Jixiao Xinshu
| Chinese military texts |
|---|







The Jixiao Xinshu (simplified Chinese: 纪效新书; traditional Chinese: 紀效新書; pinyin: Jìxiào xīnshū) or New Treatise on Military Efficiency[1] was a military manual written by the Ming dynasty general Qi Jiguang. The book discusses military strategy, combat tactics, weapons and equipment, training, armed and unarmed fighting techniques, logistics, and other aspects of warfare. The Jixiao Xinshu is one of the earliest Asian extant texts to describe armed fighting techniques, and is one of several late Ming texts to address the relevance of martial arts to military training and warfare. Several contemporary martial arts styles of Qi's era are mentioned in the book, including the staff method of the Shaolin temple.
Background
In the late 16th century the military of the Ming dynasty was in poor condition. As the Mongol forces of Altan Khan raided the northern frontier, China's coastline fell prey to wokou pirates, who were ostensibly Japanese in origin. Qi Jiguang was assigned to the defense of Zhejiang in 1555, where he created his own standards of military organization, equipment, tactics, training, and procedures.[2] He published his thoughts on military techniques, tactics, and strategies in the Jixiao Xinshu after achieving several victories in battle.
Contents
There are two editions of the Jixiao Xinshu. The first edition was written from 1560-1561 and consists of 18 chapters. It is known as the 18 chapter edition. The second edition, published in 1584 during Qi's forced retirement, included re-edited and new material compiled in 14 chapters. It is known as the 14 chapter edition.
The chapters included in the 18-chapter edition are as follows:[3]
| Chapter | Subject |
|---|---|
| 1. | Five man squads |
| 2. | Signals and commands |
| 3. | Motivating troops |
| 4. | Issuing orders; prohibitions during combat |
| 5. | Training officers |
| 6. | Evaluating soldiers; rewards and punishments |
| 7. and 8. | Field camp activities; in-camp drilling with flags and drums |
| 9. | The march |
| 10. | Use of polearms |
| 11. | Use of the shield |
| 12. | Use of swords |
| 13. | Archery |
| 14. | Quanjing Jieyao Pian (Chapter on the Fist Canon and the Essentials of Nimbleness); unarmed fighting |
| 15. | Devices and formations for defending city walls |
| 16. | Illustrations of standards, banners, and signal drums |
| 17. | Guarding outposts |
| 18. | Coastal warfare |
Mandarin duck formation
In the Jixiao Xinshu, Qi Jiguang recommended a 12 man team known as the "mandarin duck formation" (Chinese: 鴛鴦陣; pinyin: yuānyāng zhèn), which ideally consisted of 11 soldiers and one person for logistics.[4]
- 4 men with long lances (twelve feet or longer) (chang qiang shou 長槍手)
- 2 men with sabers and rattan shields, one on each side of the lancers (dun pai shou 盾牌手)
- 2 men with multiple tip bamboo spears (lang xian shou 狼筅手)
- 2 men with tridents or swords (duan bing shou 短兵手)
- 1 corporal (with the squad flag) (dui zhang 隊長)
- 1 cook/porter (logistical personnel) (fuze huoshi de huobing 負責夥食的火兵)
The mandarin duck formation was ideally symmetrical. Excluding the corporal and cook/porter, the ten remaining men could be split into two identical five-man squads. This was so that when Japanese pirates made it past the long lances, the saber-and-shield men formed a protective screen for the vulnerable lancers. In battle, the two saber-and-shield men had different roles. The one on the right would hold the advance position of the squad, while the one on the left was to throw javelins and lure the enemy closer. The two men with multiple tip bamboo spears would entangle the pirates while the lancers attacked them. The trident carriers guarded the flanks and rear.[5]
After suffering several defeats to pirates, Qi also made a recommendation for a concerted campaign to integrate musket teams into the army, based on their superior range and firepower compared to bows and arrows.[6] Qi became enamored with the musket after his defeats and became one of the primary proponents of their use in the Ming army. He favored it for its accuracy and its ability to penetrate armor.[6]
Ideally an entire musket team would have 10 musketeers, but often had 4 or 2 in practice. The optimal musket formation that Qi proposed was a 12 man musket team similar to the melee mandarin duck formation. However, instead of fighting in a hand to hand formation, they operated on the principle of volley fire, which Qi pioneered prior to the publication of the first edition of the Jixiao Xinshu.[6] The teams could be arranged in a single line, formed two layers deep with five musketeers each, or five layers deep with two muskets per layer. Once the enemy was within range, each layer would fire in succession, and afterwards a unit armed with traditional close combat weapons would move forward ahead of the musketeers. The troops would then enter into melee combat with the enemy together. Alternatively, the musketeers could be placed behind wooden stockades or other fortifications, firing and reloading continuously by turns.[7]
