Malabaricane
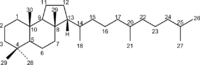 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3S*,3aR*,5aS*,9aS*,9bS*)-3a,6,6,9a-tetramethyl-3-(1,5,9-trimethyldecyl)perhydrobenz[e]indene | |
| Identifiers | |
| Properties | |
| C30H56 | |
| Molar mass | 416.77 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
The molecule malabaricane and its derivatives, the malabaricanes, are triterpene and triterpenoid compounds found in various organisms.[1] They are named after the rain forest tree Ailanthus malabarica (Ailanthus triphysa), from which they were first isolated in 1967 by scientists at the National Chemical Laboratory in Pune, India.[2] Later, great varieties of malabaricanes were discovered in other organisms, mostly in marine sponges such as Rhabdastrella globostellata.[3][4]
Isomalabaricanes are malabaricanes in which the three carbon rings of the molecule are connected in trans−syn−trans conformation, as opposed to other malabaricanes, where the rings are connected in trans−anti−trans conformation. They are of particular research interest because many of them have been reported to show anti-tumour activity in cell culture.[5][6]
References
- ↑ Buckingham J; Macdonald FM; Bradley HM; Cai Y; Munasinghe VRN; Pattenden CF. (1994–1995). Dictionary of Natural Products (PDF). London: Chapman & Hall. p. 130. ISBN 0-412-46620-1. Retrieved 2010-06-04.
- ↑ Chawla A; Dev S. (1967). "A new class of triterpenoids from Ailanthus malabarica DC derivatives of malabaricane". Tetrahedron Letters. 8 (48): 4837–4843. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)89615-5.
- ↑ Meragelman KM; McKee TC; Boyd MR. (March 2001). "New Cytotoxic Isomalabaricane Triterpenes from the Sponge Jaspis Species". Journal of Natural Products. 64 (3): 389–392. PMID 11277766. doi:10.1021/np000478g.
- ↑ Tasdemir D; Mangalindan GC; Concepción GP; Verbitski SM; Rabindran S; Miranda M; Greenstein M; Hooper JN; Harper MK; Ireland CM. (February 2002). "Bioactive Isomalabaricane Triterpenes from the Marine Sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata". Journal of Natural Products. 65 (2): 210–214. PMID 11858759. doi:10.1021/np0104020.
- ↑ Fouad M; Edrada RA; Ebel R; Wray V; Müller WE; Lin WH; Proksch P. (February 2006). "Cytotoxic Isomalabaricane Triterpenes from the Marine Sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata". Journal of Natural Products. 69 (2): 211–218. PMID 16499318. doi:10.1021/np050346t.
- ↑ McKee TC, Bokesch HR, McCormick JL, Rashid MA, Spielvogel D, Gustafson KR, Alavanja MM, Cardelline JH 2nd, Boyd MR. (May 1997). "Isolation and Characterization of New Anti-HIV and Cytotoxic Leads from Plants, Marine, and Microbial Organisms". Journal of Natural Products. 60 (5): 431–438. PMID 9170286. doi:10.1021/np970031g.