Helen Duncan
| Helen Duncan | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born |
Victoria MacFarlane 25 November 1897 Callander, Perthshire, Scotland |
| Died |
6 December 1956 (aged 59) Edinburgh, Scotland |
| Other names | Hellish Nell |
| Occupation | Medium |
| Spouse(s) | Henry Duncan (1916–1967) |
Victoria Helen McCrae Duncan (25 November 1897 – 6 December 1956) was a Scottish medium best known as the last person to be imprisoned under the British Witchcraft Act of 1735. She was famous for producing fraudulent ectoplasm made from cheesecloth.[1][2][3][4]
Early life
(Victoria) Helen MacFarlane was born in Callander, Perthshire on 25 November 1897, the daughter of a slater.[5] At school, to the distress of her mother (a member of the Presbyterian church), she alarmed her fellow pupils with her dire prophecies and hysterical behaviour.[5] After leaving school, she worked at Dundee Royal Infirmary, and in 1916 she married Henry Duncan, a cabinet maker and wounded war veteran, who was supportive of her supposed supernatural talents. In 1926 she developed from clairvoyant to medium by offering séances in which she claimed to summon the spirits of recently deceased persons by emitting ectoplasm from her mouth. A mother of six, she also worked part-time in a bleach factory.
Practising medium
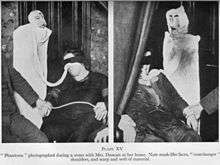
In 1928 the photographer Harvey Metcalfe attended a series of séances at the house of Duncan. During a séance he took various flash photographs of Duncan and her alleged "materialization" spirits including her spirit guide "Peggy".[6] The photographs that were taken reveal the "spirits" to be fraudulently produced, such as a doll made from a painted papier-mâché mask draped in an old sheet.[7]
In 1931, the London Spiritualist Alliance (LSA) examined Duncan's method. An early examination of pieces of Duncan's ectoplasm revealed it was made of cheesecloth, paper mixed with the white of egg and lavatory paper stuck together. One of Duncan's tricks was to swallow and regurgitate some of her ectoplasm, and she was persuaded to swallow a tablet of methylene blue before one of her séances by the LSA committee to rule out any chance of this trick being performed, and because of this no ectoplasm appeared.[8] The committee in a report concluded that the "material was swallowed by Mrs Duncan at some time previous to the sitting and subsequently regurgitated by her for the purpose of exhibition."[9]
A piece of ectoplasm from one of Duncan's early séances was obtained and secured in a bottle of distilled water. It was given to the psychical researcher Harry Price who was originally enthusiastic about the sample. However, when he gave the sample to a chemist for an analysis it was discovered to be made from egg white mixed with chemicals. Price would later duplicate Duncan's ectoplasm with similar substances.[10]

In 1931, Harry Price (director of the National Laboratory of Psychical Research) paid Duncan £50 to perform a number of test séances. She was suspected of swallowing cheesecloth which was then regurgitated as "ectoplasm".[4][11] Price had proven through analysis of a sample of ectoplasm produced by Duncan that it was made of cheesecloth.[12] She reacted violently at attempts to X-ray her, running from the laboratory and making a scene in the street, where her husband had to restrain her, destroying the controlled nature of the test. According to Price in a report of the mediumship of Duncan:
| “ | At the conclusion of the fourth seance we led the medium to a settee and called for the apparatus. At the sight of it, the lady promptly went into a trance. She recovered, but refused to be X-rayed. Her husband went up to her and told her it was painless. She jumped up and gave him a smashing blow on the face which sent him reeling. Then she went for Dr. William Brown who was present. He dodged the blow. Mrs. Duncan, without the slightest warning, dashed out into the street, had an attack of hysteria and began to tear her seance garment to pieces. She clutched the railings and screamed and screamed. Her husband tried to pacify her. It was useless. I leave the reader to visualize the scene. A seventeen-stone woman, clad in black sateen tights, locked to the railings, screaming at the top of her voice. A crowd collected and the police arrived. The medical men with us explained the position and prevented them from fetching the ambulance. We got her back into the Laboratory and at once she demanded to be X-rayed. In reply, Dr. William Brown turned to Mr. Duncan and asked him