Each squad was drilled in coordinated and mutually-supportive combat scenarios with clearly defined roles. Because Qi's troops were recruited from among peasants, and were not considered the equals of their Japanese foes, Qi Jiguang emphasized the use of combined arms and squad tactics. Units were rewarded or punished collectively: an officer was executed if his entire unit fled the enemy, and if a squad leader was killed in battle, the whole squad would be put to death.[8]
Weapons production
The standard procedure for the procurement of weapons for a commander such as Qi Jiguang was for production quotas to be assigned by provincial officials to each local district under the commander's responsibility. The resulting weapons produced under this system varied widely in quality. Muskets in particular exploded with alarming frequency, leading Qi to eschew reliance on firearms in favor of using melee tools such as swords, rattan shields, and sharpened bamboo poles.[9] However, later in his career Qi became a strong proponent of integrating muskets after suffering several defeats to the pirates. Qi's reconsideration of firearms in warfare led to the creation of the first well drilled musket teams in China. Qi was also a pioneer of the musket volley fire technique, which would later be adopted throughout China and Korea. Included in the manual are several passages detailing the usage of muskets, the volley fire technique, and an estimation of the percentage of firearms that would likely fail to fire.[10]
The manual provides the following description of the forging of swords:
| “ |
The following steps in the manufacturing process of the short sword are necessary:
|
” |
Unarmed fighting
The last chapter of the Jixiao Xinshu, the Quanjing Jieyao Pian, covers the subject of unarmed combat. Qi Jiguang regarded unarmed fighting as being useless on the battlefield. However, he recognized its value as a form of basic training to strengthen his troops, improving their physical fitness and confidence.[11] Qi selected thirty-two postures to illustrate, from among the martial arts of the period. The description of the techniques is written in verse, typically with seven characters per line.
In the chapter's introduction, Qi names sixteen different fighting styles, all of which he considered to have been handed down in an incomplete fashion, "some missing the lower part, some missing the upper".[12] Among the arts listed is the Shaolin staff method, which was later documented in detail in Cheng Zongyou's Exposition of the Original Shaolin Staff Method, published around 1610.[13] By contrast, Shaolin unarmed fighting techniques are not mentioned. The entire listing of late Ming dynasty martial arts was later copied without attribution by a manual of the Shaolin style, the Hand Combat Classic (Quanjing quanfa beiyao). However, the later manual, with a preface dated to 1784, altered the text, adding a spurious claim that the history of hand combat had originated at the Shaolin Monastery.[14]
Qi's discussion of hand-to-hand combat makes no mention of a spiritual element to the martial arts, nor to breathing or qi circulation. By contrast, Chinese martial arts texts from the Ming-Qing transition onward represent a synthesis of functional martial arts techniques with Daoist daoyin health practices, breathing exercises, and meditation.[15][16]
Influence
Qi Jiguang was one of several Ming authors to document the military tactics and martial arts techniques of the era. The earliest known documentation of specific styles of Chinese martial arts were produced during the late Ming piracy crisis, as scholars and generals such as Qi and his contemporary Yu Dayou turned their attention to reversing the decline of the Ming military. In the late 16th century, the Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98) also spurred great interest in military training methods within the Korean government. Qi Jiguang's writings were of particular interest because of his successful campaigns against Japanese pirates several decades prior. The 14-chapter edition of the Jixiao Xinshu served as a model for the oldest known extant Korean military manual, the Muyejebo, and was disseminated among Korean military thinkers. During the Qing conquest of Ming, Joseon provided 10,000 musketeers to aid the Ming army in the Battle of Sarhu and successfully fought the Manchus until their allies were defeated.
