Harley-Davidson Evolution engine
The Evolution engine (popularly known as Evo) is an air-cooled, 45-degree, V-twin engine manufactured from 1984 by Harley-Davidson for the company's motorcycles. It was made in the 1,340 cc (82 cu in) displacement for Harley-Davidson Big V-twins bikes, replacing the Shovelhead engine until 2000 when the last EVO was placed in a production factory custom FXR4 (FXR2 and FXR3 were the first CVOs). In 1999, it was replaced by the Harley-Davidson Twin Cam 88 in the Touring and Dyna model and in 2000 in the Softail models. Also available in the Sportster model beginning in 1984, it was made in the 1,100 cc (67 cu in) displacement until 1988 and is still made in the 883 cc (53.9 cu in) and 1,200 cc (73 cu in) [1] displacements for the Harley-Davidson Sportster, replacing the ironhead Sportster engine.
Most analysts consider the Evolution to be the engine that saved the reorganized Harley-Davidson company from certain bankruptcy. Harley-Davidson's official name for the engine was likely related to the company's attempt to reform its image following the 1981 management buyout from previous owner American Machine and Foundry (AMF).[2]
Both the heads and cylinders of the Evolution engine are made from aluminum to reduce weight compared to a cast iron design. Air cooling efficiency is improved as aluminum is a superior thermal conductor to cast iron. The blocky rocker boxes (thus becoming nicknamed "block head" which never caught on), aluminum heads and cylinders (also referred to as "jugs") are the only part of the Evolution engine that can be said to be essential; the Big Twin and Sportster incarnations of the Evolution are significantly different.
Evolution on the Sportster
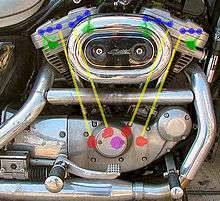
The unit construction of the Harley-Davidson Sportster, which has essentially been unchanged since its inception as the side-valve 750cc "K" Model in 1952, was retained with the Evolution engine upgrade in 1986, resulting in a unique valve train configuration. Unlike almost any other engine in production today, the Sportster Evolution uses one cam per engine overhead valve, resulting in four individual, single-lobe, gear-driven camshafts. The cam lobes are thus all located one behind another, and pushrods are arrayed in pairs (front and rear) parallel to the cylinder axis as a result. This allows each lifter and pushrod to deflect from the cam lobes perpendicular to the lobe plane. This configuration is friendly to radical, high-output cams, making the Sportster Evolution a natural choice for the once Harley-Davidson owned line of Buell Motorcycle Company sportbikes from 1986 up to late 2009 (2010 model year).
The Sportster Evolution engine has remained largely unchanged from 1986 to the present day, though changes to the transmission, final drive and motor mounts have necessitated changes to the Sportster Evolution case. Construction is almost entirely the same between 883 cc and 1,200 cc versions; the chief difference between the two is a smaller bore on the 883 cc (inherited from its earlier "ironhead" parent), along with slightly different heads. Conversions from 883 cc to 1,200 cc are relatively inexpensive and commonplace,[3] and cheaper than the price premium to go from an 883 to 1,200 engine on a new bike.[4] Carburetors were standard on Sportster engines until 2007, when they were replaced by the Delphi Electronic Sequential-Port Fuel Injection (ESPFI) system.
A simplified derivative of the engine was used on the Buell Blast entry-level motorcycle from 2000 to 2009. The Sportster engine as used on the Buell Blast was in most ways similar to the one used on Sportsters, albeit with the rear cylinder removed, along with other concessions to reduce overall cost and maintenance.
Evolution on the big bikes
The Evolution Big Twin saw a fifteen-year run in Harley-Davidson's Dyna, Softail, FXR, and Touring frames, although a limited number of Evolutions were used in the 2000 model year CVO FXR4, and 1999 FXR2 and FXR3 models. While the main case was only slightly modified from the previous Shovelhead engine, the top end was significantly improved.
The 1340cc Evolution utilizes a single, four-lobe, gear-driven camshaft located just above the crankshaft axis. While this simplifies camshaft replacement, it complicates the Big Twin valve train with tappet/lifters and pushrods that each deflect from the camshaft at wildly different angles. The Big Twin pushrods have a distinct helical appearance because the vertical plane formed by each cylinder's rockers (front-to-back) is exactly perpendicular to the vertical plane formed by the cam lobes (left-to-right). The need for one lifter and pushrod set to reach all the way out to the most outboard cam lobe gives rise to the Big Twin's tell-tale offset lifter assemblies, where the forward lifter assembly is located slightly farther out and rotated to enable the valve gear to make the reach.
The Big Twin has been accompanied by a number of different primary drives and transmissions, both on production Harley-Davidson motorcycles and in custom applications. The aftermarket selection of accessories for these closely related systems is wide, as it is for the engine itself.
The Evolution Big Twin motor was, until the introduction of the Twin Cam engine, the last of the line of single cam, overhead valve motors tracing their lineage back to the seminal Knucklehead design penned by founder Bill Harley. It is also the largest aftermarket supported Harley-Davidson design, to date, with clones of the engine being produced by third parties like S&S Cycle and several others. Harley reverted to a single cam design with the Milwaukee-Eight engine, first introduced for touring models in 2016.
See also
References
- ↑ Greg Field (2001). Harley-Davidson Evolution Motorcycles. Motorbooks. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-7603-0500-3.
- ↑ Smithsonian magazine, August 2003, pg. 36 – "Wild Thing", Robert F. Howe
- ↑ Timothy Remus (1998). How to customize your Harley-Davidson. Motorbooks. pp. 67, 78. ISBN 978-0-7603-0359-7.
- ↑ Dave Murray, Want $2000 Bucks off a 1200cc Sportster?