Heterokont
| Heterokonts | |
|---|---|
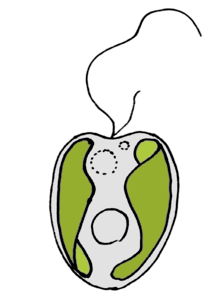 | |
| Ochromonas sp. (Chrysophyceae), with two unequal (heterokont) flagella. Mastigonemes not represented. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| (unranked): | SAR |
| Superphylum: | Heterokonta Cavalier-Smith, 1986[1] |
| Typical classes | |
|
Colored groups (alga-like)
Colorless groups
| |
| Synonyms | |
The heterokonts or stramenopiles (formally, Heterokonta or Stramenopiles) are a major line of eukaryotes[9][10] currently containing more than 25,000 known species.[11] Most are algae, ranging from the giant multicellular kelp to the unicellular diatoms, which are a primary component of plankton. Other notable members of the Stramenopiles include the (generally) parasitic oomycetes, including Phytophthora of Irish potato famine infamy and Pythium which causes seed rot and damping off.
The name "heterokont" refers to the type of motile lifecycle stage, in which the flagellated cells possess two differently shaped flagella (see zoospore).
History
In 1899, Luther created "Heterokontae" for some algae with unequal flagella, today called Xanthophyceae. Later, some authors (e.g., Copeland, 1956) would include other groups in Heterokonta, expandig its sense.
The origin of the other name of the group, "stramenopile", is explained by David (2002)[4] and Adl et al. (2005):[12]
Regarding the spelling of stramenopile, it was originally spelled stramenopile. The Latin word for ‘‘straw’’ is straˉmiˇneˇus (the macron ˉ indicates long vowels, while the breve ˇ indicates short vowels), -a, -um, adj. [stramen], made of straw—thus, it should have been spelled straminopile or straminipile (these corrections are based on the fact that the genitive of stramen required for the correct formation of a compound is ‘‘straminis’’, and that the connective used since both parts are latin is ‘‘i’’). However, Patterson (1989) clearly stated that this is a common name (hence, lower case, not capitalized) and, as a common name, it can be spelled as Patterson chooses. If he had stipulated that the name was a formal name, governed by rules of nomenclature, then his spelling would have been an orthogonal mutation and one would simply correct the spelling in subsequent publications (e.g. Straminopiles). But, it was not Patterson’s desire to use the term in a formal sense. Thus, if we use it in a formal sense, it must be formally described (and in addition, in Latin, if it is to be used botanically). However, and here is the strange part of this, many people liked the name, but wanted it to be used formally. So they capitalized the first letter, and made it Stramenopiles; others corrected the Latin spelling to Straminopiles.
Morphology
Motile cells

Many heterokonts are unicellular flagellates, and most others produce flagellated cells at some point in their lifecycles, for instance as gametes or zoospores. The name heterokont refers to the characteristic form of these cells, which typically have two unequal flagella. The anterior straminipilous flagellum is covered with one or two rows of lateral bristles or mastigonemes, which are tripartite (with three regions each), while the posterior flagellum is whiplike, smooth, and usually shorter, or sometimes reduced to a basal body. The flagella are inserted subapically or laterally, and are usually supported by four microtubule roots in a distinctive pattern.
Mastigonemes are manufactured from glycoproteins in the cell's endoplasmic reticulum before being transported to the anterior flagella's surface. When the straminipilous flagellum moves, the mastigonemes create a retrograde current, pulling the cell through the water or bringing in food. The mastigonemes have a peculiar tripartite structure, which may be taken as the defining characteristic of the heterokonts, thereby including a few protists that do not produce cells with the typical heterokont form. Mastigonemes have been lost in a few heterkont lines, most notably the diatoms.
Chloroplasts
Many heterokonts are algae with chloroplasts surrounded by four membranes, which are counted from the outermost to the innermost membrane. The first membrane is continuous with the host's chloroplast endoplasmic reticulum, or cER. The second membrane presents a barrier between the lumen of the cER and the primary endosymbiont or chloroplast, which represents the next two membranes, within which the thylakoid membranes are found. This arrangement of membranes suggests that heterokont chloroplasts were obtained from the reduction of a symbiotic red algal eukaryote, which had arisen by evolutionary divergence from the monophyletic primary endosymbiotic ancestor that is thought to have given rise to all eukaryotic photoautotrophs. The chloroplasts characteristically contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, and usually the accessory pigment fucoxanthin, giving them a golden-brown or brownish-green color.
