Hennepin County, Minnesota
| Hennepin County, Minnesota | ||
|---|---|---|
| County | ||
| Hennepin County | ||
 The Hennepin County Government Center, located in the county seat of Minneapolis. Its stylized letter "H" shape serves as the logo for Hennepin County. | ||
| ||
 Location in the U.S. state of Minnesota | ||
 Minnesota's location in the U.S. | ||
| Founded | March 6, 1852[1] | |
| Named for | Louis Hennepin | |
| Seat | Minneapolis | |
| Largest city | Minneapolis | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 607 sq mi (1,572 km2) | |
| • Land | 554 sq mi (1,435 km2) | |
| • Water | 53 sq mi (137 km2), 8.7% | |
| Population (est.) | ||
| • (2016) | 1,232,483 | |
| • Density | 2,082/sq mi (804/km²) | |
| Congressional districts | 3rd, 5th | |
| Time zone | Central: UTC-6/-5 | |
| Website |
www | |
Hennepin County (/ˈhɛnəpɪn/ HEN-ə-pin) is a county in the U.S. state of Minnesota. As of the 2010 census the population was 1,152,425.[2] It is the most populous county in Minnesota and the 35th-most populous county in the United States; more than one in five Minnesotans live in Hennepin County. Its county seat is Minneapolis,[3] the state's most populous city. The county is named in honor of the 17th-century explorer Father Louis Hennepin.[4]
Hennepin County is included in the Minneapolis-St. Paul-Bloomington, MN-WI Metropolitan Statistical Area.
The center of population of Minnesota is in Hennepin County, in the city of Minneapolis.
History
Hennepin County was created in 1852 by the Minnesota Territorial Legislature. Father Louis Hennepin's name was chosen because he originally named St. Anthony Falls and recorded some of the earliest accounts of the area for the Western world. Hennepin County's early history is closely linked to the establishment of the cities of Minneapolis and St. Anthony.[5] The history of Hennepin County is cataloged at the Hennepin History Museum, located in Minneapolis.
Geography
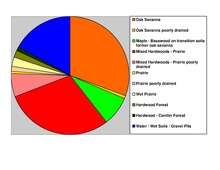
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 607 square miles (1,570 km2), of which 554 square miles (1,430 km2) is land and 53 square miles (140 km2) (8.7%) is water.[6] Hennepin is one of 17 Minnesota counties with more savanna soils than either prairie or forest soils, and is one of only two Minnesota counties with more than 75% of its area in savanna soils (the other is Wright County).
The highest waterfall on the Mississippi River, the Saint Anthony Falls (discovered by Louis Hennepin) is in Hennepin County next to downtown Minneapolis, but in the 19th century, the falls were converted to a series of dams. Barges and boats now pass through locks to move between the parts of the river above and below the dams.
Adjacent counties
- Anoka County (northeast)
- Ramsey County (east)
- Dakota County (southeast)
- Scott County (south)
- Carver County (southwest)
- Wright County (northwest)
National protected areas
- Minnesota Valley National Wildlife Refuge (part)
- Mississippi National River and Recreation Area (part)
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1860 | 12,849 | — | |
| 1870 | 31,566 | 145.7% | |
| 1880 | 67,013 | 112.3% | |
| 1890 | 185,294 | 176.5% | |
| 1900 | 228,340 | 23.2% | |
| 1910 | 333,480 | 46.0% | |
| 1920 | 415,419 | 24.6% | |
| 1930 | 517,785 | 24.6% | |
| 1940 | 568,899 | 9.9% | |
| 1950 | 676,579 | 18.9% | |
| 1960 | 842,854 | 24.6% | |
| 1970 | 960,080 | 13.9% | |
| 1980 | 941,411 | −1.9% | |
| 1990 | 1,032,431 | 9.7% | |
| 2000 | 1,116,200 | 8.1% | |
| 2010 | 1,152,425 | 3.2% | |
| Est. 2016 | 1,232,483 | [8] | 6.9% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[9] 1790-1960[10] 1900-1990[11] 1990-2000[12] 2010-2016[2] | |||

As of the 2000 census,[13] there were 1,116,200 people, 456,129 households, and 267,291 families residing in the county. The population density was 774/km² (2,005/mi²). There were 468,824 housing units at an average density of 325/km² (842/mi²). The racial makeup of the county was 80.53% White, 8.95% Black or African American, 1.00% Native American, 4.80% Asian, 0.05% Pacific Islander, 2.06% from other races, and 2.60% from two or more races. 4.07% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 22.8% were of German, 12.0% Norwegian, 7.6% Irish and 7.2% Swedish ancestry.