to turn out his pockets. He refused and would not allow us to search him. There is no question that his wife had passed him the cheese-cloth in the street. However, they gave us another seance and the "control' said we could cut off a piece of "teleplasm" when it appeared. The sight of half-a-dozen men, each with a pair of scissors waiting for the word, was amusing. It came and we all jumped. One of the doctors got hold of the stuff and secured a piece. The medium screamed and the rest of the "teleplasm" went down her throat. This time it wasn't cheese-cloth. It proved to be paper, soaked in white of egg, and folded into a flattened tube... Could anything be more infantile than a group of grown-up men wasting time, money, and energy on the antics of a fat female crook.[10] | ” |
Price in his report published photographs of Duncan in his laboratory that revealed fake ectoplasm made from cheesecloth, rubber gloves and cut-out heads from magazine covers which she pretended to her audiences were spirits.[9][13] The psychologist William McDougall who attended two of the séances pronounced her "whole performance fraudulent" in an appendice to the report.[14]
Following the report written by Price, Duncan's former maid Mary McGinlay confessed in detail to having aided Duncan in her mediumship tricks, and Duncan's husband admitted that the ectoplasm materializations were the result of regurgitation.[9][15]
In a séance on 6 January 1933 in Edinburgh, a little girl called Peggy emerged in the séance room. A sitter named Esson Maule grabbed her and the lights were turned on and the spirit was revealed to be made from a stockinette undervest.[10] The police were called and Duncan was prosecuted and fined £10.[16] The undervest was used as evidence which led to Duncan's conviction of fraudulent mediumship at the Edinburgh Sheriff Court trial on 11 May 1933.[17]
The spiritualist journal Light endorsed the court decision that Duncan was fraudulent and supported Price's investigation that revealed her ectoplasm was cheesecloth.[18] Duncan's husband was also suspected of acting as her accomplice through hiding her fake ectoplasm.[4] Duncan would frequently have nosebleeds during séances; William Brown suggested that this was another of Duncans hiding places for her fake ectoplasm.[19]
In 1936, the psychical researcher Nandor Fodor offered money to Duncan if she would be filmed with an infrared camera during a séance. She refused the offer.[20]
HMS Barham sinking

During World War II, in November 1941, Duncan held a séance in Portsmouth at which she claimed the spirit materialization of a sailor told her HMS Barham had been sunk.[9] Because the sinking of HMS Barham was revealed, in strict confidence, only to the relatives of casualties, and not announced to the public until late January 1942, the Navy started to take an interest in her activities. Two lieutenants were among her audience at a séance on 14 January 1944. One of these was a Lieutenant Worth who was not impressed as a white cloth figure had appeared behind the curtains claiming to be his aunt but he had no deceased aunt. In the same sitting another figure appeared claiming to be his sister but Worth replied his sister was alive and well.[9] Worth was disgusted by the séance and reported it to the police. This was followed up on 19 January, when undercover policemen arrested her at another séance as a white-shrouded manifestation appeared.[21] This proved to be Duncan herself, in a white cloth which she attempted to conceal when discovered, and she was arrested.[9][22]
Researcher Graeme Donald wrote that Duncan could have easily found out about HMS Barham and she had no genuine psychic powers. According to Donald:
| “ | There was no shroud of secrecy; The Times of London carried news of the disaster on the Monday. The loss of HMS Barham, torpedoed off the coast of Egypt on 25 November 1941, was indeed kept quiet for a while, but letters of condolence were sent out to families of the 861 dead, asking them to keep the secret until the official announcement. So, allowing for perhaps 10 people in each family, there were about 9,000 people who knew of the sinking; if each of them told only one other person, there were 20,000 people in the country aware of the sinking, and so on – hardly a closely guarded secret. In short, news of the sinking spread like wildfire; Duncan simply picked up the gossip and decided to turn it into profit.[23] | ” |