Most basal heterokonts are colorless. This suggests that they diverged before the acquisition of chloroplasts within the group. However, fucoxanthin-containing chloroplasts are also found among the haptophytes. These two groups may have a common ancestry, and possibly also a common phylogenetic history with cryptomonads, being grouped by some authors in the Chromista. This may be interpreted as suggesting that the ancestral heterokont was an alga, and all colorless groups arose through loss of the secondary endosymbiont and its chloroplast.
Classification
As noted above, classification varies considerably. Originally, the heterokont algae were treated as two divisions, first within the kingdom Plantae and later the Protista:
- Division Chrysophyta
- Class Chrysophyceae (golden algae)
- Class Bacillariophyceae (diatoms)
- Division Phaeophyta (brown algae)
In this scheme, however, the Chrysophyceae are paraphyletic to both other groups. As a result, various members have been given their own classes and often divisions. Recent systems often treat these as classes within a single division, called the Heterokontophyta, Chromophyta, or Ochrophyta. This is not universal, however; Round et al. treat the diatoms as a division.
The discovery that oomycetes and hyphochytrids are related to these algae, rather than fungi, as previously thought, has led many authors to include these two groups among the heterokonts. Should it turn out that they evolved from colored ancestors, the heterokont group would be paraphyletic in their absence. Once again, however, usage varies. David J. Patterson named this extended group the stramenopiles, characterized by the presence of tripartite mastigonemes, mitochondria with tubular cristae, and open mitosis. He used the stramenopiles as a prototype for a classification without Linnaean rank. Their composition has been essentially stable, but their use within ranked systems varies.
Thomas Cavalier-Smith treats the heterokonts as identical in composition with the stramenopiles; this is the definition followed here. He has proposed placing them in a separate kingdom, the Chromalveolata, together with the haptophytes, cryptomonads, and alveolates. This is one of the most common revisions to the five-kingdom system, but has not been adopted, because Chromalveolata is not a monophyletic group. A few treat the Chromalveolata as identical in composition with the heterokonts, or list them as a kingdom Stramenopila.
Some sources divide the heterokonts into the autotrophic Ochrophyta and heterotrophic Bigyra and Pseudofungi.[13] However, some modifications to these classifications have been suggested.
The name Heterokonta can be confused with the (much older) name Heterokontae, which is generally equivalent to the Xanthophyceae, a limited subset of the Heterokonta.[14]
The simplified classification of the group according to Adl et al. (2012) is:[15]
- Sar
- Stramenopiles Patterson, 1989, emend. Adl et al., 2005
- Opalinata Wenyon, 1926, emend. Cavalier-Smith, 1997 (Slopalinida Patterson, 1985)
- Blastocystis Alexeev, 1911
- Bicosoecida Grassé, 1926, emend. Karpov, 1998
- Placidida Moriya et al., 2002
- Labyrinthulomycetes Dick, 2001
- Hyphochytriales Sparrow, 1960
- Peronosporomycetes Dick, 2001 (Öomycetes Winter, 1897, emend. Dick, 1976)
- Actinophryidae Claus 1874, emend. Hartmann 1926
- Bolidomonas Guillou & Chrétiennot-Dinet, 1999 (Bolidophyceae in Guillou et al., 1999)
- Chrysophyceae Pascher, 1914
- Dictyochophyceae Silva, 1980
- Eustigmatales Hibberd, 1981
- Pelagophyceae Andersen & Saunders, 1993
- Phaeothamniophyceae Andersen & Bailey, in Bailey et al., 1998
- Pinguiochrysidales Kawachi et al., 2003
- Raphidophyceae Chadefaud, 1950, emend. Silva, 1980
- Synurales Andersen, 1987
- Xanthophyceae Allorge, 1930, emend. Fritsch, 1935 (Heterokontae Luther, 1899, Heteromonadea Leedale, 1983, Xanthophyta Hibberd, 1990)
- Phaeophyceae Hansgirg, 1886 (not Kjellman, 1891, not Pfitzer, 1894)
- Schizocladia Henry et al., in Kawai et al., 2003 (Schizocladales Kawai et al., 2003) (M)
- Diatomea Dumortier, 1821 (= Bacillariophyta Haeckel, 1878)
- Alveolata
- Rhizaria
- Stramenopiles Patterson, 1989, emend. Adl et al., 2005
Phylogeny
Based on the following works of Ruggiero et al. 2015 & Silar 2016.[16][17][18]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gallery

 Blastocystis hominis (Blastocystea)
Blastocystis hominis (Blastocystea)_Microscopy.tif.jpg)
 Potatoes with Phytophthora (Oomycetes)
Potatoes with Phytophthora (Oomycetes)

 Actinophrys sol (Actinophryida)
Actinophrys sol (Actinophryida)
 Dinobryon sp. (Chrysophyceae)
Dinobryon sp. (Chrysophyceae) Synura sp. (Synurophyceae)
Synura sp. (Synurophyceae)

 Pelagophycus porra (Phaeophyceae)
Pelagophycus porra (Phaeophyceae)
References
- ↑ Cavalier-Smith, T. (1986). The kingdom Chromista, origin and systematics. In: Round, F.E. and Chapman, D.J. (eds.). Progress in Phycological Research. 4: 309–347.
