Indium(I) bromide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Indium(I) bromide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.686 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| InBr | |
| Molar mass | 194.722 g/mol |
| Density | 4.960 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 285 °C (545 °F; 558 K) |
| Boiling point | 656 °C (1,213 °F; 929 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
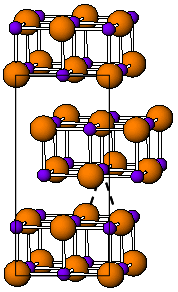
Indium(I) bromide is a chemical compound of indium and bromine. It is a red crystalline compound that is isostructural with β-TlI and has a distorted rock salt structure.[1] Indium(I) bromide is generally made from the elements, heating indium metal with InBr3. It has been used in the sulfur lamp. In organic chemistry, it has been found to promote the coupling of α, α-dichloroketones to 1-aryl-butane-1,4-diones.[2] Oxidative addition reactions with for example alkyl halides to give alkyl indium halides[3] and with NiBr complexes to give Ni-In bonds are known.[4] It is unstable in water decomposing into indium metal and indium tribromide. When indium dibromide is dissolved in water, InBr is produced as a, presumably, insoluble red precipitate, that then rapidly decomposes.[5]
See also
References
- WebElements
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-08-037941-9.
- ↑ Stephenson N.C., Mellor D.P. "The crystal structure of indium monobromide" Australian journal of scientific research A 3 (1950) 581-586
- ↑ C. Peppe and R. Pavão das Chagas (2004). "Indium(I) Bromide-Mediated Reductive Coupling of α,α-Dichloroketones to 1-Aryl-butane-1,4-diones". Synlett (7): 1187–1190. doi:10.1055/s-2004-825591.
- ↑ M. J. S. Gynane, L. G. Waterworth and I. J. Worrall (1972). "Oxidative addition reactions of group III metals in low oxidation states III. Reactions of indium monohalides with alkyl halides". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 43 (2): 257–264. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)81599-5.
- ↑ J. Weiss, T. Priermeier and R. A. Fischer (1996). "Reactions of Elemental Indium and Indium(I) Bromide with Nickel-Bromine Bonds: Structure of (η5-C5H5)(Ph3P)Ni-InBr2(O=PPh3)". Inorg. Chem. 35 (1): 71–75. doi:10.1021/ic950614i.
- ↑ R. Dronskowski (1994). "Ambient-Temperature Formation of Crystalline Indium Monohalides from Aqueous Media". Inorg. Chem. 33 (25): 5960–5963. doi:10.1021/ic00103a054.