Cupressus sempervirens
| Mediterranean cypress | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Mediterranean Cypress foliage and cones | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Cupressaceae |
| Genus: | Cupressus |
| Species: | C. sempervirens |
| Binomial name | |
| Cupressus sempervirens L. | |
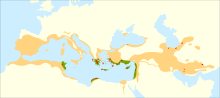 | |
| Green: probable natural range in the Mediterranean Basin Orange: range including human introductions Red (small areas): Residual natural stands | |
Cupressus sempervirens, the Mediterranean cypress (also known as Italian cypress,[1] Tuscan cypress, Persian cypress, or pencil pine), is a species of cypress native to the eastern Mediterranean region, in northeast Libya, southern Albania, southern coastal Croatia (Dalmatia), southern Montenegro, southern Greece, southern Turkey, Cyprus, northern Egypt, western Syria, Lebanon, Malta, the Palestine region, Italy, western Jordan, and also a disjunct population in Iran.
C. sempervirens is a medium-sized coniferous evergreen tree to 35 m (115 ft) tall, with a conic crown with level branches and variably loosely hanging branchlets.[2] It is very long-lived, with some trees reported to be over 1,000 years old.
The foliage grows in dense sprays, dark green in colour. The leaves are scale-like, 2–5 mm long, and produced on rounded (not flattened) shoots. The seed cones are ovoid or oblong, 25–40 mm long, with 10-14 scales, green at first, maturing brown about 20–24 months after pollination. The male cones are 3–5 mm long, and release pollen in late winter. It is moderately susceptible to cypress canker, caused by the fungus Seiridium cardinale, and can suffer extensive dieback where this disease is common. The species name sempervirens comes from the Latin for 'evergreen'.
Uses
Mediterranean Cypress has been widely cultivated as an ornamental tree for millennia away from its native range, mainly throughout the whole Mediterranean region, and in other areas with similar hot, dry summers and mild, rainy winters, including California, southwest South Africa and southern Australia. It can also be grown successfully in areas with cooler, moister summers, such as the British Isles, New Zealand and the Pacific Northwest (coastal Oregon, Washington and British Columbia). It is also planted in Florida and parts of the coastal southern United States as an ornamental tree. In some areas, particularly the United States, it is known as "Italian" or "Tuscan cypress".
The vast majority of the trees in cultivation are selected cultivars with a fastigiate crown, with erect branches forming a narrow to very narrow crown often less than a tenth as wide as the tree is tall. The dark green "exclamation mark" shape of these trees is a highly characteristic signature of Mediterranean town and village landscapes. Formerly, the species was sometimes separated into two varieties, the wild C. sempervirens var. sempervirens (syn. var. horizontalis), and the fastigiate C. s. var. pyramidalis (syn. var. fastigiata, var. stricta), but the latter is now only distinguished as a Cultivar Group, with no botanical significance.
It is also known for its very durable, scented wood, used most famously for the doors of St. Peter's Basilica in the Vatican City, Rome. Cypress used to be used in distilleries as staves to hold mash ferments to make alcohol before the invention of stainless steel.[3] Commonly seen throughout New Mexico, the Mediterranean Cypress is also known as the "drama tree" because of its tendency to bend with even the slightest of breezes.
