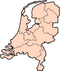
Groningen (province)
| Groningen | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Province of the Netherlands | |||
| |||
|
Anthem: "Grönnens Laid" | |||
 Location of Groningen in the Netherlands | |||
| Coordinates: 53°15′N 6°44′E / 53.250°N 6.733°ECoordinates: 53°15′N 6°44′E / 53.250°N 6.733°E | |||
| Country | Netherlands | ||
| Capital | Groningen | ||
| Government | |||
| • King's Commissioner | René Paas (CDA) | ||
| Area (2010)[1] | |||
| • Total | 2,960 km2 (1,140 sq mi) | ||
| • Land | 2,325 km2 (898 sq mi) | ||
| • Water | 635 km2 (245 sq mi) | ||
| Area rank | 7th nationally | ||
| Population (1 January 2014)[2] | |||
| • Total | 582,640 | ||
| • Rank | 9th nationally | ||
| • Density | 200/km2 (510/sq mi) | ||
| • Density rank | 8th nationally | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| ISO 3166 code | NL-GR | ||
| Website |
www | ||
Groningen (Dutch pronunciation: [ˈɣroːnɪŋə(n)]; Gronings: Grönnen or Grunn; West Frisian: Grinslân) is the northeasternmost province of the Netherlands. It borders on Friesland to the west, Drenthe to the south, the German state of Niedersachsen (districts of Leer and Emsland) to the east, and the Wadden Sea to the north. In 2014, it had a population of 582,640 and a total area of 2,960 km2 (1,140 sq mi).
The area was subsequently part of Frisia, the Frankish Empire, the Holy Roman Empire, and the Dutch Republic, which is the precursor state of the Netherlands. In the 14th century, the city of Groningen became a member of the Hanseatic League.
The capital of the province and the seat of the provincial government is the city of Groningen. Since 2016, René Paas has been the King's Commissioner in the province. A coalition of the Labour Party, People's Party for Freedom and Democracy, Democrats 66, and ChristianUnion forms the executive branch. The province is divided into 23 municipalities.
The land is mainly used for agriculture. There are sea ports in Delfzijl and Eemshaven. The Groningen gas field was discovered in 1959. The province is home to the University of Groningen and Hanze University of Applied Sciences.
History
_-_Haubois%2C_1652.jpg)

Groningen was originally a part of Frisia. It became a part of the Frankish Empire around 785. Charlemagne assigned the Christianization of this new possession to Ludger.
In the 11th century, the city of Groningen was a village in Drenthe that belonged to the Bishopric of Utrecht, while most of the province was in the Prince-Bishopric of Münster.
During the Middle Ages, central control was remote, and the city of Groningen acted as a city-state, exerting a dominating influence on the surrounding Ommelanden. In the 14th century, Groningen became one of the towns within the Hanseatic League.[3] In the years after, Groningen expanded its influence. At its peak almost all of the current province Friesland was under the influence and control of Groningen.
Shortly before 1498, Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor gave Groningen and Friesland to Albert III, Duke of Saxony, who could however not establish permanent control. In 1514/15 Groningen came to the Duchy of Guelders, and in 1536 as the Lordship of Groningen to the Habsburg Netherlands.
In 1594, Groningen was conquered by the Republic of the Seven United Provinces, precursor state of the Netherlands, to which it belonged henceforth.
During World War II, the Netherlands were occupied by Nazi Germany. In April 1945, the 2nd Canadian Division fought in the Battle of Groningen, which resulted in the liberation of the city and in the death of 130, the capture of 5,212, and the fleeing of 2,000 German soldiers. In May 1945, another 3,000 German soldiers were captured in the Battle of Delfzijl by the 5th Canadian Division, after which all of the northern provinces were liberated.[4]
East Groningen was the scene of a particularly fierce class struggle in the 19th and 20th centuries. Perhaps not coincidentally, Groningen boasts the only municipality (Beerta) where the Communist Party of the Netherlands has ever had a mayor (Hanneke Jagersma).[5]
Geography





Groningen is situated at 53°15′N 6°44′E / 53.250°N 6.733°E in the northeast of the Netherlands with to the west the province Friesland, to the south the province Drenthe, to the east the German districts Leer and Emsland in the state Lower Saxony, and to the north the North Sea, Ems, and Dollart. The northernmost point of the Netherlands is on Rottumerplaat[6] at 53°33′18″N 6°28′41″E / 53.55500°N 6.47806°E and the easternmost point of the Netherlands is in Bad Nieuweschans[6] at 53°10′49″N 7°13′40″E / 53.18028°N 7.22778°E.