There were 456,129 households out of which 28.80% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 45.30% were married couples living together, 9.90% had a female householder with no husband present, and 41.40% were non-families. 31.80% of all households were made up of individuals and 8.40% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.39 and the average family size was 3.07.
In the county 24.00% of the population was under the age of 18, 9.70% was between 18 and 24, 33.70% from 25 to 44, 21.70% from 45 to 64, and 11.00% were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 35 years. For every 100 females there were 97.00 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 94.70 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $51,711, and the median income for a family was $65,985 (these figures had risen to $60,115 and $79,970 respectively as of a 2007 estimate) Accounting for inflation, these figures rise again to $76,202.87 for individuals, and $92,353.46 for households, adjusted for 2014 dollars.[14] Males had a median income of $42,466 versus $32,400 for females. The per capita income for the county was $28,789. About 5.00% of families and 8.30% of the population were below the poverty line, including 10.50% of those under age 18 and 5.90% of those age 65 or over.
Hennepin County is the wealthiest county in Minnesota and one of the 100 highest-income counties in the United States.
Besides English, languages with significant numbers of speakers in Hennepin County include Arabic, Hmong, Khmer, Lao, Russian, Somali, Spanish, and Vietnamese.[15]
Law and government
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 28.2% 191,770 | 63.1% 429,288 | 8.7% 58,919 |
| 2012 | 35.3% 240,073 | 62.3% 423,982 | 2.4% 16,010 |
| 2008 | 34.8% 231,054 | 63.4% 420,958 | 1.8% 11,768 |
| 2004 | 39.4% 255,133 | 59.3% 383,841 | 1.2% 8,007 |
| 2000 | 39.3% 225,657 | 53.6% 307,599 | 7.1% 40,590 |
| 1996 | 33.2% 173,887 | 54.4% 285,126 | 12.5% 65,293 |
| 1992 | 30.6% 179,581 | 47.5% 278,648 | 21.9% 128,390 |
| 1988 | 44.6% 240,209 | 54.4% 292,909 | 1.0% 5,444 |
| 1984 | 48.0% 253,921 | 51.5% 272,401 | 0.6% 2,912 |
| 1980 | 38.6% 194,898 | 47.4% 239,592 | 14.0% 70,882 |
| 1976 | 43.8% 211,892 | 53.3% 257,380 | 2.9% 14,106 |
| 1972 | 51.6% 228,951 | 46.5% 205,943 | 1.9% 8,464 |
| 1968 | 41.8% 170,002 | 54.1% 220,078 | 4.2% 16,944 |
| 1964 | 39.0% 154,736 | 60.8% 241,020 | 0.2% 971 |
| 1960 | 51.3% 198,992 | 48.5% 188,250 | 0.2% 939 |
| 1956 | 55.0% 183,248 | 44.8% 149,341 | 0.2% 523 |
| 1952 | 53.5% 180,338 | 46.1% 155,388 | 0.4% 1,415 |
| 1948 | 42.9% 121,169 | 53.8% 151,920 | 3.2% 9,145 |
| 1944 | 43.7% 116,781 | 55.7% 148,792 | 0.7% 1,747 |
| 1940 | 45.5% 122,960 | 53.7% 145,168 | 0.8% 2,230 |
| 1936 | 33.1% 81,206 | 58.8% 144,289 | 8.1% 19,985 |
| 1932 | 41.9% 91,087 | 54.8% 119,234 | 3.3% 7,245 |
| 1928 | 60.2% 125,472 | 38.8% 80,851 | 1.0% 2,124 |
| 1924 | 59.0% 101,120 | 6.3% 10,806 | 34.7% 59,401 |
| 1920 | 64.6% 90,517 | 20.6% 28,911 | 14.8% 20,741 |
| 1916 | 40.8% 27,957 | 53.1% 36,395 | 6.1% 4,204 |
| 1912 | 29.6% 14,379 | 32.0% 15,530 | 38.3% 18,596[17] |
| 1908 | 58.7% 27,787 | 34.2% 16,169 | 7.1% 3,357 |
| 1904 | 73.7% 31,437 | 13.4% 5,708 | 12.9% 5,503 |
| 1900 | 62.4% 26,902 | 33.6% 14,498 | 3.9% 1,695 |
| 1896 | 55.5% 26,786 | 42.5% 20,515 | 2.0% 987 |
| 1892 | 49.9% 20,603 | 39.9% 16,448 | 10.2% 4,209 |
Commissioners
Like all counties in Minnesota, Hennepin is governed by an elected and nonpartisan board of commissioners. In Minnesota, county commissions usually have five members, but Hennepin, Ramsey, Dakota, Anoka and St Louis counties have seven members. Each commissioner represents a district of approximately equal population. In Hennepin the county commission appoints the medical examiner, county auditor-treasurer and county recorder. The sheriff and county attorney are also elected on a nonpartisan ticket. The county government's headquarters are in downtown Minneapolis in the Hennepin County Government Center. The county oversees the Hennepin County Library system (which merged with the Minneapolis Public Library system in 2008), and Hennepin County Medical Center.
