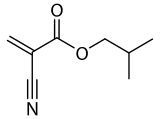
Isobutyl cyanoacrylate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylpropyl 2-cyanoprop-2-enoate | |
| Other names
2-Methylpropyl 2-cyanopropenoate Isobutyl 2-cyanoacrylate Bucrylate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.690 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 153.18 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Isobutyl cyanoacrylate is an isomer of butyl cyanoacrylate. It is used in medical procedures either to close incisions and lacerations without the use of sutures, or as an adjunct to strengthen the suturing.[1] This use is possible because it is a bactericidal liquid monomer which, in the presence of small amounts of moisture, rapidly polymerizes to form a strong adhesive.[2]
References
- ↑ de Blanco LP (February 1994). "Lip suture with isobutyl cyanoacrylate". Endodontics & Dental Traumatology. 10 (1): 15–8. PMID 8005074. doi:10.1111/j.1600-9657.1994.tb00592.x.
- ↑ J. E. Hale (July 1970). "Isobutyl cyanoacrylate as a skin". Postgraduate Medical Journal. 46 (537): 447–450. doi:10.1136/pgmj.46.537.447.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.