Groningen is the 7th largest province of the Netherlands. It has a total area of 2,960 km2 (1,140 sq mi), with 2,325 km2 (898 sq mi) of land and 635 km2 (245 sq mi) of water. About 80% of the land or 1,876 km2 (724 sq mi) is used for agriculture. The rest of the land is: 9% or 158 km2 (61 sq mi) of built-up or semi built-up area, 6% or 144 km2 (56 sq mi) of nature, 3% or 66 km2 (25 sq mi) of infrastructure, and 2% or 43 km2 (17 sq mi) of recreational area.[1]
The land in Groningen is flat. A large area of the province is below sea level.[7] The Hasseberg near Sellingen of 14.6 m (48 ft) above sea level is the highest point.[8]
The Groningen gas field near Slochteren is the 8th largest[9] natural gas field in the world. Since 1986, the exploitation of this gas field has caused earthquakes in the region with magnitudes up to 3.6.[10]
In the Wadden Sea of Groningen, a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2009,[11] are the sandbank Simonszand and the natural reserve Rottum consisting of the three uninhabited islands Rottumeroog, Rottumerplaat, and Zuiderduintjes. The national park Lauwersmeer (IUCN category II) is located on the border between Groningen and Friesland.
Subdivisions
The province of Groningen is also called Stad en Ommelanden, which means the city of Groningen and its surrounding lands, which are the historical regions of Fivelingo, Hunsingo, Oldambt, Westerkwartier, and Westerwolde.[12]
The province (Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics or NUTS level 2) is divided into three COROP regions (NUTS level 3): East Groningen, Delfzijl and surroundings, and the rest of Groningen. The COROP regions are used for statistical purposes.[13]
The province is also divided into 23 municipalities with each their own local government. There are plans to merge these municipalities into six new municipalities in 2018.[14][15] Currently, Groningen is the most populated and most densely populated municipality,[16][17] containing the largest city, and Eemsmond is the largest municipality, containing a large part of the Wadden Sea in the province.[17] Ten Boer is the least populated, De Marne is the least densely populated, and Appingedam is the smallest municipality.[16][17]
The nine municipalities Bedum, Groningen, Haren, Hoogezand-Sappemeer, Leek, Slochteren, Ten Boer, Winsum, and Zuidhorn are part of the interprovincial Groningen-Assen Region[18] and the seventeen municipalities Appingedam, Bellingwedde, Delfzijl, Eemsmond, Groningen, Grootegast, Haren, Hoogezand-Sappemeer, Leek, Menterwolde, Oldambt, Pekela, Slochteren, Stadskanaal, Veendam, Vlagtwedde, and Zuidhorn are part of the international Ems Dollart Region (EDR).[19]
| Municipality | Population[16] | Total Area[17] | Population density[16][17] | COROP Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appingedam | 12004 | 24.58 km2 (9.49 sq mi) | 505/km2 (1,310/sq mi) | Delfzijl and surroundings |
| Bedum | 10459 | 44.96 km2 (17.36 sq mi) | 235/km2 (610/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
| Bellingwedde | 9039 | 110.08 km2 (42.50 sq mi) | 83/km2 (210/sq mi) | East Groningen |
| Boer, TenTen Boer | 7447 | 45.73 km2 (17.66 sq mi) | 164/km2 (420/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
| Delfzijl | 25651 | 227.50 km2 (87.84 sq mi) | 193/km2 (500/sq mi) | Delfzijl and surroundings |
| Eemsmond | 15864 | 543.35 km2 (209.79 sq mi) | 84/km2 (220/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
| Groningen | 197823 | 83.75 km2 (32.34 sq mi) | 2,535/km2 (6,570/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
| Grootegast | 12181 | 87.74 km2 (33.88 sq mi) | 140/km2 (360/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
