Haryana
| Haryana | ||
|---|---|---|
| State | ||
| ||
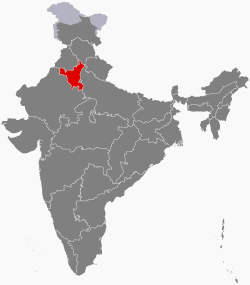 Location of Haryana in India | ||
| Coordinates (Chandigarh): 30°44′N 76°47′E / 30.73°N 76.78°ECoordinates: 30°44′N 76°47′E / 30.73°N 76.78°E | ||
| Country |
| |
| Statehood | 1 November 1966 | |
| Capital | Chandigarh | |
| Largest city | Faridabad | |
| Districts | 22 | |
| Government | ||
| • Governor | Kaptan Singh Solanki | |
| • Chief Minister | Manohar Lal Khattar (BJP) | |
| • Legislature | Unicameral (90 seats) | |
| • Parliamentary constituency |
Rajya Sabha 5 Lok Sabha 10 | |
| • High Court | Punjab and Haryana High Court | |
| Area[1] | ||
| • Total | 44,212 km2 (17,070 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | 21st | |
| Population (2016) | ||
| • Total | 27,761,063 | |
| • Rank | 18th | |
| • Density | 573/km2 (1,480/sq mi) | |
| • Density rank | 11 | |
| Demonym(s) | Haryanvi | |
| Languages | ||
| • Official | Hindi[2] | |
| • Additional official | Punjabi[3] | |
| Time zone | IST (UTC+05:30) | |
| ISO 3166 code | IN-HR | |
| Vehicle registration | HR-xx | |
| HDI |
| |
| HDI rank | 17th (2011) | |
| Website |
haryana | |
| Symbols of Haryana | ||
| Animal |
| |
| Bird |
 | |
| Flower |
| |
| Tree |
| |
Haryana (IPA: [ɦərɪˈjaːɳaː]) is one of the 29 states in India, situated in North India. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 November 1966 on a linguistic basis. It stands 21st in terms of its area, which is spread about 44,212 km2 (17,070 sq mi).[1] As of 2011 census of India, the state is eighteenth largest by population with 25,353,081 inhabitants. The city of Chandigarh is its capital while the National Capital Region city of Faridabad is the most populous city of the state and the city of Gurugram is financial hub of NCR with major Fortune 500 companies located in it.[4]
Haryana is one of the wealthiest states of India and has the third highest per capita income in the country at ₹119,158 (US$1,900) in the year 2012–13 and ₹132,089 (US$2,100) in the year 2013–14,[5][6] The state is one of the most economically developed regions in South Asia, and its agricultural and manufacturing industries have experienced sustained growth since the 1970s.[7] Since 2000, the state has emerged as the largest recipient of investment per capita in India.[8]
It is bordered by Punjab and Himachal Pradesh to the north, and by Rajasthan to the west and south. The river Yamuna defines its eastern border with Uttar Pradesh. Haryana surrounds the country's capital Delhi on three sides, forming the northern, western and southern borders of Delhi. Consequently, a large area of south Haryana is included in the National Capital Region for purposes of planning for development.
Etymology
The name Haryana is found in the works of the 12th-century AD Apabhramsha writer Vibudh Shridhar (VS 1189–1230).[9]
The name Haryana has been derived from the Sanskrit words Hari (the Hindu god Vishnu) and ayana (home), meaning "the Abode of God".[10] However, scholars such as Muni Lal, Murli Chand Sharma, HA Phadke and Sukhdev Singh Chib believe that the name comes from a compound of the words Hari (Sanskrit Harit, "green") and Aranya (forest).[11]
History
Pre-history

Vedic state of Brahmavarta is claimed to be located in a new research in south Haryana, where initial Vedic scriptures were composed after the great floods some 10,000 years ago.[12] Manusmriti, a flood time document composed by Manu and Bhrigu is now dated 10,000 years old.[13] Rakhigarhi village in the Hisar district is home to the largest and one of the oldest ancient Indus Valley Civilization sites, dated as over 5,000 years old. Evidence of paved roads, a drainage system, a large-scale rainwater collection storage system, terracotta brick and statue production, and skilled metal working (in both bronze and precious metals) have been uncovered. According to archeologists, Rakhigarhi may be the origin of Harappan civilisation, which arose in the Ghaggar basin in Haryana and gradually and slowly moved to the Indus valley.[14]
Medieval
Ancient idols of Jain Tirthankara (made of bronze and stone) were found in archaeological expeditions in Badli, Bhiwani (Ranila, Charkhi Dadri, Badhara village), Dadri, Gurgaon (Ferozpur Jhirka), Hansi, Hisar (Agroha), Kasan, Nahad, Narnaul, Pehowa, Rewari, Rohad, Rohtak (Asthal-Abohar) and Sonepat in Haryana.[15] From there he proceeded to Kaithal whose residents were massacred and plundered, destroying all villages along the way. On the next day, he came to Assandh whose residents were "fire-worshippers" according to Yazidi had fled to Delhi. Next he traveled to and subdued Tughlaqpur fort and Salwan before reaching Panipat whose residents had already fled. He then marched on to Loni fort.[16][17]

