Cupeño language
| Cupeño | |
|---|---|
| Kupangaxwicham Pe'memelki | |
| Region | Southern California, United States |
| Ethnicity | Cupeño people |
| Extinct | 1987, with the death of Roscinda Nolasquez |
| Latin | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 |
cup |
| Glottolog |
cupe1243[1] |
 | |
Cupeño is an extinct Uto-Aztecan language, formerly spoken by the Cupeño people of Southern California, United States, who now speak English.
Roscinda Nolasquez (d. 1987) was the last native speaker of Cupeño.[2]
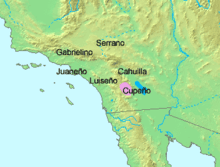
Region
The language was originally spoken in Cupa, Wilaqalpa, and Paluqla, San Diego County, California, and later around the Pala Indian Reservation.
Morphology
Cupeño is an agglutinative language, where words use suffix complexes for a variety of purposes with several morphemes strung together.
Cupeño inflects its verbs for transitivity, tense, aspect, mood, person, number, and evidentiality.
Evidentiality is expressed in Cupeño with clitics, which generally appear near the beginning of the sentence. =ku'ut 'reportative' (mu=ku'ut 'and it is said that...') =am 'mirative' =$he 'dubitative'
There are two inflected moods, realis =pe and irrealis =e'p.
Pronouns
The pronominals of Cupeño appear in many different forms and structures. The following appear attached only to past-tense verbs.
| Person | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ne- | chem- |
| 2 | e- | em- |
| 3 | pe- | pem- |
Tense-Aspect system
Future simple verbs are unmarked. Past simple verbs have past-tense pronouns; past imperfect add the imperfect modifier shown below.
| Number | Present | Imperfect | Fut. Imp | Customary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | -qa | -qal | -nash | -ne |
| Plural | -we | -wen | -wene | -wene |
Phonology
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
| High | i, i: | u, u: | |
| Mid | ɛ, ɛ: | ə, ə: | o, o: |
| Low | a, a: |
/ɛ/ and /o/ appear largely in Spanish loanwords, but also as allophones of /ə/ in native Cupeño words.
/i/ can also be realized as [ɪ] in closed syllables, and [e] in some open syllables.
/u/ may reduce to schwa in unstressed syllables.
/ə/ also appears as [ɨː] when long and stressed, [o] after labials and [q], and as [ɛ] before [w].
/a/ is also realized as [ɑ] before uvulars.
Consonants
| Bilabial | Coronal | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| laminal | apical | plain | labial. | ||||||
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | |||||
| Plosive | p | t | (t)ʃ 2 | k | kʷ1 | q | ʔ | ||
| Fricative | voiceless | s | ʂ | x ~ χ1 | xʷ | h | |||
| voiced | v3 | ð3 | ɣ | ||||||
| Approximant | j | w | |||||||
| Lateral | l | ʎ | |||||||
| Trill | ɾ3 | ||||||||
1 /kʷ/ is realized as [qʷ] before unstressed /a/ or /e/. [x] and [χ] appear to be in free variation.
2 /tʃ/ is realized as [ʃ] in syllable codas.
3 /v/, /ð/, and /ɾ/ appear only in Spanish loanwords.
See also
References
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Cupeno". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Hill, Jane H. (2005-10-18). A Grammar of Cupeño. UC Publications in Linguistics. 136. University of California Press.
External links
- The Cupeño language, Four Directions Institute
- Cupeño language, Survey of California and Other Indian Languages
- OLAC resources in and about the Cupeño language