Hyūga, Miyazaki
| Hyūga 日向市 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||
|
Top left: Umagase in Nippo Coast Quasi National Park. Top right: Statue of Bokushu Wakayama in Hyūga. Middle left: View of platform at Hyugashi Station. Middle right: Hyottoko dancing event in August. Bottom: Old Traditional Town in Mimitsu. | |||
| |||
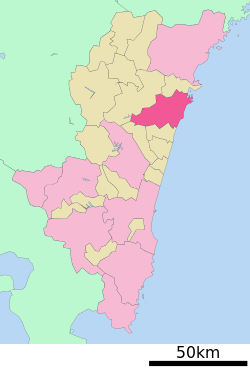 Location of Hyūga in Miyazaki Prefecture | |||
 Hyūga Location in Japan | |||
| Coordinates: 32°25′N 131°37′E / 32.417°N 131.617°ECoordinates: 32°25′N 131°37′E / 32.417°N 131.617°E | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Kyushu | ||
| Prefecture | Miyazaki Prefecture | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor | Kōhei Toya | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 336.29 km2 (129.84 sq mi) | ||
| Population (November 2015) | |||
| • Total | 63,011 | ||
| • Density | 188/km2 (490/sq mi) | ||
| Symbols | |||
| • Tree | Osmanthus | ||
| • Flower | Sunflower | ||
| Time zone | Japan Standard Time (UTC+9) | ||
| City hall address |
10-5 Honmachi, Hyūga-shi, Miyazaki-ken 883-8555 | ||
| Website |
www | ||
Hyūga (日向市 Hyūga-shi) is a port city in Miyazaki Prefecture, Japan. The city was founded on April 1, 1951 with the joint merger of Tomishima Town and Iwawaki Village.[1]
As of February 2014, the city has an estimated population of 63,676 making it the 4th largest city in Miyazaki Prefecture.[2] It has a population density of 189 persons per km² and a total area of 336.29 km².
On February 25, 2006, the town of Tōgō (from Higashiusuki District) was merged into Hyūga.
Hyūga is a port city known for the production of Go stones and for beaches, many of which are popular surfing spots
History
Archaeologists working in Hyūga have reported finding artifacts such as stone tools and stone piles from as much as 30,000 years ago, the Japanese Paleolithic period. There is also evidence of inhabitation during the Jomon Period. Archaeological digs uncovering pottery from this time period continue today in parts of the city.[3]
Origin of name
Hyuga City took its name from Hyūga Province (日向国 Hyūga/Hinata no kuni), the historical name of what is now Miyazaki Prefecture. According to Japanese legend in the Nihon Shoki, following the conquest of the Kumaso people, Emperor Keikō watched the sunrise over the ocean and said "This country faces straight toward the sunrise" (この国は真っ直ぐに日の出る方に向いている Kono kuni wa massugu ni hinoderu hou ni muite iru). From that time, the province was known as Hyuga or Hinata (the country facing the sun) until the Meiji Restoration when it was renamed Miyazaki. [4]
Municipal consolidation
Modern Hyuga City is a result of the merger of numerous smaller towns and villages. These mergers began at the start of the Meiji Period when the han system was abolished and the concept of towns and cities arose. This time period, between 1888 and 1889, became known as the Great Meiji Consolidation. Following this, towns continued to merge mainly due to population limitations or financial limitations. The most recent merger in 2006 with Togo was part of the Great Heisei Consolidation. This was a government initiative to counter population declines and financial problems while promoting decentralization of the national government. This merger increased Hyuga City's population, tax money, and autonomy.[5]
| Before April 1, 1889 | April 1, 1889 | 1898 | 1921 | 1937 | April 1, 1951 | 1955 | 1969 | February 25, 2006 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hichiya Village 日知屋村 |
Tomitaka Village 富高村 |
Tomitaka Town 富高町 |
Tomishima Town 富島町 |
Hyuga City 日向市 |
Hyuga City 日向市 |
Hyuga City 日向市 | ||
| Shiomi Village 塩見村 | ||||||||
| Zaikoji Village 財光寺村 | ||||||||
| Tomitaka Village 富高村 | ||||||||