| Haren | 18832 | 50.73 km2 (19.59 sq mi) | 413/km2 (1,070/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
| Hoogezand-Sappemeer | 34326 | 72.99 km2 (28.18 sq mi) | 515/km2 (1,330/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
| Leek | 19626 | 64.28 km2 (24.82 sq mi) | 310/km2 (800/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
| Loppersum | 10174 | 111.99 km2 (43.24 sq mi) | 92/km2 (240/sq mi) | Delfzijl and surroundings |
| Marne, DeDe Marne | 10208 | 240.33 km2 (92.79 sq mi) | 61/km2 (160/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
| Marum | 10343 | 64.89 km2 (25.05 sq mi) | 160/km2 (410/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
| Menterwolde | 12233 | 81.62 km2 (31.51 sq mi) | 152/km2 (390/sq mi) | East Groningen |
| Oldambt | 38495 | 295.96 km2 (114.27 sq mi) | 169/km2 (440/sq mi) | East Groningen |
| Pekela | 12709 | 50.20 km2 (19.38 sq mi) | 259/km2 (670/sq mi) | East Groningen |
| Slochteren | 15546 | 158.87 km2 (61.34 sq mi) | 103/km2 (270/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
| Stadskanaal | 32715 | 119.94 km2 (46.31 sq mi) | 278/km2 (720/sq mi) | East Groningen |
| Veendam | 27752 | 78.68 km2 (30.38 sq mi) | 365/km2 (950/sq mi) | East Groningen |
| Vlagtwedde | 15878 | 170.55 km2 (65.85 sq mi) | 95/km2 (250/sq mi) | East Groningen |
| Winsum | 13781 | 102.53 km2 (39.59 sq mi) | 136/km2 (350/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
| Zuidhorn | 18756 | 128.37 km2 (49.56 sq mi) | 149/km2 (390/sq mi) | Rest of Groningen |
Climate
The province of Groningen has an oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification: Cfb).
| Climate data for Nieuw-Beerta (1981–2010 averages) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 4.7 (40.5) |
5.6 (42.1) |
9.2 (48.6) |
13.9 (57) |
17.3 (63.1) |
20.0 (68) |
22.7 (72.9) |
22.7 (72.9) |
18.8 (65.8) |
13.6 (56.5) |
8.5 (47.3) |
4.7 (40.5) |
13.5 (56.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.3 (36.1) |
2.7 (36.9) |
5.3 (41.5) |
8.7 (47.7) |
12.2 (54) |
14.9 (58.8) |
17.4 (63.3) |
17.4 (63.3) |
14.2 (57.6) |
9.8 (49.6) |
6.0 (42.8) |
2.4 (36.3) |
9.5 (49.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −0.2 (31.6) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
1.4 (34.5) |
3.5 (38.3) |
6.9 (44.4) |
9.4 (48.9) |
12.1 (53.8) |
12.1 (53.8) |
9.9 (49.8) |
6.3 (43.3) |
3.3 (37.9) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
5.4 (41.7) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 90 | 89 | 85 | 80 | 80 | 82 | 82 | 81 | 85 | 88 | 92 | 92 | 86 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | N/A | N/A | 134.3 | 187.2 | 222.4 | 208.4 | 215.8 | 189.9 | 149.3 | 120.1 | 60.3 | 59.6 | N/A |
| Percent possible sunshine | N/A | N/A | 36 | 45 | 45 | 41 | 42 | 42 | 39 | 37 | 23 | 25 | N/A |
| Source: Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute[20] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1899 | 299,602 | — |
| 1930 | 392,436 | +0.87% |
| 1960 | 474,657 | +0.64% |
| 1965 | 497,472 | +0.94% |
| 1970 | 517,305 | +0.78% |
| 1975 | 536,106 | +0.72% |
| 1980 | 553,709 | +0.65% |
| 1985 | 561,119 | +0.27% |
| 1990 | 553,862 | −0.26% |
| 1995 | 557,995 | +0.15% |
| 2000 | 562,646 | +0.17% |
| 2005 | 575,072 | +0.44% |
| 2010 | 576,668 | +0.06% |
| 2015 | 582,649 | +0.21% |
| Source: CBS[21][22][23] | ||
On 1 January 2014, the province of Groningen had a population of 582,640 and a population density of 196.8/km2 (510/sq mi), which make it the 9th most populous province and 8th most densely populated province of the Netherlands.[1][2] The city of Groningen is the most populous city in the province and the 7th most populous city in the Netherlands.
