Terazosin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Hytrin |
| Synonyms | [4-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-quinazolin-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl]-tetrahydrofuran-2-yl-methanone |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a693046 |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 90-94% |
| Biological half-life | 12 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.118.191 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H25N5O4 |
| Molar mass | 387.433 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Terazosin (marketed as Hytrin or Zayasel) is a selective alpha-1 antagonist used for treatment of symptoms of an enlarged prostate (BPH). It also acts to lower the blood pressure, and is therefore a drug of choice for men with hypertension and prostate enlargement. It is available in 1 mg, 2 mg, 5 mg or 10 mg doses.[1]
It works by blocking the action of adrenaline on smooth muscle of the bladder and the blood vessel walls.
Most common side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, headache, constipation, loss of appetite, fatigue, nasal congestion or dry eyes, but they generally go away after only a few days of use. Therapy should always be started with a low dose to avoid first dose phenomenon.[2] Sexual side effects are rare, but may include priapism or erectile dysfunction.
Synthesis
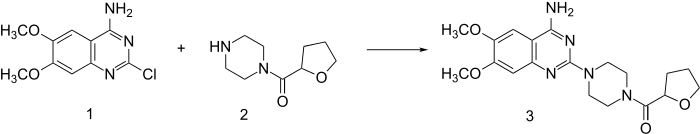
Reaction of piperazine with 2-furoyl chloride followed by catalytic hydrogenation of the furan ring leads to 2. This, when heated in the presence of 2-chloro-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-amine (1) undergoes direct alkylation to terazocin (3).
See also
References
- ↑ Terazosin Hydrochloride Capsule, DailyMed, National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health
- ↑ Hytrin (Terazosin Hcl) drug warnings and precautions - prescription drugs and medications at RxList
- ↑ M. Winn, J. Kyncl, D. A. Dunnigan, and P. H. Jones, {{US Patent|4,026,894}} (1977); Chem. Abstr., 87; 68411m (1977).