In Japan both the 14 and 18 chapter editions were published several times, and some methods from the Jixiao Xinshu were transferred over to the Heiho Hidensho (Okugisho), a Japanese strategy book written by Yamamoto Kanasuke in the 16th century.
Gallery
 Layout of the 'mandarin duck formation.'
Layout of the 'mandarin duck formation.' The 'second power formation' is a split 'mandarin duck squad.'
The 'second power formation' is a split 'mandarin duck squad.' The 'lesser third power formation.'
The 'lesser third power formation.' The 'third power formation.'
The 'third power formation.' A marching column contained sixteen 'mandarin duck formations' divided into four platoons. Three platoons stand in the front, left, and right individually to protect the middle platoon, which consisted of musketeers.
A marching column contained sixteen 'mandarin duck formations' divided into four platoons. Three platoons stand in the front, left, and right individually to protect the middle platoon, which consisted of musketeers. The army prepares for combat and deploys in battle lines.
The army prepares for combat and deploys in battle lines. The 'deployment maneuver' splits the second and third platoon while the musketeers move to the front in five ranks and commence firing on signal.
The 'deployment maneuver' splits the second and third platoon while the musketeers move to the front in five ranks and commence firing on signal. First and fourth platoons advance to cover the firing squad and engage in melee combat with the enemy. Second and third platoons move to flank the enemy.
First and fourth platoons advance to cover the firing squad and engage in melee combat with the enemy. Second and third platoons move to flank the enemy. All platoons conduct a feigned retreat. If the enemy takes bait, engage in a pincer movement.
All platoons conduct a feigned retreat. If the enemy takes bait, engage in a pincer movement.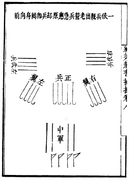 If the feigned retreat is successful, turn back and attack the enemy.
If the feigned retreat is successful, turn back and attack the enemy. A fortified camp formation from the Jixiao Xinshu.
A fortified camp formation from the Jixiao Xinshu.
References
- ↑ Shahar 2008, p. 62
- ↑ Huang 1981, p. 159
- ↑ Gyves 1993, pp. 16–18
- ↑ Huang 1981, p. 168
- ↑ Huang 1981, pp. 168–169
- 1 2 3 Andrade 2016, p. 172.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 174.
- ↑ Huang 1981, pp. 167–169
- ↑ Huang 1981, pp. 170–171
- ↑ Huang 1981, p. 172
- ↑ Gyves 1993, p. 33
- ↑ Gyves 1993, pp. 34–35
- ↑ Shahar 2008, pp. 56–57
- ↑ Shahar 2008, pp. 116–117
- ↑ Shahar 2008, pp. 148–149
- ↑ Lorge 2011, p. 202
Bibliography
- Andrade, Tonio (2016), The Gunpowder Age: China, Military Innovation, and the Rise of the West in World History, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-13597-7.
- Gyves, Clifford M. (1993), An English Translation of General Qi Jiguang's "Quanjing Jieyao Pian" (PDF), University of Arizona
- Huang, Ray (1981), 1587, a Year of No Significance: The Ming Dynasty in Decline, New Haven: Yale University Press, ISBN 978-0-300-02518-7
- Lorge, Peter A. (2011), Chinese Martial Arts: From Antiquity to the Twenty-First Century, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-87881-4
- Shahar, Meir (2008), The Shaolin Monastery: History, Religion, and the Chinese Martial Arts, Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press, ISBN 978-0-8248-3349-7