On 1 January 2013, 92.2% of the total provincial population was born in the Netherlands; and of the 7.8% that was born abroad, the ten most common foreign countries of origin are the neighbour Germany (1.09%), the former colonies and dependencies Indonesia (0.60%), Netherlands Antilles and Aruba (0.55%), Suriname (0.54%), and other countries Turkey (0.41%), Soviet Union (0.36%), China (0.32%), Poland (0,26%), Yugoslavia (0.26%), and United Kingdom (0.18%).[24]
In 1999, a 59% majority of the population of Groningen was not affiliated with any religion; 29% was Protestant (15% Reformed and 14% Dutch Reformed; since 2004 united in Protestant Church in the Netherlands), 7% was Roman Catholic (Diocese of Groningen-Leeuwarden), and 6% had another religion.[25]
Economy


The city of Groningen is the economic center of the province.[26] In the 14th century, the city became a member of the Hanseatic League.[3] Currently some of the city's major employers[26] are University Medical Center Groningen with 12,141 employees,[27] University of Groningen with 5,591 employees,[28] Municipality of Groningen with 3,063 employees,[29] Education Implementation Service (DUO) with 2,000 employees,[30] and Gasunie with 1,748 employees.[31]
The other economically important area is the Ems delta with the sea ports of Delfzijl and Eemshaven.[26][32] In 2015, a total of 11,589 cargo vessels arrived at the two Groningen Seaports combined, 7,111 sea vessels and 4,478 inland vessels. The ports had a cargo throughput of 11,309,000 tonnes.[33] The chemical industry near Delfzijl is located at the Chemie Park in Farmsum, with factories of AkzoNobel, Lubrizol, and Teijin Aramid.[34] Both GDF Suez[35] and Nuon Energy[36] have a natural gas-fired power plant in Eemshaven, and Essent[37] is building a coal-fired power plant there.
In 1959, the Groningen gas field near Slochteren was discovered,[38] and the NAM started to exploit the field in 1963.[10] This caused Dutch disease and induced earthquakes.
In 2013, Groningen had a labor force of 268 thousand people and unemployment rate of 9.6%, which is the second highest unemployment for a province in the Netherlands.[39]
Culture
Language
Groningen is home to the Low Saxon dialect called Gronings (Grönnegs / Grunnegs in Gronings regional language), In the eastern part of Friesland variations of the Groninger 'language' is spoken. Gronings has local nuances, for example, the people in the eastern part speak Gronings with more German influence. Nowadays, many inhabitants of the province don't speak the dialect, especially in the city of Groningen where many outsiders have moved.
Cuisine
Traditional dishes and delicacies from Groningen are boerenkoolstamppot, droge worst, krentjebrij, oudewijvenkoek, poffert, and spekdik. Traditional alcoholic drinks are boerenjongens, boerenmeisjes, fladderak, and heet bier.
