkessia.
In January 1992, Russian President Boris Yeltsin was prepared to accept the division of Karachay-Cherkessia and introduced draft laws to the Supreme Soviet of Russia for the reconstitution of the Karachai Autonomous Oblast and Cherkess Autonomous Oblast within the Russian Federation. A commission was established Supreme Education Council three autonomous regions - Karachai, Cherkess and Batalpashinsk.
On March 28, 1992, a referendum was held in which, according to official results, the majority of the population of Karachay-Cherkessia voted against splitting the republic and, on December 9, 1992, the republic was recognized as the Karachay-Cherkess Republic.[15]
Administrative divisions
Demographics
Population: 477,859 (2010 Census);[8] 439,470 (2002 Census);[16] 417,560 (1989 Census).[17]
Vital statistics
| Average population (x 1000) | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1000) | Crude death rate (per 1000) | Natural change (per 1000) | Total fertility rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 346 | 6,021 | 2,153 | 3,868 | 17.4 | 6.2 | 11.2 | |
| 1975 | 357 | 6,619 | 2,288 | 4,331 | 18.5 | 6.4 | 12.1 | |
| 1980 | 373 | 7,044 | 2,794 | 4,250 | 18.9 | 7.5 | 11.4 | |
| 1985 | 394 | 8,119 | 3,350 | 4,769 | 20.6 | 8.5 | 12.1 | |
| 1990 | 422 | 7,218 | 3,496 | 3,722 | 17.1 | 8.3 | 8.8 | |
| 1991 | 427 | 7,145 | 3,713 | 3,432 | 16.7 | 8.7 | 8.0 | |
| 1992 | 431 | 6,846 | 3,915 | 2,931 | 15.9 | 9.1 | 6.8 | |
| 1993 | 433 | 5,569 | 4,336 | 1,233 | 12.9 | 10.0 | 2.8 | |
| 1994 | 434 | 5,786 | 4,598 | 1,188 | 13.3 | 10.6 | 2.7 | |
| 1995 | 437 | 5,633 | 4,501 | 1,132 | 12.9 | 10.3 | 2.6 | |
| 1996 | 439 | 5,281 | 4,683 | 598 | 12.0 | 10.7 | 1.4 | |
| 1997 | 440 | 4,987 | 4,615 | 372 | 11.3 | 10.5 | 0.8 | |
| 1998 | 441 | 4,990 | 4,537 | 453 | 11.3 | 10.3 | 1.0 | |
| 1999 | 441 | 4,523 | 4,707 | - 184 | 10.3 | 10.7 | -0.4 | |
| 2000 | 440 | 4,666 | 4,961 | - 295 | 10.6 | 11.3 | -0.7 | |
| 2001 | 440 | 4,778 | 4,911 | - 133 | 10.9 | 11.2 | -0.3 | |
| 2002 | 440 | 4,927 | 5,207 | - 280 | 11.2 | 11.8 | -0.6 | |
| 2003 | 442 | 5,088 | 5,427 | - 339 | 11.5 | 12.3 | -0.8 | |
| 2004 | 446 | 5,190 | 5,059 | 131 | 11.6 | 11.3 | 0.3 | |
| 2005 | 450 | 5,194 | 5,131 | 63 | 11.5 | 11.4 | 0.1 | |
| 2006 | 454 | 5,032 | 4,924 | 108 | 11.1 | 10.8 | 0.2 | |
| 2007 | 459 | 6,066 | 4,626 | 1,440 | 13.2 | 10.1 | 3.1 | |
| 2008 | 465 | 6,364 | 4,731 | 1,633 | 13.7 | 10.2 | 3.5 | |
| 2009 | 470 | 6,200 | 4,711 | 1,489 | 13.2 | 10.0 | 3.2 | 1,55 |
| 2010 | 476 | 6,139 | 4,737 | 1,402 | 12.9 | 10.0 | 2.9 | 1,51 |
| 2011 | 477 | 6,289 | 4,664 | 1,625 | 13.1 | 9.7 | 3.4 | 1,54 |
| 2012 | 475 | 6,499 | 4,633 | 1,866 | 13.7 | 9.8 | 3.9 | 1,63 |
| 2013 | 471 | 6,547 | 4,464 | 2,083 | 13.9 | 9.5 | 4.4 | 1,67 |
| 2014 | 470 | 6,318 | 4,553 | 1,765 | 13.5 | 9.7 | 3.8 | 1,65 |
| 2015 | 468 | 5,803 | 4,523 | 1,280 | 12.4 | 9.6 | 2.8 | 1,54 |
| 2016 | 467 | 5,575 | 4,393 | 1,182 | 11.9 | 9.4 | 2.5 | 1,52(e) |
Sources: 1970 to 2008;[18] 2009-2013[19]
Ethnic groups
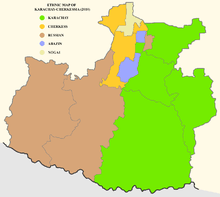