The county commission elects a chair who presides at meetings. Commissioners as of January 3, 2017
| District | Commissioner | In office since | Current term expires in January |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | Mike Opat | 1993 | 2021 |
| 2nd | Linda Higgins | 2012 | 2019 |
| 3rd | Marion Greene | 2014 | 2019 |
| 4th | Peter McLaughlin | 1991 | 2019 |
| 5th | Debbie Goettel | 2017 | 2021 |
| 6th | Jan Callison (chair) | 2009 | 2021 |
| 7th | Jeff Johnson | 2009 | 2021 |
Key staff
Hennepin County's normal operations are coordinated by the County Administrator David Hough, Deputy County Administrator for Health and Human Services Jennifer DeCubellis, Assistant County Administrator for Operations Judy Regenscheid, Assistant County Administrator for Human Services Rex A. Holzemer, Assistant County Administrator for Public Works Carl Michaud, and Assistant County Administrator for Public Safety Mark Thompson. Under Administrator Hough's leadership, the number senior management positions in the county has grown by 40%.
Transportation
Major highways
 Interstate 35W
Interstate 35W Interstate 94
Interstate 94 Interstate 394
Interstate 394 Interstate 494
Interstate 494 Interstate 694
Interstate 694 US Highway 12
US Highway 12 US Highway 52
US Highway 52.svg.png) US Highway 169
US Highway 169.svg.png) US Highway 212
US Highway 212  Minnesota State Highway 5
Minnesota State Highway 5 Minnesota State Highway 7
Minnesota State Highway 7 Minnesota State Highway 47
Minnesota State Highway 47 Minnesota State Highway 55
Minnesota State Highway 55 Minnesota State Highway 62
Minnesota State Highway 62 Minnesota State Highway 65
Minnesota State Highway 65 Minnesota State Highway 77
Minnesota State Highway 77 Minnesota State Highway 100
Minnesota State Highway 100 Minnesota State Highway 101
Minnesota State Highway 101 Minnesota State Highway 121
Minnesota State Highway 121 Minnesota State Highway 252
Minnesota State Highway 252 Minnesota State Highway 610
Minnesota State Highway 610 Hennepin County Road 17 (France Avenue)
Hennepin County Road 17 (France Avenue) Hennepin County Road 61
Hennepin County Road 61 Hennepin County Road 81
Hennepin County Road 81 Hennepin County Road 122
Hennepin County Road 122- Other county roads
Airports
- Minneapolis–Saint Paul International Airport (MSP) serves the Twin Cities area. It is the 17th-busiest airport in the United States by passenger traffic and serves as a hub for Delta Air Lines.
- Crystal Airport (MIC) enhances service to the county and surrounding communities.
Economy
Hennepin County has major economic centers in downtown Minneapolis and Bloomington.
Mall of America
The Mall of America is located in the southernmost portion of the county in the city of Bloomington. The Mall is the largest in the United States and 31st largest in the world, if the indoor amusement park is not counted. Including the park, Nickelodeon Universe, the Mall is largest on the continent and 12th largest in the world. The famous shopping center contributes to the City of Bloomington having more jobs per capita than Minneapolis. Bloomington is also home to several large corporations, including HealthPartners and Ceridian.
