Chidamide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Epidaza |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
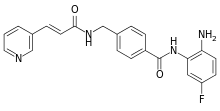
| Formula | C22H19FN4O2 |
| Molar mass | 390.4 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Chidamide (Epidaza) is an histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDI) developed wholly in China.[1] It was also known as HBI-8000.[2] It is a benzamide HDI and inhibits Class I HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, as well as Class IIb HDAC10.[3]
Chidamide is approved by the Chinese FDA for relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL), and has orphan drug status in Japan.[2] As of April 2015 it is only approved in China.[1]
Chidamide is being researched as a treatment for pancreatic cancer.[4][5][6] However, it is not FDA approved for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
References
- 1 2 "China's First Homegrown Pharma.". April 2015.
- 1 2
- ↑ HUYA Bioscience International Grants An Exclusive License For HBI-8000 In Japan And Other Asian Countries To Eisai. Feb 2016
- ↑ Qiao, Z (2013-04-26). "Chidamide, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, synergistically enhances gemcitabine cytotoxicity in pancreatic cancer cells.". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 434 (1): 95–101. PMID 23541946. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.03.059.
- ↑ Guha, Malini (2015-04-01). "HDAC inhibitors still need a home run, despite recent approval". Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 14: 225–226. PMID 25829268. doi:10.1038/nrd4583.
- ↑ Wang, Shirley S. (2015-04-02). "A New Cancer Drug, Made in China". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 13 April 2015.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.