The area that is now Haryana has been ruled by major empires of India. Panipat is known for three seminal battles in the history of India. In the First Battle of Panipat (1526), Babur defeated the Lodis. In the Second Battle of Panipat (1556), Akbar defeated the local Haryanvi Hindu Emperor of Delhi, who belonged to Rewari. Hem Chandra Vikramaditya, had earlier won 22 battles across India from Punjab to Bengal defeating Mughals and Afghans. Hemu had defeated Akbar's forces twice at Agra and Battle of Delhi in 1556 to become last Hindu Emperor of India with formal Coronation at Purana Quila in Delhi on 7th Oct. 1556. In the Third Battle of Panipat (1761), the Afghan king Ahmad Shah Abdali defeated the Marathas.[18]
Formation
Haryana state was formed on 1 November 1966. The Indian government set up the Shah Commission under the chairmanship of Justice JC Shah on 23 April 1966 to divide the existing Punjab, India and determine the boundaries of the new state of Haryana after consideration of the languages spoken by the people. The commission delivered its report on 31 May 1966 whereby the then-districts of Hisar, Mahendragarh, Gurgaon, Rohtak and Karnal were to be a part of the new state of Haryana. Further, the tehsils of Jind and Narwana in the Sangrur district—along with Naraingarh, Ambala and Jagadhri—were to be included.[19]
The commission recommended that the tehsil of Kharad, which includes Chandigarh, the state capital of Punjab, should be a part of Haryana. However, only a small portion of Kharad was given to Haryana.[20] The city of Chandigarh was made a union territory, serving as the capital of both Punjab and Haryana.[21]
Bhagwat Dayal Sharma became first Chief Minister of Haryana.[22]
Geography
Haryana is a landlocked state in northern India. It is between 27°39' to 30°35' N latitude and between 74°28' and 77°36' E longitude.[23] The total geographical area of the state is 4.42 m ha, which is 1.4% of the geographical area of the country.[24] The altitude of Haryana varies between 700 and 3600 ft (200 metres to 1200 metres) above sea level.[25] As per India State of Forest Report, FSI, 2013, the Forest Cover in the state is 1586 km2 which is 3.59% of the state's geographical area and the Tree Cover in the state is 1282 km2 which is 2.90% of the geographical area. Thus the Forest and Tree Cover of the Haryana state is 6.49% of its geographical area.[26]
Haryana has four main geographical features.[27]
- The Yamuna-Ghaggar plain forming the largest part of the state
- The Shivalik Hills to the northeast
- Semi-desert sandy plain to the southwest
- The Aravali Range in the south
Rivers

The Yamuna flows along the state's eastern boundary while the ancient Sarasvati River is said to have flowed from Yamuna Nagar, but has now disappeared.[28]
Haryana's main seasonal river, the Ghaggar rises in the outer Himalayas, between the Yamuna and the Satluj and enters the state near Pinjore in the Panchkula district. Passing through Ambala and Sirsa, it reaches Bikaner in Rajasthan and runs for 460 km (290 mi) before disappearing into the deserts of Rajasthan. Important tributaries include the Chautang and Tangri.[29]
The seasonal Markanda River is a stream, which in ancient times was known as the Aruna. It originates from the lower Shivalik Hills and enters Haryana west of Ambala. During monsoons, this stream swells into a raging torrent notorious for its devastating power. The surplus water is carried on to the Sanisa Lake where the Markanda joins the Saraswati and later the Ghaggar.[29]
Three other rivulets in and around the Mewat hills, the Indori, Dohan and Kasavati all flow from East to West and once were tributaries of the Drishadwati/Saraswati rivers.[30][31][32]
Climate
Haryana is extremely hot in summer at around 45 °C (113 °F) and mild in winter. The hottest months are May and June and the coldest December and January.[30] The climate is arid to semi-arid with average rainfall of 354.5 mm. Around 29% of rainfall is received during the months from July to September, and the remaining rainfall is received during the period from December to February.[24]
Flora and fauna
| Formation day | 1 November (Day of separation from Punjab) |
| State mammal | Black buck[33] |
| State bird | Black francolin |
| State tree | Peepal[33] |
| State flower | Lotus[33] |