Target Field
In August 2006, the Board voted 4–3 to levy a 0.15% sales tax within the county to fund the majority of the cost of a baseball stadium for the Minnesota Twins. Legislation passed by the Minnesota Legislature in the waning hours of the 2005-2006 session, and signed by Governor Tim Pawlenty, authorized the county to levy the tax without a voter referendum. It also created the Minnesota Ballpark Authority which constructed and manages the stadium on behalf of the county. The tax will be in effect for 30 years, with clauses allowing it to be increased by the board of commissioners. The stadium, Target Field, opened in April 2010.
Education
Colleges and universities in the county include:
- Augsburg College in Minneapolis
- Dunwoody College of Technology in downtown Minneapolis
- Hamline University has a location in St. Louis Park, though its main branch is in St. Paul
- Hennepin Technical College in Brooklyn Park and Eden Prairie
- Metropolitan State University in downtown Minneapolis and Brooklyn Park
- Minneapolis College of Art and Design in Minneapolis
- Minneapolis Community and Technical College in downtown Minneapolis
- Minnesota State University, Mankato in Edina
- Normandale Community College in Bloomington
- North Central University in downtown Minneapolis
- North Hennepin Community College in Brooklyn Park
- Northwestern Health Sciences University in Bloomington
- Saint Mary's University of Minnesota, Twin Cities Campus in South Minneapolis
- University of Minnesota, Twin Cities Campus in Minneapolis
- University of St. Thomas Minneapolis Campus in downtown Minneapolis
Culture
The Hennepin History Museum, established in 1957, provides exhibits related to the history of the county. Records of Hennepin County are available for research use. They include school records, district and municipal court files, county attorney files, Hennepin County Sheriff records, birth and death records, marriage records, tax lists, and agency history records.
Communities
Cities
- Bloomington
- Brooklyn Center
- Brooklyn Park
- Champlin
- Corcoran
- Crystal
- Dayton (partial)
- Deephaven
- Eden Prairie
- Edina
- Excelsior
- Golden Valley
- Greenfield
- Greenwood
- Hanover (partial)
- Hopkins
- Independence
- Long Lake
- Loretto
- Maple Grove
- Maple Plain
- Medicine Lake
- Medina
- Minneapolis (county seat)
- Minnetonka
- Minnetonka Beach
- Minnetrista
- Mound
- New Hope
- Orono
- Osseo
- Plymouth
- Richfield
- Robbinsdale
- Rockford (partial)
- Rogers
- Shorewood
- Spring Park
- St. Anthony Village (partial)
- St. Bonifacius
- St. Louis Park
- Tonka Bay
- Wayzata
- Woodland
Unorganized territory
See also
References
- ↑ "Minnesota Place Names". Minnesota Historical Society. Retrieved March 18, 2014.
- 1 2 "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 1, 2013.
- ↑ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on 2011-05-31. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- ↑ Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Govt. Print. Off. p. 155.
- ↑ JoEllen Haugo and Mary Jo Laakso (2001). "History of Minneapolis". Minneapolis Public Library. Archived from the original on August 15, 2007. Retrieved September 7, 2007.
- ↑ "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on October 6, 2014. Retrieved October 15, 2014.
- ↑ Nelson, Steven (2011). Savanna Soils of Minnesota. Minnesota: Self. pp. 49-52. ISBN 978-0-615-50320-2.
- ↑ "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- ↑ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on May 12, 2015. Retrieved October 15, 2014.
- ↑ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved October 15, 2014.
- ↑ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved October 15, 2014.
- ↑ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved October 15, 2014.
- ↑ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ↑ http://www.dollartimes.com/calculators/inflation.htm
- ↑ "Welcome Languages." Hennepin County Public Library. Retrieved on July 8, 2010.
- ↑ http://uselectionatlas.org/RESULTS
- ↑ The leading "other" candidate, Progressive Theodore Roosevelt, received 11,489 votes, while Socialist candidate Eugene Debs received 5,820 votes, Prohibition candidate Eugene Chafin received 668 votes, and Socialist Labor candidate Arthur Reimer received 619 votes.
External links
- Hennepin County Government website
- Hennepin County Library website
- Bloomington Convention & Visitors Bureau
- Minneapolis Northwest Convention & Visitors Bureau
Coordinates: 45°00′N 93°28′W / 45.00°N 93.47°W