- ↑ Patterson, D. J. (1989). Stramenopiles: Chromophytes from a protistan perspective. in The Chromophyte Algae: Problems and Perspectives. Green, J.C., Leadbeater, B. S. C. and Diver, W. L. (eds.), Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK.
- ↑ Vørs, N (1993). "Marine heterotrophic amoebae, flagellates and heliozoa from Belize (Central America) and Tenerife". Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 40: 272–287. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.1993.tb04917.x.
- 1 2 David, J. C. (2002). A preliminary catalogue of the names of fungi above the rank of order. Constancea 83: 1–30, .
- ↑ van den Hoek, C., Mann, D.G. and Jahns, H.M. (1995). Algae An Introduction to Phycology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. ISBN 0-521-30419-9.
- ↑ Alexopoulos, C. J., Mims, C. W. and Blackwell, M. (1996). Introductory Mycology, 4th ed. New York: J. Wiley.
- ↑ Dick, M. W. (2001). Straminipilous fungi. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers. 670 p., .
- ↑ "Stramenipila M.W. Dick (2001)". MycoBank. International Mycological Association.
- ↑ "stramenopiles". Retrieved 2009-03-08.
- ↑ Hoek, C. van den; D. G. Mann; H. M. Jahns (1995). Algae: An Introduction to Phycology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 104, 124, 134, 166. ISBN 0-521-31687-1.
- ↑ Chapman, A. D. (2009). Numbers of living species in Australia and the world.
- ↑ Adl SM, Simpson AG, Farmer MA, et al. (2005). "The new higher level classification of eukaryotes with emphasis on the taxonomy of protists". J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 52 (5): 399–451. PMID 16248873. doi:10.1111/j.1550-7408.2005.00053.x.
- ↑ Riisberg I, Orr RJ, Kluge R, et al. (May 2009). "Seven gene phylogeny of heterokonts". Protist. 160 (2): 191–204. PMID 19213601. doi:10.1016/j.protis.2008.11.004.
- ↑ Blackwell, W. H. (2009). "Chromista revisited: A dilemma of overlapping putative kingdoms, and the attempted application of the botanical code of nomenclature" (PDF). Phytologia. 91 (2).
- ↑ http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1550-7408.2012.00644.x/pdf
- ↑ Ruggiero; et al. (2015), "Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms", PLoS ONE, 10 (4): e0119248, PMC 4418965
 , PMID 25923521, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119248
, PMID 25923521, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0119248 - ↑ Silar, Philippe (2016), "Protistes Eucaryotes: Origine, Evolution et Biologie des Microbes Eucaryotes", HAL archives-ouvertes: 1–462
- ↑ Cavalier-Smith, Thomas; Scoble, Josephine Margaret (2013). "Phylogeny of Heterokonta: Incisomonas marina, a uniciliate gliding opalozoan related to Solenicola (Nanomonadea), and evidence that Actinophryida evolved from raphidophytes". European Journal of Protistology. 49: 328–353. doi:10.1016/j.ejop.2012.09.002.
External links
| Wikispecies has information related to: Heterokonta |