According to the 2010 Census, Karachays make up 41% of the republic's population, followed by Russians (32%), and Cherkes and Abazins together make up 20%.[8]
| Ethnic group |
1926 Census1 | 1939 Census | 1959 Census | 1970 Census | 1979 Census | 1989 Census | 2002 Census | 2010 Census3 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| Karachays | 53,175 | 31.3% | 70,932 | 29.2% | 67,830 | 24.4% | 97,104 | 28.2% | 109,196 | 29.7% | 129,449 | 31.2% | 169,198 | 38.5% | 194,324 | 41.0% |
| Cherkess | 16,1862 | 9.5% | 17,667 | 7.3% | 24,145 | 8.7% | 31,190 | 9.0% | 34,430 | 9.4% | 40,241 | 9.7% | 49,591 | 11.3% | 56,466 | 11.9% |
| Abazins | 13,731 | 8.1% | 14,138 | 5.8% | 18,159 | 6.5% | 22,896 | 6.6% | 24,245 | 6.6% | 27,475 | 6.6% | 32,346 | 7.4% | 36,919 | 7.8% |
| Russians | 40,072 | 23.6% | 118,785 | 48.8% | 141,843 | 51.0% | 162,442 | 47.1% | 165,451 | 45.1% | 175,931 | 42.4% | 147,878 | 33.6% | 150,025 | 31.6% |
| Nogais | 6,263 | 3.7% | 6,869 | 2.8% | 8,903 | 3.2% | 11,062 | 3.2% | 11,872 | 3.2% | 12,993 | 3.1% | 14,873 | 3.4% | 15,654 | 3.3% |
| Ukrainians | 32,518 | 19.1% | 4,104 | 1.7% | 4,011 | 1.4% | 4,819 | 1.4% | 4,555 | 1.2% | 6,308 | 1.5% | 3,331 | 0.8% | 1,990 | 0.4% |
| Others | 8,082 | 4.8% | 10,703 | 4.4% | 13,068 | 4.7% | 15,138 | 4.4% | 17,362 | 4.7% | 22,573 | 5.4% | 22,253 | 5.1% | 18,892 | 4.0% |
| 1 The results of the 1926 census refer to the present territory, which is a combination of the Cherkess ND, the Karachay AO and adjacent areas. The latter areas were mainly inhabited by Russians and Ukrainians.[20]
2 13,496 Kabardins and 2,690 Cherkess. 3 3,499 people were registered from administrative databases, and could not declare an ethnicity. It is estimated that the proportion of ethnicities in this group is the same as that of the declared group.[21] | ||||||||||||||||
Religion
According to a 2012 survey[22] 48% of the population of Karachay-Cherkessia adheres to Islam, 13.6% to the Russian Orthodox Church, 12% to the Karachay and Circassian native faith, 2% are unaffiliated generic Christians, 1% are unchurched Orthodox Christian believers or members of non-Russian Orthodox churches. In addition, 12% of the population declares to be "spiritual but not religious", 7% is atheist and 4.4% follows other religions or did not answer to the question.[22]
Politics
The head of the government in Karachay-Cherkessia is the Head (until June 28, 2012 the official title was "President"). Until February 2011, the President was Boris Safarovich Ebzeyev, a former judge of the Constitutional Court of Russian Federation. Rashid Temrezov is currently the Head of the republic.[6]
Ethnic tension is a considerable problem in the republic. In May 1999 Karachay-Cherkessia conducted its first ever free regional presidential election. When Vladimir Semyonov, a Karachay, won the election over Stanislav Derev, a Circassian, there were protests by supporters of Derev, with widespread allegations of fraud. A court ruling later upheld the election result, prompting thousands of Derev's supporters to march in protest, many advocating partition of the republic.