Museums

Museumhuis Groningen is an umbrella organization for museums and other heritage organizations in the province of Groningen and has 58 members.[40][41] The Groninger Museum is the most visited museum in the province with 209,195 visitors in 2015. The other museums and heritage organizations with more than 25 thousand visitors in 2015 are Fort Bourtange in Bourtange, Noordelijk Scheepvaartmuseum in Groningen, Ter Apel Monastery in Ter Apel, Fraeylemaborg in Slochteren, Nationaal Bus Museum in Hoogezand, and Museumspoorlijn STAR in Stadskanaal.[42]
Heritage sites
- Martinitoren, icon of the provincial capital of Groningen
 Der Aa-kerk in Groningen
Der Aa-kerk in Groningen
 Hanging kitchens of Appingedam
Hanging kitchens of Appingedam Star fort of Bourtange
Star fort of Bourtange Windmill Goliath in Eemshaven
Windmill Goliath in Eemshaven Strawboard factory in Scheemda
Strawboard factory in Scheemda
Sports

FC Groningen from the city of Groningen is the only football club from the province in the Eredivisie.[43] Their home stadium Euroborg has a capacity of 22,550 seats.[44] In the 2012–2013 competition, FC Groningen became 7th of the 18 teams.[45] SC Veendam played in the Eerste Divisie, but filed for bankruptcy in 2013.[46]
The city of Groningen is also the base of basketball club GasTerra Flames, volleyball club Lycurgus, and korfball club Nic..[47]
The ice rink at the multi-sport center Kardinge in the city of Groningen is used for national speed skating championships, most recently the 2013 KNSB Dutch Sprint Championships.[48]
Politics

A provincial government in the Netherlands consists of a Provincial Council, the directly elected legislative branch, and a Provincial Executive, the executive branch. The King's Commissioner, who is appointed by the national government, is chairman of both branches.[49] The Provincial Council of Groningen consists of 43 members and the Provincial Executive consists of the King's Commissioner and six deputies.[50] The government has its seat in the city of Groningen, which is the provincial capital.
René Paas, member of the Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA), has been the King's Commissioner since 18 April 2016.[51] He succeeded Max van den Berg who was the King's Commissioner in Groningen from 2007 to 2016.[49]
In the provincial elections of 2011, the Labour Party became the largest party with nearly 25% of the votes and 12 seats in the Provincial Council. The next three largest parties are the People's Party for Freedom and Democracy (VVD) and the Socialist Party (SP) with 6 seats each, and the Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA) with 5 seats.[52] In 2011, two months after the elections, the member of the Party for the North (PvhN) continued as an independent under the name Free Mandate.[53][54] The next provincial elections are planned for 18 March 2015.[55]
Following the 2011 elections, the Provincial Executive was formed by a coalition of the Labour Party, the People's Party for Freedom and Democracy, Democrats 66 (D66), and GreenLeft (GL).[56] In 2013, GreenLeft left the coalition and was replaced by the ChristianUnion (CU).[57] The Labour Party has three deputies, the other coalition parties have one deputy each.[58]
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Socialist Party | 39,093 | 16.19 | 8 | |||
| Labour Party | 29,711 | 12.30 | 6 | |||
| Christian Democratic Appeal | 27,160 | 11.25 | 5 | |||
| Democrats 66 | 23,422 | 9.70 | 4 | |||
| People's Party for Freedom and Democracy | 22,089 | 9.15 | 4 | |||
| Christian Union | 21,124 | 8.75 | 4 | |||
| Party for Freedom | 19,340 | 8.01 | 3 | |||
| Groninger Belang | 15,869 | 6.57 | 3 | |||
| GroenLinks | 15,701 | 6.50 | 3 | |||
| Party for the Animals | 9,078 | 3.76 | 2 | |||
| Party for the North | 5,173 | 2.14 | 1 | |||
| Other parties | 13,719 | 5.68 | 0 | |||
| Total | 241,479 | 100 | 43 | |||
Transportation
Roads

In the province of Groningen, there are three national roads (Dutch: rijkswegen), which are maintained by Rijkswaterstaat.[60][61] The motorway A7 (E22) connects the city of Groningen with the provinces of Friesland and North Holland in the west and with Winschoten and Germany in the east. The motorway is interrupted for the ring road of the city of Groningen, where it is the expressway N7.[62] The motorway A28 (E232) starts at the city of Groningen and runs south connecting it with the provinces of Drenthe, Overijssel, Gelderland, and Utrecht.[63] The expressway N33 runs south from Eemshaven, via Appingedam and Veendam, to Drenthe.[64] Other roads are overseen by the province (N roads), municipalities, or water boards.[60]
Public transport


Public transport falls under the rules for government procurement in the European Union. Tenders for regional bus and railway services are selected by the province of Groningen. Qbuzz is contracted for bus services in the period 2009–2015 and Arriva for railway services in the period 2005–2020.[65] Nederlandse Spoorwegen operates the railway services from Groningen railway station southward to Drenthe and beyond.
