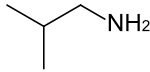
Isobutylamine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylpropan-1-amine | |
| Other names
(2-Methylpropyl)amine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | B00498 |
| 385626 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.042 |
| EC Number | 201-145-4 |
| 81862 | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | isobutylamine |
| PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number | NP9900000 |
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1214 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H11N | |
| Molar mass | 73.14 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Fishy, ammoniacal |
| Density | 736 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −86.6 °C; −124.0 °F; 186.5 K |
| Boiling point | 67 to 69 °C; 152 to 156 °F; 340 to 342 K |
| Miscible | |
| -59.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.397 |
| Viscosity | 500 μPa s (at 20 °C) |
| Thermochemistry | |
| 194 J K−1 mol−1 | |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−133.0–−132.0 kJ mol−1 |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH |
−3.0139–−3.0131 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    |
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| H225, H301, H314 | |
| P210, P280, P301+310, P305+351+338, P310 | |
| Flash point | −9 °C (16 °F; 264 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
224 mg kg−1 (oral, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanamines |
|
| Related compounds |
2-Methyl-2-nitrosopropane |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Isobutylamine is an organic chemical compound (specifically, an amine) with the formula (CH3)2CHCH2NH2, and occurs as a colorless liquid.[1][2] Isobutylamine is one of the four isomeric amines of butane, the others being n-butylamine, sec-butylamine and tert-butylamine.
References
- ↑ Isobutylamine chemicalbook.com
- ↑ Isobutylamine Chemblink.com
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.