A leak concerning HMS Barham was later discovered. A secretary of the First Lord had been indiscreet to Professor Michael Postan of the Ministry of Economic Warfare. Postan escaped arrest by insisting that he had made a mistake by believing the information had been imparted on an official basis.[24]
Duncan was found to be in possession of a mocked-up HMS Barham hat-band.[25] This apparently related to an alleged manifestation of the spirit of a dead sailor on HMS Barham, although Duncan appeared unaware that after 1939, sailors' hat bands carried only 'H.M.S.' and did not identify the ship they were serving on.[9] She was initially arrested under section 4 of the Vagrancy Act 1824, a minor offence tried by magistrates. The authorities regarded the case as more serious, and eventually discovered section 4 of the Witchcraft Act 1735, covering fraudulent "spiritual" activity, which was triable before a jury. Charged alongside her for conspiracy to contravene this Act were Ernest and Elizabeth Homer, who operated the Psychic centre in Portsmouth, and Frances Brown, who was Duncan's agent who went with her to set up séances. There were seven counts in total, two of conspiracy to contravene the Witchcraft Act, two of obtaining money by false pretences, and three of public mischief (a common law offence). The prosecution may be explained by the mood of suspicion prevailing at the time: the authorities were afraid that she could continue to reveal classified information, whatever her source was.[26] There were also concerns that she was exploiting the recently bereaved, as the Recorder noted when passing sentence.[27]
Duncan's trial for fraudulent witchcraft was a minor cause célèbre in wartime London. Alfred Dodd, an historian and senior Freemason, testified he was convinced she was authentic. The trial was complicated by the fact that a police raid on the séance in Portsmouth, leading to the arrest of Helen Duncan, yielded no physical evidence of the fraudulent use of cheesecloth, and was therefore based entirely on witness testimony, the majority of which denied any wrongdoing.[28] Duncan was barred by the judge from demonstrating her alleged powers as part of her defence against being fraudulent. The jury brought in a guilty verdict on count one, and the judge then discharged them from giving verdicts on the other counts, as he held that they were alternative offences for which Duncan might have been convicted had the jury acquitted her on the first count. Duncan was imprisoned for nine months, Brown for four months and the Homers were bound over.[28] After the verdict, Winston Churchill wrote a memo to Home Secretary Herbert Morrison, complaining about the misuse of court resources on the "obsolete tomfoolery" of the charge.[29]
Repeal of the Witchcraft Act
In 1944, Duncan was one of the last people convicted under the Witchcraft Act 1735, which made falsely claiming to procure spirits a crime. She was sentenced to nine months' imprisonment. When convicted, she cried out "I have done nothing; is there a God?".[27][30]
On her release in 1945, Duncan promised to stop conducting séances, but she was arrested during another one in 1956. She died at her home in Edinburgh a short time later.[5] Duncan's trial almost certainly contributed to the repeal of the Witchcraft Act, which was contained in the Fraudulent Mediums Act 1951 promoted by Walter Monslow, Labour Member of Parliament for Barrow-in-Furness. The campaign to repeal the Act had largely been led by Thomas Brooks, another Labour MP, who was a spiritualist. Duncan's original conviction still stood, and it was the subject of a sustained campaign to have it overturned.[31][32]
Death
Contrary to what some spiritualists have written there was nothing strange or unusual about the death of Duncan and it was not caused by her "trance" being disturbed by the police. Duncan's medical records showed that she had a long history of ill-health and as early as 1944 she was described as an obese woman who could only move slowly as she suffered from heart trouble.[9]
Legacy
After her death, Duncan was cited in paranormal and parapsychological books as an example of a fraudulent medium.[33] However, she retained supporters amongst the spiritualist community.[34] On this, Jenny Hazelgrove has noted:
Her Opponents condemned her mediumship out of hand while her supporters took up the opposite position. Any suspicious aspects of the Duncan mediumship – the wood-pulp 'ectoplasm', the 'ectoplasmic' drapery that resembled cheese cloth – were glossed over by her followers in the interests of producing a wholly idealised picture of her life and mediumship.[35]
