Hamburg Stadtpark
| Hamburg Stadtpark | |
|---|---|
|
View of the Stadtpark from atop of Hamburg Planetarium | |
| Type | Public park |
| Location |
Saarlandstraße 1 22303 Hamburg, Germany |
| Coordinates | 53°35′55″N 10°01′27″E / 53.598745°N 10.02403°ECoordinates: 53°35′55″N 10°01′27″E / 53.598745°N 10.02403°E |
| Area | 148 ha (1.48 km2) |
| Opened | 1914 |
| Managed by | BSU |
| Open | All year |
| Public transit access |
|
| Website | www.hamburg.de |
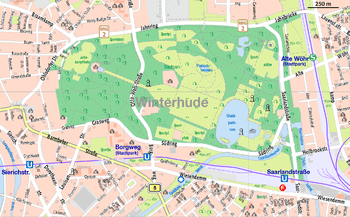
Hamburg Stadtpark is a 148 hectares (366 acres) large urban park in the Hamburg district of Winterhude, in the borough of Hamburg-Nord. Alongside Altona Volkspark, it is the largest park in the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg, Germany. The Stadtpark is regarded as the "green heart" of the city, despite being located some 3km from the inner city. The largest parks in the city center are Planten un Blomen and the Alsterpark.
Opened in 1914, Hamburg Stadtpark is an important example of German landscape design and the transformation from an urban garden to an urban park.
History
Like many cities during the Age of Industrialization, Hamburg grew substantially in the later decades of the 19th century and many former open spaces had been built over. In order to counterbalance this development, in 1901 the Senate of Hamburg and Hamburg Parliament agreed to purchase the so-called Sierich Grove (Sierichsches Gehölz), and to develop an urban park. In 1908 a public design competition was hosted, however no consensus could be reached. In January 1909, head engineer Fritz Sperber presented two designs - based on the results of the competition - on behalf of the senate, one landcaped and painterly, the other geometric. In June 1909, Fritz Schumacher was made director of the city's Department of Planning and Building Inspection, and in January 1910 he and Fritz Sperber presented a design to the Parliament which was subsequently approved. The park was opened four years later, though it would be another 14 years before it was finally completed. After 1918, the gardening and landscaping work was principally carried out by Otto Linne, the first horticultural director of Hamburg.
During the bombing of Hamburg in World War II, a couple of buildings within the park were destroyed, and not rebuilt after the war. Need for additional office space in the 1960s led to the development of City Nord,[1] a decentralized commercial district located to the north-east of Hamburg Stadtpark.
Overview
.Blick_vom_Planetarium.240mm.30809.ajb.jpg)
The park's most famous landmark is the Hamburg Planetarium, a former water tower. At night, the tower is illuminated in various colours. The 64 metre tall brick tower was designed by Oskar Menzel and built in 1914. Since 1930 it has housed Germany's largest planetarium. The tower is located in the western half of the park and can be reached via a 500 metre long avenue on its eastern side. This avenue leads onto the Great Meadow (Festwiese), which borders onto the artificial Stadtpark Lake (Stadtparksee).
Midway, the park is crossed by a street. Most of the parks's western half and the park's edges are made up of wild woods. Around the edge of the park there are also a number of sporting grounds and sporting halls, an outdoor lido and an athletics stadium. Dozens of playgrounds and sport facilities are spread throughout the park.[2] The home stadium of Hamburg Rugby Club is at Saarlandstraße in the north-east of the park. In the very north-eastern corner lies the Freilichtbühne, an open air stage for music concerts.
The lake is connected to Hamburg's extensive network of waterways via the Goldbekkanal. Alster ferries run services between the Stadtpark and Jungfernstieg in the inner city.[3]
Every year in September, a vintage car race takes place at Hamburg Stadtpark (Stadtpark-Revival).
 Planetarium
Planetarium Lake
Lake Pathway
Pathway Pathway and meadows
Pathway and meadows Planetarium
Planetarium
Public art
22 privately sponsored pieces of mostly stone and bronze public art are displayed throughout Hamburg Stadtpark.[4] Here are some of them:
 Diana with dogs (1911) by Oscar Troplowitz
Diana with dogs (1911) by Oscar Troplowitz Diana on a doe (1910) by Georg Wrba
Diana on a doe (1910) by Georg Wrba Bathing Women (1926) by Reinhold Begas
Bathing Women (1926) by Reinhold Begas Boy with fishes (1925) by Oscar E. Ulmer
Boy with fishes (1925) by Oscar E. Ulmer.jpg) Gargoyle (1930) by Richard Haizmann; original labelled degenerate art and destroyed by the Nazis, replica of 1994
Gargoyle (1930) by Richard Haizmann; original labelled degenerate art and destroyed by the Nazis, replica of 1994 Dancing Girls (1935) by Karl August Ohrt
Dancing Girls (1935) by Karl August Ohrt
References
- ↑ "City Nord". city-nord.eu. Retrieved 9 October 2014.
- ↑ "Wo finde ich was?". hamburger-stadtpark.de (in German). Retrieved 9 October 2014.
- ↑ "Alster Boat Trips" (PDF). alstertouristik.de. Alster-Touristik GmbH (ATG). Retrieved 9 October 2014.
- ↑ "Skulpturen im Hamburger Stadtpark". hamburg-stadtpark.de (in German). Retrieved 9 October 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hamburger Stadtpark. |
- Stadtparkverein Hamburg e.V. (friends' association) (in German)
.Blick_vom_Planetarium.18mm.30809.ajb.jpg)