Thorny, dry, deciduous forest and thorny shrubs can be found all over the state. During the monsoon, a carpet of grass covers the hills. Mulberry, eucalyptus, pine, kikar, shisham and babul are some of the trees found here. The species of fauna found in the state of Haryana include black buck, nilgai, panther, fox, mongoose, jackal and wild dog. More than 450 species of birds are found here.[34][35][36]
Protected wildlife areas
Haryana has two national parks, eight wildlife sanctuaries, two wildlife conservation areas, four animal and bird breeding centers, one deer park and three zoos, all of which are managed by the Haryana Forest Department of the Government of Haryana.[37][38]
Administrative divisions

The state is divided into six divisions for administrative purposes: Ambala, Rohtak, Gurugram, Hisar, Karnal, Faridabad Within these there are 22 districts, 72 sub-divisions, 93 tehsils, 50 sub-tehsils and 140 blocks. Haryana has a total of 154 cities and towns and 6,841 villages, villages panchayats 6212 .[39]
Districts
| Divisions | Districts |
|---|---|
| Ambala | Ambala, Kurukshetra, Panchkula, Yamuna Nagar |
| Faridabad | Faridabad, Palwal, Nuh |
| Gurugram | Gurugram, Mahendragarh, Rewari, |
| Hisar | Fatehabad, Jind, Hisar, Sirsa, |
| Rohtak | Jhajjar, Charkhi Dadri, Rohtak, Sonipat, bhiwani[27] |
| Karnal | Karnal, Panipat, Kaithal |
Governance
On 28 December 2015, the Panchkula district of Haryana was awarded for being the top-performing district in the state under the Digital India campaign.[40] The Common Service Centres (CSCs) have been upgraded in all districts and the number of e-services has now reached 105, which includes application of new water connection, sewer connection, electricity bill collection, ration card member registration, result of HBSE, admit cards for board examinations, online admission form for government colleges, long route booking of buses, admission forms for Kurukshetra University and HUDA plots status inquiry.[40] Haryana has become the first state to implement Aadhaar-enabled birth registration in all the districts.[40]
Law and order
Haryana Police force is the law enforcement agency of Haryana. It has a cybercrime investigation cell, in Gurgaon's Sector 51. High level of initiative is being taken by the government to ensure absolute safety.[41]
The judicial authority is the Punjab and Haryana High Court. It has an e-filing facility.[42]
Economy
The economy of Haryana relies on manufacturing, business process outsourcing, agriculture and retail.
Agriculture


There are two Agroclimatic zones in Haryana. The North-Western part (also referred as Paddy belt) which is suitable for Rice, Wheat, Vegetables and Temperate Fruits, and the South-Western part (also referred as the Cotton belt or Dry belt) which is suitable for Cotton, Millets, coarse cereals, tropical fruits, exotic vegetables and herbal & medicinal plants.
As Kharif season cultivation depends on rainfalls & the Northern part receives ample rains, rice is extensively cultivated in this part. Punjab bordering area from Cheeka-Kaithal to Karnal-Kurukshetra is major belt of Basmati rice cultivation & most millers of Basmati rice are present in Karnal-Kurukshetra. The cotton belt which receives less rainfall grows Cotton, however farmers with irrigation still prefer growing Rice. Sirsa, Fatehabad, Hisar & Jind are among major cotton producing areas of Haryana. Southern districts of Bhiwani, Rewari, Jhajjar and Mahendragarh in Haryana which are usually arid are major producer of Millets like Bajra & Jowar.
During Rabi season, major crops in Haryana are Wheat, Gram & Mustard.
Sugarcane cultivation is done in parts adjoining the Yamuna river & in some internal pockets where irrigation facility is available. The cultivable area is 3.7 m ha, which is 84% of the geographical area of the state. 3.64 m ha, i.e. 98% of cultivable area, is under cultivation. The gross cropped area of the state is 6.51 m ha and net cropped area is 3.64 m ha with a cropping intensity of 184.91%.[24][43][44]
Manufacturing

- Faridabad is one of the biggest industrial city of Haryana as well as North India.[45]
- Rohtak has the largest wholesale cloth market of Asia, known as shori market. As of 2012, Haryana State Industrial and Infrastructure Development Corporation (HSIIDC) has developed an Industrial Model Township (IMT). MNCs like Maruti Suzuki, Asian Paints, Suzuki Motorcycle, Nippon Carbide, Lotte India Corporation Limited along with Tata Tea Plant, Shivam Autotech Ltd., Vita Milk Plant, Amul Dairy, Lakshmi Precision Screws, LPS BOSSARD, Aisin Automotive and many more launched work on projects.
