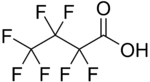
Heptafluorobutyric acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,2,3,3,4,4,4-Heptafluorobutanoic acid | |
| Other names
Heptafluorobutanoic acid; Perfluorobutanoic acid; Perfluorobutyric acid; PFBA | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | HFBA |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.170 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4HF7O2 | |
| Molar mass | 214.04 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.64 g/ml |
| Boiling point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) |
| high | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | strong acid |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Heptafluorobutyric acid (HFBA) is an organofluorine compound with the formula C3F7CO2H. As the fluorinated derivative of butyric acid, this colourless liquid is prepared by electrofluorination of the corresponding butyryl fluoride.[1]
Applications
HFBA has a variety of niche applications in analytical and synthetic chemistry. It is an ion pair reagent for reverse-phase HPLC. It is used in the sequencing, synthesis, and solubilizing of proteins and peptides.
Esters derived from HFBA readily undergo condensation, owing to their electrophilicity. Specialized ligands for metal ions are generated capitalizing on this property, such as Eufod.
References
- ↑ Günter Siegemund, Werner Schwertfeger, Andrew Feiring, Bruce Smart, Fred Behr, Herward Vogel, Blaine McKusick "Fluorine Compounds, Organic" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_349
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.