Guifi.net
 | |
| Website |
Map of coverage: guifi |
|---|---|
| Primary ASN | 49835 |
|---|---|
| Peering policy | Open |

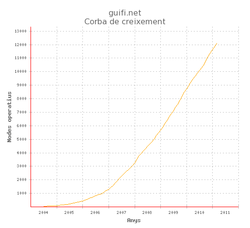
Guifi.net is a free, open and neutral, mostly wireless telecommunications community network, with over 33,000 active nodes and about 46,000 km of wireless links (as of April 2017).[1] The majority of these nodes are located in Catalonia and the Valencian Community, in Spain. but the network is growing in other parts of the world. The network is self-organized and operated by the users using unlicensed wireless links and open optical fibre links.
The nodes of the network are contributed by individuals, companies and administrations that freely connect to an open network of telecommunications and extend the network wherever the infrastructure and content might not otherwise be accessible. Nodes join the network following the self-provision model since the whole structure is explicitly open to facilitate understanding how it is structured, so that everyone can create new sections as required. That results in an network infrastructure commons that provides abundant connectivity.[2]
Guifi.net is supported by the Guifi.net Foundation, which has been registered as an operator with the Spanish Telecommunications Market Commission (CMT) since April 2009. In August 2009, the first deployment of optical fiber was started, known as the Fiber From The Farms (FFTF) Broadband Initiative,[3][4] covering about 2 km and linking dozens of farms and farmhouses in the town of Gurb.
Since early 2011, guifi.net is connected to the Catalonia Neutral Internet Exchange Point (CATNIX),[5][6] which exchanges data with other international telecommunications operators such as Cogent Communications and Hurricane Electric. This Internet connection is used by several associations that offer their members Internet access to low-cost at high speeds,[7] which other Internet service providers currently do not offer. The model is oriented to cost sharing, the compensation mechanism.[8]
The basic principle of operation are based on the Wireless Commons License.[9][10]
References
- ↑ "What is guifi.net?".
- ↑ Baig, Roger; Roca, Ramon; Freitag, Felix; Navarro, Leandro (2015-10-29). "guifi.net, a crowdsourced network infrastructure held in common" (PDF). Computer Networks. Crowdsourcing. 90: 150–165. doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2015.07.009.
- ↑ "Comunicaciones Electrónicas - CNMC - Comisión Nacional de los Mercados y la Competencia". Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ↑ "My big idea for the Digital Agenda". Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ↑ "RIS Tools and Web Interfaces". Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ↑ "guifi.net connects to CATNIX". Retrieved 26 November 2015.
- ↑ guifi.net + EXO
- ↑ Baig, Roger; Dalmau, Lluís; Roca, Ramon; Navarro, Leandro; Freitag, Felix; Sathiaseelan, Arjuna (2016-01-01). "Making Community Networks Economically Sustainable, the Guifi.Net Experience" (PDF). Proceedings of the 2016 Workshop on Global Access to the Internet for All. GAIA '16. New York, NY, USA: ACM: 31–36. ISBN 9781450344234.
- ↑ http://guifi.net/en/WCL_EN - The Wireless Commons License
- ↑ Oliver, M.; Zuidweg, J.; Batikas, M. (2010-06-01). "Wireless Commons against the digital divide". 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Technology and Society: 457–465. doi:10.1109/ISTAS.2010.5514608.
External links
- What is guifi.net?
- Services on guifi.net
- guifi.net Autonomous System Number
- guifi.net + EXO
- Official repository of guifi.net on Github
- guifi.net documentation wiki
- (in Catalan) Guifi.net presentation