- Bahadurgarh is an important developing industrial town with glass, steel, tiles manufacturing and biscuits production.
- Panipat has heavy industry, including a refinery operated by the Indian Oil Corporation, a urea manufacturing plant operated by National Fertilizers Limited and a National Thermal Power Corporation power plant. It is known for its woven modhas or round stools.[46]
- Hissar is another developing city and the hometown of Navin Jindal and Subhash Chandra of Zee TV fame. Savitri Jindal, Navin Jindal's mother, has been listed by Forbes as the third richest woman in world.[47]
Transport



Airports
Nearest airports with the scheduled regular passenger flights services are the Chandigarh International Airport at state capital Chandigarh and the Indira Gandhi International Airport at the national capital Delhi. Though the state has several airports, one of these have scheduled regular passenger flights, Bhiwani Airport, Hisar Airport, Karnal Airport, Narnaul Airport and Pinjore Airport. The Ambala Air Force Station and Sirsa Air Force Station are also located within the state.
Metro
Delhi Metro connects the national capital Delhi with parts of Haryana state within NCR, including Bahadurgarh, Faridabad and with Rapid MetroRail Gurgaon. Faridabad has the longest metro network in the NCR Region consisting of 9 stations and track length being 14 km.[48]
The proposed Chandigarh Metro plan envisages connecting Panchkula to the state capital.
Railway
The railway network in Haryana is under North Western Railway zone (covering Hisar, Bhiwani, Charkhi Dadri, Mahendragarh and Rewari districts in the western and south western parts of the state) and Northern Railway zone (in the remaining areas in the north, east and central parts of the state).
Roads and Highways
Haryana has a total road length of 23,684 kilometres (14,717 mi). There are 29 national highways with a total length of 1,461 kilometres (908 mi) and many state highways, which have a total length of 2,494 kilometres (1,550 mi). The most remote parts of the state are linked with metaled roads. Its modern bus fleet of 3,864 buses covers a distance of 1.15 million km per day, and it was the first state in the country to introduce luxury video coaches.[49]
The Grand Trunk Road, commonly abbreviated to GT Road, is one of South Asia's oldest and longest major roads. It passes through the districts of Sonipat, Panipat, Karnal, Kurukshetra and Ambala in north Haryana where it enters Delhi and subsequently the industrial town of Faridabad on its way. The state government proposes to construct Express highways and freeways for speedier vehicular traffic. The 135.6 kilometres (84.3 mi) Kundli-Manesar-Palwal Expressway(KMP) will provide a high-speed link to northern Haryana with its southern districts such as Sonepat, Gurgaon, Jhajjar and Faridabad. The work on the project has already started and was scheduled to be completed by July 2013.[50]
The Delhi-Agra Expressway (NH-2) that passes through Faridabad is being widened to six lanes from current four lanes.[51] It will further boost Faridabad's connectivity with Delhi.
