Iodine trichloride
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
iodine trichloride | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.582 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| I2Cl6 | |
| Molar mass | 466.5281 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
| Density | 3.11 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 63 °C (145 °F; 336 K) |
| −90.2·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
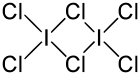
Iodine trichloride is an interhalogen compound of iodine and chlorine. It is bright yellow and in the solid state is present as a planar dimer I2Cl6, Cl2I(μ-Cl)2ICl2, with two bridging Cl atoms.[1]
It can be prepared by reacting iodine with an excess of liquid chlorine at −70 °C. In the melt it is conductive, which may indicate dissociation:[2]
- I2Cl6 ⇌ ICl2+ + ICl4−
Iodine trichloride can be created by heating a mixture of liquid iodine and chlorine gas to 105 °C.
It is an oxidizing agent, capable of causing fire on contact with organic materials.
References
- ↑ K. H. Boswijk; E. H. Wiebenga (1954). "The crystal structure of I2Cl6 (ICl3)". Acta Crystallographica. 7 (5): 417–423. doi:10.1107/S0365110X54001260.
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-08-037941-9.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.