The psychical researcher Simeon Edmunds also noted that spiritualists have a history of ignoring the evidence of fraud in the Duncan case. He criticized the spiritualist press such as Psychic News for biased reporting and distorting facts.[9] Science writer Mary Roach in her book Spook: Science Tackles the Afterlife (2007) favorably mentioned Price's methods in debunking Duncan as a fraudulent medium.[4] Richard Denham's book Weird War Two focuses on the absurdity of Duncan being charged and convicted as a witch in the paranoia of wartime Britain, particularly the frustration of Winston Churchill, who himself had been ordained into the Ancient Order of Druids
Inspired by her legacy, new wave of British heavy metal band Seventh Son recorded and released a song 'The Last Witch In England' in 2009, depicting her life and her 'prediction' of the sinking of HMS Barham.[36]
The naval investigation and subsequent trial was dramatized as a radio play. The Last Witch Trial by Melissa Murray, starring Joanna Monro as Duncan and Indira Varma as the undercover investigator, was broadcast by BBC Radio 4 on 4 June 2010.[37]
Descendants and supporters of Duncan have campaigned on several occasions to have her posthumously pardoned of witchcraft charges. Petitions for a posthumous pardon were rejected by the Scottish Parliament in 2001, 2008, and 2012.[38] Duncan's supporters maintain a website and online petition where they continue to campaign for her pardon.[39]
Notes
- ↑ Georgess McHargue. (1972). Facts, Frauds, and Phantasms: A Survey of the Spiritualist Movement. Doubleday. pp. 90–92. ISBN 978-0385053051
- ↑ Renée Haynes. (1982). The Society for Psychical Research 1882–1982: A History. MacDonald & Co. p. 144. ISBN 978-0356078755 "An investigation by Harry Price and other members of the Society for Psychical Research, to which he belonged at the time, showed that she certainly did use cheesecloth on occasion."
- ↑ Ruth Paley, Simon Fowler. (2005). Family Skeletons: Exploring the Lives of our Disreputable Ancestors. The National Archives. p. 220. ISBN 978-1903365540 "Price revealed that Duncan's ectoplasmic manifestations were pieces of cheesecloth that Duncan swallowed and regurgitated at will."
- 1 2 3 4 Mary Roach. (2007). Six Feet Over: Adventures in the Afterlife. Canongate books. pp. 122–130. ISBN 978-1847670809
- 1 2 3 Gaskill, Malcolm (January 2008). "Duncan [née MacFarlane], (Victoria) Helen McCrae (1897–1956)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press.
- ↑ Malcolm Gaskill. (2001). Hellish Nell: Last of Britain's Witches. Fourth Estate. p. 100. ISBN 978-1841151090
- ↑ Jason Karl. (2007). An Illustrated History of the Haunted World. New Holland Publishers. p. 79. ISBN 978-1845376871
- ↑ Renée Haynes. (1982). The Society for Psychical Research 1882–1982: A History. MacDonald & Co. p. 144. ISBN 978-0356078755 "The London Spiritualist Alliance had fifty sittings with her between October 1930 and June 1931; for these sittings she was stripped, searched and dressed in 'seance garments'. Two interim reports in Light were favorable, a third found indications of fraud. Pieces of 'ectoplasm' found from time to time differed in composition. Two early specimens consisted of paper or cloth mixed with something like white of egg. Two others were pads of surgical gauze soaked in 'a resinous fluid'; yet another consisted of layers of lavatory paper stuck together. The most usual material for 'ectoplasm' however, seemed to be butter muslin or cheesecloth, probably swallowed and regurgitated. Distressing choking noises were sometimes heard from within the cabinet; and it was interesting that when she was persuaded to swallow a tablet of methylene blue before one of the seances at the London Spiritualist Alliance, no ectoplasm whatsoever appeared."
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Simeon Edmunds. (1966). Spiritualism: A Critical Survey. Aquarian Press. pp. 137–144
- 1 2 3 Paul Tabori. (1961). The Art of Folly. Prentice-Hall International, Inc. pp. 180–182. ISBN 978-1111236632
- ↑ Harry Price. (1942). Search for Truth: My Life for Psychical Research. Collins. p. 182
- ↑ Marina Warner. (2008). Phantasmagoria: Spirit Visions, Metaphors, and Media into the Twenty-first Century. Oxford University Press. p. 299. ISBN 978-0199239238
- ↑ Harry Price. (1933). Leaves from a Psychist's Case-Book. Victor Gollancz Ltd. pp. 203–207
- ↑ Valentine, Elizabeth R. (2011). Spooks and Spoofs: Relations Between Psychical Research and Academic Psychology in Britain in the Inter-War Period. History of the Human Sciences 25: 67-90.