Sky Way
The Haryana and Delhi governments have constructed the 4.5-kilometre (2.8 mi) international standard Delhi Faridabad Skyway, the first of its kind in North India, to connect Delhi and Faridabad.[52]
Demographics
According to the 2011 census, Hindus (87.46%) constitute the majority of the state's population with Sikhs (4.91%), Muslims (7.03%) (mainly Meos) being the largest minorities.[53]
Muslims are mainly found in the Mewat and Yamuna Nagar districts, while Sikhs live mostly in the districts adjoining Punjab, Hisar, Sirsa, Jind, Fatehabad, Kaithal, Kurukshetra, Ambala, Narnaul and Panchkula karnal. Haryana has the second largest Sikh population in India after the state of Punjab. In May 2014, the Haryana Government published the Haryana Anand Marriages Registration Rules, 2014, allowing Sikhs to register their marriages under these rules.[54]
Agriculture and related industries have been the backbone of the local economy. Since 2001, the state has witnessed a massive influx of immigrants from across the nation, primarily from Bihar, Bengal, Uttrakhand, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and from the country, Nepal.Scheduled Castes form 19.3% of the population.[55]
Hindi is the sole official language of Haryana and is spoken by the majority of the population (87.31%).[2] Punjabi is given the status of additional official language. Haryana comprises second largest Punjabi speaking population in India.[3][56]
Education

Literacy rate in Haryana has seen an upward trend and is 76.64 percent as per 2011 population census. Male literacy stands at 85.38 percent, while female literacy is at 66.67 percent. In 2001, the literacy rate in Haryana stood at 67.91 percent of which male and female were 78.49 percent and 55.73 percent literate respectively.[57] As of 2013, Gurgaon city had the highest literacy rate in Haryana at 86.30% followed by Panchkula at 81.9 per cent and Ambala at 81.7 percent.[58] In terms of districts, as of 2012 Rewari had the highest literacy rate in Haryana at 74%, higher than the national average of 59.5%: male literacy was 79%, and female 67%.[59]
Hisar has three universities: Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University - Asia's largest agricultural university,[60] Guru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology, Lala Lajpat Rai University of Veterinary & Animal Sciences); several national agricultural and veterinary research centres (National Research Centre on Equines),[61] Central Sheep Breeding Farm,[62] National Institute on Pig Breeding and Research,[63] Northern Region Farm Machinery Training and Testing Institute[64] and Central Institute for Research on Buffaloes (CIRB);[65] and more than 20 colleges including Maharaja Agrasen Medical College, Agroha.[66]
In 2001–02, there were 11,013 primary schools, 1,918 middle schools, 3,023 high schools and 1,301 senior secondary schools in the state.[67] Haryana Board of School Education, established in September 1969 and shifted to Bhiwani in 1981, conducts public examinations at middle, matriculation, and senior secondary levels twice a year. Over seven lac candidates attend annual examinations in February and March; 150,000 attend supplementary examinations each November. The Board also conducts examinations for Haryana Open School at senior and senior secondary levels twice a year.[68] The Haryana government provides free education to women up to the bachelor's degree level.
Union Minister Ravi Shankar Prasad announced on 27 February 2016 that National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology (NIELIT) would be set up in Kurukshetra to provide computer training to youth and a Software Technology Park of India (STPI) would be set up in Panchkula’s existing HSIIDC IT Park in Sector 23.[69] Hindi and English are compulsory languages in schools whereas Punjabi, Sanskrit and Urdu are chosen as optional languages.[70]
Healthcare
The Total Fertility Rate of Haryana is 2.3. The Infant Mortality Rate is 41 (SRS 2013) and Maternal Mortality Ratio is 146 (SRS 2010–2012).[71]
Communication and media
Haryana has a statewide network of telecommunication facilities. Haryana Government has its own statewide area network by which all government offices of 22 districts and 126 blocks across the state are connected with each other thus making it the first SWAN of the country.[73][74][75] Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited and most of the leading private sector players (such as Reliance Infocom, Tata Teleservices, Bharti Telecom, Idea Vodafone Essar, Aircel, Uninor and Videocon) have operations in the state. Important areas around Delhi are an integral part of the local Delhi Mobile Telecommunication System. This network system would easily cover major towns like Faridabad and Gurgaon.
Electronic media channels include, MTV, 9XM, Star Group, SET Max, News Time, NDTV 24x7 and Zee Group. The radio stations include All India Radio and other FM stations.
The major newspapers of Haryana include Dainik Bhaskar, Punjab Kesari, Jag Bani, Dainik Jagran, The Tribune, Amar Ujala, Hindustan Times, Dainik Tribune, The Times of India and Hari-Bhumi.
Utilities
Haryana State has always given high priority to the expansion of electricity infrastructure, as it is one of the most important inputs for the development of the state. Haryana was the first state in the country to achieve 100% rural electrification in 1970 as well as the first in the country to link all villages with all-weather roads and provide safe drinking water facilities throughout the state.[76]
Power in the state are:
- Coal-fired power stations
- Nuclear-powered power stations
- Gorakhpur Nuclear Power Plant in Fatehabad district
- Solar-powered power Stations
- Faridabad Solar Power Station: The Haryana Power Generation Corporation Ltd (HPGCL) is setting up a solar power plant at the site of a defunct thermal power plant in Faridabad. The power generator plans to set up the plant over 151.78 acres near Bata Chowk in the district that generated coal-based energy in the past.[77]
Sports


Haryana has produced some of the best Indian players in a variety of sports. The State has an old wrestling tradition, and thus some of the finest wrestlers of India hail from Haryana. These include Mahavir Singh Phogat, Mahender singh khatri, Sushil Kumar, Yogeshwar Dutt, Sakshi Malik, Vinesh Phogat, Geeta Phogat and Babita Kumari. The non-descript town of Bhiwani in the middle of Haryana has produced several of India's best boxers, such as Kavita Chahal, Vijender Singh, Jitender Kumar, Akhil Kumar and Vikas Krishan Yadav.