| Hososhima Town 細島町 | ||||||||
| Hiraiwa Village 平岩村 |
Iwawaki Village 岩脇村 | |||||||
| Saiwaki Village 幸脇村 | ||||||||
| Mimitsu Town 美々津町 |
Mimitsu Village 美々津村 |
Mimitsu Town 美々津町 | ||||||
| Takamatsu Village 高松村 | ||||||||
| Yamage Village 山陰村 |
Togo Village 東郷村 |
Togo Town 東郷町 | ||||||
| Haebaru-Sakanouchi Village 八重原・迫野内村 | ||||||||
| Tsuboya Village 坪谷村 | ||||||||
| Shimosange Village 下三ケ村 | ||||||||
| source: Current Status and Problems of Hyuga City (2008)[6] | ||||||||
Demographics
As of November 2015, Hyūga had a total population of 63,011 people; 30,150 males and 32,861 females.[7]
| Population of Hyūga | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In 2006, Togo was merged into the city, adding about 1,750 people to the population. This accounts for part of the increase in that year. Source: [7][8] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Geography
Hyūga is mainly centered on Hyūgashi Station. The greater Hyūga area is 336.29 km², much larger than the city limits as a result of mergers with other smaller towns such as Togo and Mimitsu. Hyūga City is a small port city located in Miyazaki Prefecture, just south of Nobeoka. The city itself is located on flatlands between the Kyushu Mountains and the Hyūga Sea. The area along Cape Hyūga with its exposed hexagonal pillar rocks and ria (saw tooth) coastline are designated as part of the Nippo-Kaigan Quasi-National Park. A bit south are beaches such as Ise-ga-hama, Okura-ga-hama, and Kane-ga-hama, known for their surfing.
Climate
Hyūga is located in the humid subtropical climate zone (Köppen climate classification: Cfa), exhibiting four distinct seasons.[9] It has a mild, but humid subtropical climate with no dry season. The climate is comparable to the southern coastal areas of the United States or southern Europe. The average summer daytime temperature is about 30 °C (86 °F) with 80% humidity. The average winter daytime temperature is about 13 °C (56 °F) with 60% humidity. Early summer is marked with the rainy season in June and July. This is followed by a hot, humid summer and daily sunshine, but is often accompanied by typhoons. Winter is mild with small amounts of rain.
| Climate data for Hyūga, Miyazaki | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 12.3 (54.1) |
13.2 (55.8) |
16.1 (61) |
20.7 (69.3) |
24.0 (75.2) |
26.2 (79.2) |
30.3 (86.5) |
31.1 (88) |
28.4 (83.1) |
24.1 (75.4) |
19.3 (66.7) |
14.4 (57.9) |
21.68 (71.02) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.7 (44.1) |
7.8 (46) |
10.9 (51.6) |
15.5 (59.9) |
19.3 (66.7) |
22.4 (72.3) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.8 (80.2) |
24.0 (75.2) |
18.9 (66) |
13.8 (56.8) |
8.7 (47.7) |
16.75 (62.14) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.9 (35.4) |
2.8 (37) |
5.9 (42.6) |
10.6 (51.1) |
15.0 (59) |
19.2 (66.6) |
22.9 (73.2) |
23.5 (74.3) |
20.5 (68.9) |
14.8 (58.6) |
9.4 (48.9) |
3.9 (39) |
12.53 (54.55) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 60.1 (2.366) |
93.8 (3.693) |
166.1 (6.539) |
226.8 (8.929) |
266.0 (10.472) |
439.5 (17.303) |
256.9 (10.114) |
266.2 (10.48) |
343.9 (13.539) |
221.6 (8.724) |
115.2 (4.535) |
63.6 (2.504) |
2,519.7 (99.198) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 190.2 | 172.3 | 182.4 | 187.2 | 171.5 | 112.2 | 182.4 | 194.3 | 164.5 | 184.5 | 167.1 | 185.8 | 2,094.4 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency(1976-2015) [10] | |||||||||||||
Districts
- Shinmachi (新町地区 Shinmachi-chiku)
Shinmachi (新町) is Hyūga's downtown area. Hyūga City has been engaged in large scale urban renewal, slowly widening roads, creating new businesses, beautifying, and modernizing the city center. As such, Shinmachi is relatively new and modern. This region is centered on Hyūgashi Station.