Although activity by separatists in the region pales in comparison with Chechnya and Dagestan, militant groups exist in Karachay-Cherkessia.[24] A car-bomb that killed two people in March 2001 was blamed on Chechen separatists. Muslim separatist groups have formed and dozens of their members have been killed by the Russian authorities.[24] In September 2007, the FSB killed ethnic Abazin Rustam Ionov ("Abu-Bakar"), head of the Karachaevo Jamaat (assembly), along with his wife.[25]
Science
The republic is the home of what was the largest telescope of the world from 1975 until 1993 (the BTA-6), a very large radio telescope (600 meters in diameter, RATAN-600), and the Special Astrophysical Observatory of the Russian Academy of Science dedicated to the study of astronomy. These facilities are located on the bank of the Zelenchuk River, between the villages of Zelenchukskaya and Arkhyz.
See also
References
Notes
- ↑ Law #410-XXII
- ↑ Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", №20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000.).
- ↑ Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
- ↑ Law #1539-I
- 1 2 Constitution of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic, Article 4
- 1 2 Official website of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic. Rashid Borispiyevich Temrezov, Head of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic (in Russian)
- ↑ Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Территория, число районов, населённых пунктов и сельских администраций по субъектам Российской Федерации (Territory, Number of Districts, Inhabited Localities, and Rural Administration by Federal Subjects of the Russian Federation)". Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved 2011-11-01.
- 1 2 3 4 Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). "Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1" [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года (2010 All-Russia Population Census) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved June 29, 2012.
- ↑ The density value was calculated by dividing the population reported by the 2010 Census by the area shown in the "Area" field. Please note that this value may not be accurate as the area specified in the infobox is not necessarily reported for the same year as the population.
- ↑ Karachay-Cherkess Republic Territorial Branch of the Federal State Statistics Service. Оценка численности постоянного населения КЧР на 1 января 2014 года (in Russian)
- ↑ Правительство Российской Федерации. Федеральный закон №107-ФЗ от 3 июня 2011 г. «Об исчислении времени», в ред. Федерального закона №271-ФЗ от 03 июля 2016 г. «О внесении изменений в Федеральный закон "Об исчислении времени"». Вступил в силу по истечении шестидесяти дней после дня официального опубликования (6 августа 2011 г.). Опубликован: "Российская газета", №120, 6 июня 2011 г. (Government of the Russian Federation. Federal Law #107-FZ of June 31, 2011 On Calculating Time, as amended by the Federal Law #271-FZ of July 03, 2016 On Amending Federal Law "On Calculating Time". Effective as of after sixty days following the day of the official publication.).
- ↑ Official throughout the Russian Federation according to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia.
- 1 2 Constitution of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic, Article 11.1
- ↑ Президиум Верховного Совета СССР. Указ от 9 февраля 1957 г. «О преобразовании Черкесской автономной области в Карачаево-Черкесскую автономную область». (Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR. Decree of 9 February 1957 On Transformation of Cherkess Autonomous Oblast into Karachay-Cherkess Autonomous Oblast. ).
- ↑ Закон РФ от 9 декабря 1992 г. N 4061-I «Об изменениях и дополнениях Конституции (Основного Закона) Российской Федерации — России» (принят седьмым Съездом народных депутатов РФ) (in Russian)
- ↑ Russian Federal State Statistics Service (May 21, 2004). "Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек" [Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000] (XLS). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian). Retrieved August 9, 2014.