In the 2010 Commonwealth Games at Delhi, 22 out of 38 gold medals that India won came from Haryana.[78] During the 33rd National Games held in Assam in 2007, Haryana stood first in the nation[79] with a medal tally of 80, including 30 gold, 22 silver and 28 bronze medals.
Cricket is very popular in Haryana. The 1983 World-Cup-winning captain Kapil Dev is from Haryana. Other notable players from Haryana cricket team include Chetan Sharma, Ajay Jadeja, Amit Mishra, Aashish Nehra and Mohit Sharma and Virender Sehwag. Nahar Singh Stadium was built in Faridabad in the year 1981 for international cricket. This ground has the capacity to hold around 25,000 people as spectators.[80] Tejli Sports Complex is an Ultra-Modern sports complex in Yamuna Nagar. Tau Devi Lal Stadium in Gurgaon is a multi-sport complex.[81]
Chief Minister of Haryana Manohar Lal Khattar announced the "Haryana Sports and Physical Fitness Policy", a policy to support 26 Olympic sports, on 12 January 2015 with the words "We will develop Haryana as the sports hub of the country."[82][83]
Haryana is home to Haryana Gold, one of India's eight professional basketball teams which compete in the country's UBA Pro Basketball League.
Tourism
There are 21 tourism hubs created by Haryana Tourism Corporation Limited, which are located in Ambala, Bhiwani, Faridabad, Fatehabad, Gurgaon, Hisar, Jhajjar, Jind, Kaithal, Karnal, Kurukshetra, Panchkula, Sirsa, Sonipat, Panipat, Rewari, Rohtak, Yamunanagar, Pinjore.Morni Hills, Palwal and Mahendergarh.[84]
See also
- List of Monuments of National Importance in Haryana
- List of State Protected Monuments in Haryana
- Outline of Haryana
- Politics of Haryana
Notes
- 1 2 "Haryana at a Glance". Government of Haryana. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 "Report of the Commissioner for linguistic minorities: 50th report (July 2012 to June 2013)" (PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. Retrieved 4 December 2016.
- 1 2 "Haryana grants second language status to Punjabi". Hindustan Times. 28 January 2010.
- ↑ "This is NCR's new foodie magnet; have you been yet?". India Today. 26 March 2017.
- ↑ http://pib.nic.in/archieve/others/2014/aug/d2014070801.pdf
- ↑ Anand Giridharadas (19 October 2005). "Poor rural India? It's a richer place". International Herald Tribune. Archived from the original on 19 September 2008.
- ↑ Byres, T.J. Rural labour relations in India. Taylor & Francis, 1999. ISBN 978-0-7146-8046-0.
- ↑ "Haryana Hurricane". indianexpress.com.
- ↑ An Early Attestation of the Toponym Ḍhillī, by Richard J. Cohen, Journal of the American Oriental Society, 1989, pp. 513–519
- हरियाणए देसे असंखगाम, गामियण जणि अणवरथ काम|
- परचक्क विहट्टणु सिरिसंघट्टणु, जो सुरव इणा परिगणियं|
- रिउ रुहिरावट्टणु बिउलु पवट्टणु, ढिल्ली नामेण जि भणियं|
- Translation: there are countless villages in Haryana country. The villagers there work hard. They don't accept domination of others, and are experts in making the blood of their enemies flow. Indra himself praises this country. The capital of this country is Dhilli.
- ↑ Haryana Britannica Online Encyclopedia
- ↑ Bijender K Punia (1993). Tourism management: problems and prospects. APH. p. 18. ISBN 978-81-7024-643-5.
- ↑ "The Tribune, Chandigarh, India - Haryana Plus". www.tribuneindia.com. Retrieved 4 August 2016.
- ↑ "Underworld Review - Graham Hancock Official Website". Retrieved 13 August 2016.
- ↑ Rakhigarhi, the biggest Harappan site, The Hindu, 27 March 2014
- ↑ Atul Kumar Sinha & Abhay Kumar Singh 2007, p. 401.
- ↑ Elliot, Sir Henry Miers; Dowson, John (1871). The History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians. The Muhammadan Period: Ed. from the Posthumous Papers of the Late Sir H. M. Elliot ... Trübner and Company. pp. en.
- ↑ Phadke, H.A. (1990). Haryana, Ancient and Medieval. Harman Publishing House. p. 123.