- ↑ Paul Tabori. (1961). The Art of Folly. Prentice-Hall International, Inc. p. 182 ISBN 978-1111236632 "In November 1931, Harry Price's report was issued, whereupon a Miss Mary McGinlay, came forward. She was Mrs Duncan's personal maid at the time of the séances and she made a statutory declaration before a Commissioner of Oaths that she used to purchase for Mrs. Duncan lengths of cheesecloth which she had to wash out after a séance. She also swore on oath that Mr. Duncan had informed her on the night of the scene at the National Laboratory that his wife had "passed a roll of butter muslin to him when they were alone in the street."
- ↑ Raymond Buckland. (2005). The Spirit Book: The Encyclopedia of Clairvoyance, Channeling, and Spirit Communication Visible Ink Press. p. 117. ISBN 978-1578592135
- ↑ Harry Price. (1933). Leaves from a Psychist's Case-book. Gollancz. p. 176
- ↑ Hazelgrove, Jenny. (2000). Spiritualism and British Society Between the Wars. Manchester University Press. p. 279. ISBN 978-0719055584
- ↑ Malcolm Gaskill. (2001). Hellish Nell: Last of Britain's Witches. Fourth Estate. p. 237. ISBN 978-1841151090
- ↑ Ruth Paley, Simon Fowler. (2005). Family Skeletons: Exploring the Lives of our Disreputable Ancestors. The National Archives. p. 220. ISBN 978-1903365540
- ↑ Correspondent (24 March 1944). "Alleged Séance Deception". The Times. London (49813): 8.
- ↑ Correspondent (25 March 1944). "Alleged Séance deceptions. Further evidence for the prosecution.". The Times. London (49814): 2.
- ↑ Graeme Donald. (2009). Loose Cannons: 101 Things They Never Told You About Military History. Osprey Publishing. p. 48. ISBN 978-1846033773
- ↑ Nigel West. (2010). Historical Dictionary of Naval Intelligence. Scarecrow Press. p. 98. ISBN 978-0810867604
- ↑ Correspondent (31 January 1998). "British Lion, the Witch and Her Wardrobe.". The Times. London (49814): 2.
- ↑ Spell broken for 20th century witch. BBC, 31 January 1998
- 1 2 "Medium Sentenced For Fraud". The Times. London, England: The Times Digital Archive. 1944-04-04. p. 2.
- 1 2 Helena Normanton. (1945). The Trial of Mrs. Duncan. Edited with a Foreword by C. E. Bechhofer Roberts. Jarrolds Publishers.
- ↑ Mantel, Hilary (3 May 2001). "Unhappy medium". Essays from the London Review of Books. The Guardian. Retrieved 2008-02-29.
- ↑ McSmith, Andy (29 February 2008). "Toil and trouble: the last witch?". The Independent. London. Retrieved 1 June 2012.
- ↑ Howie, Craig (24 October 2005). "Fraudulent medium or powerful psychic: the trial of a Scottish witch". The Scotsman. Edinburgh. Retrieved 12 September 2011.
"Mediums demand pardon for the murder of Helen Duncan'.
- ↑ "Hellish Nell: Witch-hunt that led to capture of fake medium". The Scotsman. 24 February 2009. Retrieved 31 May 2012.
many spiritualists, who have campaigned to have her 1944 conviction quashed
- ↑ Paul Tabori, (1961). Simeon Edmunds. (1966). Georgess McHargue, (1972). Renée Haynes, (1982). Paul Kurtz, (1985). Mary Roach, (2007).
- ↑ Maurice Barbanell, (1945). Alan Crossley, (1976). Manfred Cassirer, (1996). Hartley, (2007).