- ↑ Demoscope Weekly (1989). "Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 г. Численность наличного населения союзных и автономных республик, автономных областей и округов, краёв, областей, районов, городских поселений и сёл-райцентров" [All Union Population Census of 1989: Present Population of Union and Autonomous Republics, Autonomous Oblasts and Okrugs, Krais, Oblasts, Districts, Urban Settlements, and Villages Serving as District Administrative Centers]. Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года [All-Union Population Census of 1989] (in Russian). Институт демографии Национального исследовательского университета: Высшая школа экономики [Institute of Demography at the National Research University: Higher School of Economics]. Retrieved August 9, 2014.
- ↑ Russian Federal State Statistics Service Archived January 3, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Демографический ежегодник России [Demographic Yearbook of Russia] (in Russian). Russian Federal State Statistics Service.
- ↑ http://www.ethno-kavkaz.narod.ru/rnkchr.html
- ↑ http://www.perepis-2010.ru/news/detail.php?ID=6936
- 1 2 3 Arena - Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in Russia. Sreda.org
- ↑ 2012 Survey Maps. "Ogonek", № 34 (5243), 27/08/2012. Retrieved September 24, 2012.
- 1 2 Mairbek Vatchagaev (21 June 2012). "The Karachay Jamaat: Alive and Operational". Eurasia Daily Monitor. The Jamestown Foundation. 9 (118). Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ↑ Fatima Tlis (31 January 2008). "Karachaevo-Cherkessia: A Small War with Big Repercussions". North Caucasus Analysis. The Jamestown Foundation. 9 (4). Retrieved 23 January 2015.
Sources
- Народное Собрание Карачаево-Черкесской Республики. Закон №410-XXII от 9 апреля 1998 г. «О государственном гимне Карачаево-Черкесской Республики», в ред. Закона №85-РЗ от 6 декабря 2013 г. «О внесении изменений в отдельные законодательные акты Карачаево-Черкесской Республики в связи с установлением административной ответственности за неправомерное использование государственных символов Карачаево-Черкесской Республики». Вступил в силу с момента опубликования, за исключением статей 2 и 3, вступающих в силу с 15 мая 1998 г.. Опубликован: "День Республики", №48(15471), 25 апреля 1998 г. (People's Assembly of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic. Law #410-XXII of April 9, 1998 On the State Anthem of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic, as amended by the Law #85-RZ of December 6, 2013 On Amending Various Legislative Acts of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic Due to the Introduction of Administrative Sanctions for Misuse of the Symbols of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic. Effective as of the moment of publication, with the exception of Articles 2 and 3, which take effect on May 15, 1998.).
- 5 марта 1996 г. «Конституция Карачаево-Черкесской Республики», в ред. Конституционного Закона №49-РКЗ от 27 июня 2012 г. «О внесении изменений в Конституцию Карачаево-Черкесской Республики». Вступил в силу со дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Сборник Законов и Постановлений КЧР 1995–1999 гг", Часть I. (March 5, 1996 Constitution of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic, as amended by the Constitutional Law #49-RKZ of June 27, 2012 On Amending the Constitution of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic. Effective as of the day of the official publication.).
- Верховный Совет РСФСР. Закон №1539-I от 3 июля 1991 г. «О порядке преобразования Адыгейской, Горно-Алтайской, Карачаево-Черкесской и Хакасской автономных областей в Советские Социалистические Республики в составе РСФСР». (Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR. Law #1539-I of July 3, 1991 On the Process of Transformation of Adyghe, Mountain Altai, Karachay-Cherkess, and Khakass Autonomous Oblasts into Soviet Socialist Republics Within the RSFSR. ).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Karachay-Cherkessia. |
- (in Russian) Official website of the Karachay-Cherkess Republic, kchr.info
- (in English) (in Russian) Collection of images of Karachay-Cherkessia, trombicula.narod.ru
- Images of Karachay-Cherkessia, travel-images.com
- An account of the disputed 1999 election, nupi.no
- Collection of images of Karachay-Cherkessia, with a focus on caves, tls-msu.narod.ru
- (in English) (in Turkish) Ulu Cami: A Karachay Mosque serving Muslim Community in Northern Jersey, ulucami.org
- Folk Song Mingitav, tika.gov.tr
- Tika.gov.tr
- Circassianworld.com
- Karachay-Cherkess Republic News Portal
- Medical institute of north caucasian state humanitarian and technological academy