- ↑ Arnold P. Kaminsky; Roger D. Long (2011). India Today: An Encyclopedia of Life in the Republic. ABC-CLIO. p. 300. ISBN 978-0-313-37462-3.
- ↑ the punjab reorganisation act, 1966 - Chief Secretary, Haryana (PDF)
- ↑ History of Haryana - Haryana Day: A new state is born!, archived from the original on 2 October 2013
- ↑ Haryana will get Chandigarh, Punjab can claim Lahore or Shimla, says a peeved Hooda, 25 July 2013
- ↑ List of Haryana Chief Ministers from November 1, 1966 till date, The Indian Express, 21 October 2014
- ↑ NIDM, p. 2.
- 1 2 3 Home, Department of Agriculture (Haryana)
- ↑ Organizations
- ↑ Welcome To Our Website, Haryana Forest Department
- 1 2 NIDM, p. 3.
- ↑ "River Saraswati is for real, found in Haryana", Zee Nees, 8 May 2015
- 1 2 Geography- others, District Administration, Kurukshetra
- 1 2 "Geography of Haryana - Map, Shivaliks, Ghaggar, Yamuna, Saraswati, Morni - India". haryana-online.com. Archived from the original on 1 February 2016.
- ↑ Siwach, Sukhbir (7 December 2014), "Haryana to meet Rajasthan over stopping of river waters", Times of India
- ↑ Sudhir Bhargava,"Location of Brahmavarta and Drishadwati River is important to find earliest alignment of Saraswati River", International Conference, 20–22 Nov. 2009, "Saraswati-a perspective" pages 114–117, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra, Organised by: Saraswati Nadi Shodh Sansthan, Haryana.
- 1 2 3 "State animals, birds, trees and flowers" (PDF). Wildlife Institute of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 June 2007. Retrieved 5 March 2012.
- ↑ Flora and Fauna
- ↑ Conservation of Wildlife
- ↑ Fauna of Haryana, archived from the original on 2 December 2015
- ↑ Parks, Reserves and Other Protected Areas in Haryana
- ↑ "Protected Area". haryanaforest.gov.in. Retrieved 4 August 2016.
- ↑ NIDM, p. 4.
- 1 2 3 "Digital India campaign: Panchkula comes out on top among all districts of Haryana". The Indian Express. 26 December 2015.
- ↑ "Haryana Police", Haryana Police
- ↑ "HC starts e-filing, gets Wi-Fi complex", The Tribune, Chandigarh, Tribune News Service, 1 December 2014
- ↑ http://agriharyana.nic.in/AMapRabi.htm
- ↑ http://agriharyana.nic.in/AMapKharif.htm
- ↑ "The Tribune, Chandigarh, India - Delhi and neighbourhood". tribuneindia.com.
- ↑ "Haryana culture". Indian mirror.
- ↑ "Savitri Jindal and family". Forbes. Retrieved 13 July 2012.
- ↑ "NCR's longest Metro line in Faridabad | delhi". Hindustan Times. 2012-01-23. Retrieved 2015-11-03.
- ↑ Why Haryana? - Economic Infrastructure
- ↑ "KMP Expressways to be completed by 2009". indianexpress.com.
- ↑ "NH-2 widening to claim 25,000 trees in Faridabad dist | india". Hindustan Times. 2012-06-06. Retrieved 2015-11-03.
- ↑ "Projects - Delhi - Faridabad Elevated Expressway Project (dfskyway TM) (NH - 2)". HCC Infrastructure. 2010-11-29. Retrieved 2015-11-03.
- 1 2 "Population by religion community - 2011". Census of India, 2011. The Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Archived from the original on 25 August 2015.
- ↑ "Haryana government announced the formation of rules to register Anand Karaj, the Sikh marriage ceremony".
- ↑ Govt. of India, Census (2001). "Census India 2001" (PDF). Retrieved March 28, 2013.
- ↑ "Punjabi gets second language status in Haryana". Zee news. 28 January 2010.
- ↑ Census 2011, Chapter 6 (State of Literacy) (PDF), pp. 114–117
- ↑ In Haryana, Gurgaon tops literacy rate but has worst sex ratio, Indian Express, 2013-05-23, retrieved 2015-11-03
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 May 2014. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
- ↑ "About HAU". Haryana Agricultural University. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Vision 2030" (PDF). National Research Centre on Equines. Retrieved 7 June 2012.
- ↑ "Central sheep breeding farm". Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying & Fisheries, GoI. Archived from the original on 22 November 2012. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Climate of Hisar". PPU. Archived from the original on 5 May 2012. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "About us". Northern Region Farm Machinery Training and Testing Institute. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "About CIRB". Central Institute for Research on Buffaloes. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Official website". Maharaja Agrasen Medical College. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ↑ "Education in Haryana - Universities - Colleges - Schools - Institutions - Engineering - Medical". haryana-online.com. Archived from the original on 1 February 2016.
