İsa Bey Mosque
| İsa Bey Mosque | |
|---|---|
 İsabey Mosque as it appears today | |
| Basic information | |
| Location | Selçuk, Turkey |
| Affiliation | Islam |
| District | Selçuk |
| Province | İzmir |
| Region | Aegean Region |
| Country | Turkey |
| Architectural description | |
| Architect(s) | Şamlı Dımışklıoğlu Ali |
| Architectural type | Mosque |
| Architectural style | Islamic, Seljuk architecture |
| Completed | 1374–75 |
| Specifications | |
| Length | 56 metres (184 ft) |
| Width | 48 metres (157 ft) |
| Dome(s) | 2 |
| Dome dia. (outer) | 9.4 metres (31 ft) and 8.4 metres (28 ft) |
| Minaret(s) | 1 |
| Materials | cut stone, marble, brick |
The İsabey Mosque (Turkish: İsa Bey Camii), constructed in 1374–75,[1] is one of the oldest and most impressive works of architectural art remaining from the Anatolian beyliks. The mosque is situated on the outskirts of the Ayasluğ Hills at Selçuk, İzmir.
History
It was built by the architect, 'Ali b. Mushaimish Dımışklıoğlu, in honor of the Aydinid İsa Bey.[2] The plans for the mosque are based on the Great Mosque of Damascus.[3]
The mosque has two main entrances, to the east and to the west and contains a fountain court.[3] The western wall has inscriptions and geometric shapes engraved. These walls are covered with marble, whereas the façades on the remaining sides are made of cut stone. It is built asymmetrically on a 48-by-56-metre (157 by 184 ft) base. The rims of its domes, with diameters of 9.4 metres (31 ft) and 8.1 metres (27 ft), are decorated with İznik (Nicaea) tiles. Twelve round columns stand inside its courtyard encircled with porches. Its brick minaret is built on an octagonal base, and the upper part from the balcony is ruined. The mosque had another minaret on the west, which is totally destroyed now. The mihrab (niche or altar) was moved to another mosque, due to a door opened there. There is an octagonal Seljuk türbe made of stone and bricks, with a pyramid shaped roof, right next to the mosque.
By 1829, the mosque was in ruins and by 1842 the minaret had fallen down.[4] In the 19th century, it was also used as a caravanserai.
Gallery
 Entrance of the courtyard
Entrance of the courtyard Entrance of the mosque
Entrance of the mosque Interior of the mosque
Interior of the mosque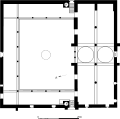 Plan
Plan
See also
- Aydinid dynasty
- Anatolian beyliks
- Islamic architecture
- Islamic art
- List of mosques
- Timeline of Islamic history
Notes
- ↑ The Evolution of Architectural Form in Turkish Mosques (1300-1700), Suut Kemal Yetkin, Studia Islamica, No. 11 (1959), 76-77.
- ↑ On the Transmission of Designs in Early Islamic Architecture, Jonathan M. Bloom, Muqarnas, Vol. 10, Essays in Honor of Oleg Grabar (1993), 24.
- 1 2 Architecture:Anatolia, Beyliks, Grove Encyclopedia of Islamic Art & Architecture, Vol. I, ed. Jonathan M. Bloom and Sheila S. Blair, (Oxford University Press, 2009), 142.
- ↑ Michael Greenhalgh, From the Romans to the Railways: The Fate of Antiquities in Asia Minor, (Brill, 2013), 90.
References
- Bayrak, Orhan M. (1994). p. 407, Türkiye Tarihi Yerler Rehberi (expanded 3rd edition). İnkılâp Kitabevi. ISBN 975-10-0705-4.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Isabey Mosque. |
Coordinates: 37°57′08″N 27°21′57″E / 37.95222°N 27.36583°E