- Hososhima (細島地区 Hososhima-chiku)
The southern part of Hososhima is centered on Hyūga's commercial fishing port between Komenoyama and Makishimayama. This is an older less frequented part of Hyūga. The streets are narrow and there are numerous old Edo Period buildings.
The northern part of Hososhima is far more industrial. This region has several manufacturing plants and large areas for storage of goods and raw materials. Hososhima Industrial Port currently serves as the main international port in northern Miyazaki Prefecture handling materials and goods import and export in the region. Hososhima Industrial Port is designated as a Special Major Port and was selected as a focus port by the Japanese government in 2010. There continues to be major development and expansion of the port and its available services. Hososhima Port was selected by the Japanese government as Port of the Year 2015.[11]
- Mimitsu area (美々津地区 Mimitsu-chiku)
Mimitsu was a port town to the south of Hyūga which merged in 1955. It is famous for washi paper and fishing. It is also supposedly the port from which the first Japanese Emperor, Jimmu, launched his military expedition to conquer Yamato and establish it as the center of power.
In the 19th century, it was a prosperous commercial port that was a hub for trade with the cities of Kyoto, Osaka, and Kobe, with so many houses belonging to merchants and shipping agents crowded together that people used to refer to the thousand houses of Mimitsu (Mimitsu-sengen). It fell into sharp decline with the advent of railroads. In 1986, it was designated as a national important preservation district for groups of historic buildings, and much of the 19th-century atmosphere, including traditional buildings, earthen walls, and stone pavements, remains.[12]
- Togo (東郷地区 Togo-chiku)
Tōgō was a small mountain town which merged with Hyūga on February 25, 2006. Togo was the home town of the Japanese writer Bokusui Wakayama.
Neighboring cities and towns
Culture
Annual cultural events
- Hyottoko Summer Festival (ひょっとこ夏祭り hyottoko natsu matsuri) takes place the first Friday and Saturday of August every year. This is the largest festival in Hyuga City attracting visitors from all over Japan. The rather peculiar dance associated with this festival is not exclusive to Hyuga City, but this is the most famous Hyottoko dance in Japan; as such it and the characters in the dance have become symbols of the city.[13]
- Hyuga Jugoya Festival (日向十五夜祭 hyuga jugoya matsuri) takes place during September or October in accordance to the harvest moon. In Hyuga City, this event features two dances, the more traditional Jugoya dance and a traditional dance specific to the Togo region. This is the second largest festival in Hyuga City.[14]
Museums and other points of interest
- Hyuga Historical and Folk Museum (日向市歴史民俗資料館 Hyūgashi rekishi minzoku shiryōkan)
- Bokusui Wakayama Memorial Museum of Literature (若山牧水記念文学館 Wakayama bokusui kinen bungaku-kan)
- Hososhima Port Museum (細島みなと資料館旧高鍋屋 Hososhima Minato shiryōkan kyū Takanabe-ya)
Transportation
Rail

Hyūga is served by the Nippo Main Line, a line run by JR Kyushu which serves eastern and southern Kyushu. This provides access to other parts of Miyazaki Prefecture, and other areas of Kyushu as far as Kagoshima and Fukuoka. Stations on the Nippo Main Line include Hyugashi Station, Zaikoji Station, Minami-Hyuga Station, and Mimitsu Station.
Highways
National Route 10 runs straight through central Hyuga connecting it to most other major cities in western Kyushu. Route 15 is a very short stretch of highway connecting the industrial district with the Expressway. National Route 327 runs through the mountains connecting Hyuga with Misato, Morotsuka, and Shiiba.
The Higashikyushu Expressway is a tolled two-lane expressway linking most major cities in Kyushu. The Hyuga Interchange (IC) has become a major gateway in and out of Hyuga in part due to the dramatically reduced travel times to and from other cities.