- ↑ History, Haryana Board of School Education
- ↑ "Under the Digital India initiative: Software Technology Park of India", The Indian Express, 28 February 2016
- ↑ [nclm.nic.in/shared/linkimages/NCLM47thReport.pdf National Committee for Linguistic Minorities]
- ↑ State Wise Information, National Rural Health Mission
- ↑ Health Department of Haryana
- ↑ Egovonline.net Archived 30 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Punjabnewsline.com Archived 1 January 2008 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "The Tribune India". The Tribune. Retrieved 2008-02-06.
- ↑ General Information
- ↑ "Haryana aims to install solar plants to replace old thermal plants", The Economic Times, 15 March 2016
- ↑ Mizoramexpress.com Archived 26 November 2010 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Official site for the 33rd National Games 2007, Guwahati
- ↑ "Nahar Singh Stadium - India - Cricket Grounds - ESPN Cricinfo". Cricinfo.
- ↑ "Tau Devi Lal Cricket Stadium - India - Cricket Grounds - ESPN Cricinfo". Cricinfo.
- ↑ News Details, Office of Chief Minister of Haryana
- ↑ GoH 2015, p. 27.
- ↑ Tourism Hubs in Haryana, Haryana Tourism
References
- GoH (12 January 2015), Haryana Sports and Physical Fitness Policy (PDF), Government of Haryana
- Atul Kumar Sinha; Abhay Kumar Singh, eds. (2007), Udayana New Horizons in History, Classics and Inter-Cultural studies, Anamika Publishers, ISBN 81-7975-168-6
- NIDM, National Disaster Risk Reduction Portal - Haryana (PDF), National Institute of Disaster Management (MHA, GOI)
- Sharma, Suresh K (2006). Haryana: Past and Present. New Delhi: Mittal Publications. p. 763. ISBN 81-8324-046-1. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Khanna, C. L. (2008). Haryana General Knowledge. Agra: Upkar Prakashan. p. 75. ISBN 81-7482-383-2. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Yadav, Ram B. (2008). Folk Tales & Legends of Haryana. Gurgaon: Pinnacle Technology. p. 305. ISBN 81-7871-162-1. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Mittal, Satish Chandra (1986). Haryana, a Historical Perspective. New Delhi: Atlantic Publishers & Distributors. p. 183. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Singh, Mandeep; Kaur, Harvinder (2004). Economic Development Of Haryana. New Delhi: Deep and Deep Publications. p. 234. ISBN 81-7629-558-2. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Gandhi, Mahatma (1977). Gandhiji and Haryana: A collection of his speeches and writings pertaining to Haryana. Usha Publications. p. 158. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Phadke, H. A. (1990). Haryana, ancient and medieval. Harman Publishing House. p. 256. ISBN 81-85151-34-2. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Singh, Chattar (2004). Social and economic change in Haryana. National Book Organisation. p. 252. ISBN 81-87521-10-4. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Yadav, Kripal Chandra (2002). Modern Haryana: History and culture, 1803–1966. Manohar Publishers & Distributors. p. 320. ISBN 81-7304-371-X. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Rai, Gulshan (1987). Formation of Haryana. B.R. Publishing Corporation. p. 223. ISBN 81-7018-412-6. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Handa, Devendra (2004). Buddhist remains from Haryana. Sundeep Prakashan. p. 97. ISBN 81-7574-153-8. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Haryana at a glance: Statistical overview & development indicators. Jagran Research Centre. 2007. p. 157. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Singh, Chander Pal (2003). Early medieval art of Haryana. Koshal Book Depot. p. 168. ISBN 81-86049-07-X. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Handa, Devendra (2006). Sculptures from Haryana: Iconography and style. Indian Institute of Advanced Study. p. 286. ISBN 81-7305-307-3. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Journal of Haryana Studies. Kurukshetra: Kurukshetra University. 2008. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
- Harvey, Bill; Harvey, William; Devasar, Nikhil; Grewal, Bikram; Oriental Bird Club (2006). Atlas of the birds of Delhi and Haryana. Rupa & Co. p. 352. ISBN 81-291-0954-9. Retrieved July 11, 2012.
External links
- Government
- General information
- Haryana Encyclopædia Britannica entry
- Haryana at DMOZ
-
 Geographic data related to Haryana at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Haryana at OpenStreetMap