In cosmetics it is used as astringent, firming, anti-seborrheic, anti-dandruff, anti-aging and as fragrance.[4] It is also the traditional wood used for Italian harpsichords.[5]
Iran's ancient cypresses
Cypress, Cupressus sempervirens, was the first choice for Iranian Gardens. In all of the famous Persian Gardens, such as Fin Garden, Shazdeh Garden, Dowlat-Abad, and others, this tree plays a central role in their design. The oldest living Cypress is the Sarv-e-Abarkooh in Iran's Yazd Province. Its age is estimated to be approximately 4,000 years.[6]
Symbolism


In classical antiquity, the cypress was a symbol of mourning and in the modern era it remains the principal cemetery tree in both the Muslim world and Europe. In the classical tradition, the cypress was associated with death and the underworld because it failed to regenerate when cut back too severely. Athenian households in mourning were garlanded with boughs of cypress.[7] Cypress was used to fumigate the air during cremations.[8] It was among the plants that were suitable for making wreaths to adorn statues of Pluto, the classical ruler of the underworld.[9]
The poet Ovid, who wrote during the reign of Augustus, records the best-known myth that explains the association of the cypress with grief. The handsome boy Cyparissus, a favorite of Apollo, accidentally killed a beloved tame stag. His grief and remorse were so inconsolable that he asked to weep forever. He was transformed into cupressus sempervirens, with the tree's sap as his tears.[10] In another version of the story, it was the woodland god Silvanus who was the divine companion of Cyparissus and who accidentally killed the stag. When the boy was consumed by grief, Silvanus turned him into a tree, and thereafter carried a branch of cypress as a symbol of mourning.[11]
In Greek mythology, besides Cyparissus, the cypress is also associated with Artemis and Hecate, a goddess of magic, crossroads and the underworld. Ancient Roman funerary rites used it extensively.
The most famous Muslim cemetery in Turkey where C. sempervirens is used widely is Istanbul Karacaahmet Cemetery. In Istanbul Turkish the tree is referred to as "Mezarlık Selvisi" (Cemetery Tree); its common name in Turkish and the name used in Turkish forestry is "Kara Selvi" (Black Cypress). Cypresses are mentioned extensively in the Shahnameh, the great Iranian epic poem by Ferdowsi.
In popular culture Italian Cypress is often stereotypically associated with vacation destinations to the Mediterranean region; Italy in particular. Often seen in travel posters for decades.[12][13]
Other characteristics
In July 2012, a forest fire for five days devastated 20,000 hectares of forest in the Valencian village of Andilla. However, amid the charred landscape, a group of 946 cypress trees about 22 years old was virtually unharmed, and only 12 cypress were burned. Andilla cypresses were planted by the CypFire European project studying various aspects of the cypresses, including fire resistance.[14]
Notes
- ↑ "BSBI List 2007". Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland. Archived from the original (xls) on 2015-01-25. Retrieved 2014-10-17.
- ↑ See also Uses section for the differing cultivated variants
- ↑ Makers Mark
- ↑ Carrasco, F. (2009). "Ingredientes Cosméticos". Diccionario de Ingredientes\ 4ª Ed. www.imagenpersonal.net. p. 267. ISBN 978-84-613-4979-1.
- ↑ Hubbard, Frank (1965). Three Centuries of Harpsichord Making. Harvard University Press. p. 201. ISBN 0-674-88845-6.
- ↑ Craig Glenday, ed. (2011). Guinness World Records.
- ↑ Servius, note to Vergil's Aeneid 3.680.
- ↑ Isidore of Seville, Etymologiae 17.7.34.
- ↑ Natalis Comes, Mythologiae 2.9.
- ↑ Ovid, Metamorphoses 10.106ff.
- ↑ Servius, note to Vergil's Georgics 1.20.
- ↑ "Image: Italian_Lakes,_travel_poster_for_ENIT,_ca._1930.jpg, (3091 × 5015 px)". upload.wikimedia.org. 2009-04-15. Retrieved 2015-09-06.
- ↑ "Image: 01422-2T.jpg, (300 × 453 px)". postercorner.com. Retrieved 2015-09-06.
- ↑ "The curious case of Valencia's flameproof cypresses". sociedad.elpais.com. Retrieved 2015-09-06.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cupressus sempervirens. |
- Farjon, A. 2013 Cupressus sempervirens. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2014.2
- Farjon, A. (2005). Monograph of Cupressaceae and Sciadopitys. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. ISBN 1-84246-068-4.
- Zsolt Debreczy, Istvan Racz (2012). Kathy Musial, ed. Conifers Around the World (1st ed.). DendroPress. p. 1089. ISBN 9632190610.
External links
- Cupressus sempervirens - information, genetic conservation units and related resources. European Forest Genetic Resources Programme (EUFORGEN)