Bus
The Miyazaki Kotsu serves Hyūga and nearby areas. It has local routes, as well as routes connecting to nearby Nobeoka (via Kadogawa Town), as well as routes from Hyūga to Misato Town and Shiba Village.
The Puratto Bus community bus service runs through central Hyūga.
The Hakko Liner express bus service connects Hyūga and northern Miyazaki with Fukuoka.
Shopping
- Aeon Town Shopping Mall
Friendship cities
Notable people from Hyūga
- Norichika Aoki, Major League Baseball player
Education
High schools
- Hyūga High School
- Tomishima High School
- Hyūga Industrial High School
Junior high schools
- Iwawaki Junior High School
- Zaikoji Junior High School
- Daiodani Academy - Junior High School
- Hyūga Junior High School
- Mimitsu Junior High School
- Tomishima Junior High School
- Togo Junior High School
Elementary schools
- Shiomi Elementary School
- Saiwaki Elementary School
- Hososhima Elementary School
- Zaikoji Elementary School
- Zaikoji Minami Elementary School
- Daiodani Academy - Elementary School
- Hichiya Elementary School
- Hichiya Higashi Elementary School
- Mimitsu Elementary School
- Tomitaka Elementary School
- Hiraiwa Elementary School
- Togo Elementary School
- Tsuboya Elementary School
References
- ↑ "町村の廃置分合" [Municipality Splitting and Merging] (in Japanese). Hyūga City. Retrieved 8 February 2016.
- ↑ "Japan: Miyazaki". Thomas Brinkhoff. Retrieved 9 March 2016.
- ↑ Hyūga Historical Compilation Committee, ed. (1 October 2010). 日向市史通史編 [An Overview History of Hyūga City] (in Japanese). Hyūga, Miyazaki, Japan.
- ↑ 上田 恣 (ed.). "景行天皇(十五)日向の地名説話と思邦歌" [Origin of Hyuga's name narrative and the Kunishinobi Song] (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 27 April 2016. Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- ↑ "The Development of Municipal mergers in Japan" (PDF). Council of Local Authorities for International Relations. Retrieved 10 May 2016.
- ↑ "日向市の現況と課題" [Current Status and Problems of Hyūga] (PDF) (in Japanese). Hyūga City Hall. Retrieved 26 April 2016.
- 1 2 "日向市ホームページ" [Hyūga City Homepage] (in Japanese). Hyūga City. Archived from the original on 9 February 2016. Retrieved 8 February 2016.
- ↑ "人口の推移" [Population Change] (in Japanese). Hyūga City. 29 May 2015. Archived from the original on 9 February 2016. Retrieved 8 February 2016.
- ↑ "World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated". University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna. November 6, 2008. Archived from the original on September 6, 2010. Retrieved March 1, 2016.
- ↑ "過去の気象データ検索 日向" [Past Meteorological Data Retrieval: Hyūga] (in Japanese). Japan Meteorological Agency. Retrieved 25 April 2016.
- ↑ "ポート・オブ・ザ・イヤー2015」に細島港が決定" [Hososhima Port Selected as Port of the Year 2015]. Ports of Miyazaki Prefecture (in Japanese). Miyazaki Prefecture Port Sales Council. January 15, 2016. Retrieved February 29, 2016.
- ↑ Hyūga - Japan National Tourism Organization Official Website (in English)
- ↑ "ひょっとこ夏祭り" [Hyottoko Summer Festival]. Hyottoko Festival homepage (in Japanese). Hyuga City Tourism Incorporated Association (日向市観光協会 hyūgashi kankō kyōkai). 1 March 2016. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- ↑ "日向十五夜祭" [Hyuga Jugoya Festival]. Hyuga Chamber of Commerce and Industry (in Japanese). Hyuga Chamber of Commerce and Industry (日向商工会議所 hyūga shōkō kaigi-sho). 26 September 2012. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- ↑ "友好都市" [Friendship Cities] (in Japanese). Hyūga City. 22 September 2014. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hyuga, Miyazaki. |
-
 Hyūga travel guide from Wikivoyage
Hyūga travel guide from Wikivoyage - Official website
- Hyuga City Incorporated Tourism Association (in Japanese)