- ↑ Jenny Hazelgrove. (2000). Spiritualism and British Society Between the Wars. Manchester University Press. p. 222. ISBN 978-0719055591
- ↑ "Spirit World, Tracklisting". iTunes Store. Retrieved 13 December 2015.
- ↑ "Afternoon Drama, The Last Witch Trial". BBC Online. Retrieved 30 May 2012.
- ↑ "Britain's 'last witch': Campaign to pardon Helen Duncan". BBC.com. Retrieved 29 May 2016.
- ↑ "The Official Helen Duncan". Retrieved 29 May 2016.
References
- Mary Armour. (2001). Helen Duncan: My Living Has Not Been in Vain. Pembridge Publishing. ISBN 978-0953481620
- Maurice Barbanell. (1945). The Case of Helen Duncan. Psychic Press.
- Gena Brealey, Kay Hunter. The Two Worlds of Helen Duncan. Saturday Night Press Publications. ISBN 978-0955705038
- Manfred Cassirer. (1996). Medium on Trial. PN Publishing. ISBN 978-1900671002
- Simeon Edmunds. (1966). Spiritualism: A Critical Survey. Aquarian Press. ISBN 978-0850300130
- Robert Hartley. (2007). Helen Duncan The Mystery Show Trial. HPR Publishing. ISBN 978-0955342080
- Alan Crossley. (1976). The Story of Helen Duncan: Materialisation Medium. Arthur H. Stockwell Ltd. ISBN 978-0722308400
- Malcolm Gaskill. "Britain's Last Witch". History Today 51 (2001).
- Malcolm Gaskill. (2001). Hellish Nell: Last of Britain's Witches. Fourth Estate. ISBN 978-1841151090
- Renée Haynes. (1982). The Society for Psychical Research 1882–1982: A History. MacDonald & Co. ISBN 978-0356078755
- Jenny Hazelgrove. (2000). Spiritualism and British Society Between the Wars. Manchester University Press. ISBN 978-0719055591
- "Hellish Nell". The Daily Mirror. 6 December 2006: 24.
- Paul Kurtz. (1985). A Skeptic's Handbook of Parapsychology. Prometheus Books. ISBN 978-0879753009
- Georgess McHargue. (1972). Facts, Frauds, and Phantasms: A Survey of the Spiritualist Movement. Doubleday. ISBN 978-0385053051
- Helena Normanton. (1945). The Trial of Mrs Duncan. London: Jarrolds.
- Harry Price. (1931). Regurgitation and the Duncan Mediumship. (Bulletin I of the National Laboratory of Psychical Research, 120pp with 44 illustrations.)
- Harry Price. (1933). The Cheese-Cloth Worshippers. In Leaves from a Psychist's Case-Book. Victor Gollancz Ltd.
- Harry Price. (1936). Confessions of a Ghost-Hunter. Putnam.
- Harry Price. (1942). Search for Truth: My Life for Psychical Research. Collins.
- Mary Roach. (2007). Six Feet Over: Adventures in the Afterlife. Canongate Books Ltd. ISBN 978-1-84767-080-9
- Nina Shandler. (2006). The Strange Case of Hellish Nell. Da Capo Press. ISBN 9780306814389
- Roy Stemman. (1976). The Supernatural. Danbury Press. ISBN 978-0717281053
- Paul Tabori. (1961). The Art of Folly. Prentice-Hall International, Inc. ISBN 978-1111236632
- Paul Tabori. (1966). Harry Price: The Biography of a Ghosthunter. Living Books.
- "The Last Witch-hunt". The Daily Mail. 7 February 2005: 15.
- Donald J. West. (1946). The Trial of Mrs Duncan. Proceedings of the Society for Psychical Research 48: 32-64.
External links
- Inside story: 301 Copnor Road by Roger Wilkes
- Helen Duncan website
- Article in World War II magazine about Duncan and HMS Barham
- The Harry Price Website – Psychical researcher Harry Price's 1931 examination of Helen Duncan's séance room practices.
- Photograph of an alleged spirit manifestation by Helen Duncan
- Article about Helen Duncan and the implications of subsequent legislation.
- Campaign to have Helen Duncan posthumously pardoned
- Hellish Nell Medium Helen Duncan's Spirited Day in Court