The railway network in the Netherlands is maintained by ProRail.[66] There are six railways located partially or entirely in the province of Groningen. The railway station Groningen connects several of these railways.[67]
| Trajectory | Railway stations in Groningen[67] |
|---|---|
| Groningen–Delfzijl | Groningen – Groningen Noord – Sauwerd – Bedum – Stedum – Loppersum – Appingedam – Delfzijl West – Delfzijl |
| Harlingen–Nieuweschans | Friesland – Grijpskerk – Zuidhorn – Groningen – Groningen Europapark – Kropswolde – Martenshoek – Hoogezand-Sappemeer – Sappemeer Oost – Zuidbroek – Scheemda – Winschoten – Bad Nieuweschans |
| Ihrhove–Nieuweschans | Germany – Bad Nieuweschans |
| Meppel–Groningen | Drenthe – Haren – Groningen Europapark – Groningen |
| Sauwerd–Roodeschool | Sauwerd – Winsum – Baflo – Warffum – Usquert – Uithuizen – Uithuizermeeden – Roodeschool |
| Stadskanaal–Zuidbroek | Veendam – Zuidbroek |
Airports

The international airport that serves Groningen is Groningen Airport Eelde, which is located in Eelde in the province of Drenthe. The airport is co-owned by the provinces of Groningen and Drenthe and the municipalities of Groningen, Assen, and Tynaarlo.[68] Its summer destinations are Antalya, Faro, Girona, Gran Canaria, Heraklion, Kos, Palma de Mallorca, and Tenerife. Its winter destinations are Innsbruck and Salzburg.[69] Starting on 5 June 2014, there will also be flights to London.[70] For other international destinations, Amsterdam Airport Schiphol is the nearest airport. The general aviation airports in the province are Oostwold Airport in Oostwold[71] and Stadskanaal Airfield in Stadskanaal.[72]
Science and education

The University of Groningen in the city of Groningen was founded in 1614[73] and is the only research university (universiteit) in the province. On 1 September 2013, it had 29,407 students and 5,238 full-time equivalent of staff members.[74] The university has ten faculties: Arts, Behavioural and Social Sciences, Economics and Business, Law, Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Medical Sciences, Philosophy, Spatial Sciences, Theology and Religious Studies, and University College Groningen.[75]
The Hanze University of Applied Sciences, the NHL University of Applied Sciences, and the Stenden University of Applied Sciences in the city of Groningen are the province's publicly funded universities of applied sciences (hogescholen).
Media
The Dagblad van het Noorden is a regional daily newspaper based in the city of Groningen and is owned by NDC Mediagroep. It was founded in 2002 by merging the Nieuwsblad van het Noorden, the Groninger Dagblad, and the Drentse Courant.[76] In 2015, the newspaper had a circulation of 96,515.[77]
RTV Noord is a regional public broadcaster of radio and television based in the city of Groningen, with Radio Noord and TV Noord.[78] Their radio station has 121,000 daily listeners and a market share of 28% (2012) and their TV station has 171,000 daily viewers and a market share of 26.7% (2012).[79][80]
Notable residents
People from the province of Groningen:
|
|
References
- 1 2 3 (in Dutch) Bodemgebruik; uitgebreide gebruiksvorm, per gemeente, Statistics Netherlands, 2013. Retrieved on 14 April 2014.
- 1 2 (in Dutch) Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand, Statistics Netherlands, 2014. Retrieved on 12 March 2014.
- 1 2 Hanseatic city, Toerisms Groningen. Retrieved on 27 January 2014.
- ↑ Groningen, Canadiansoldiers.com. Retrieved on 8 April 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) "Hanneke Jagersma burgemeeste Beerta", Nieuwsblad van het Noorden, 1982. Retrieved on 8 April 2014.
- 1 2 (in Dutch) Uitersten, Oude stafkaarten verzamelen. Retrieved on 2 June 2014.
- ↑ Groningen province, University of Groningen, 2012. Retrieved on 14 April 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Hasseberg (Gemeente Vlagtwedde), RTV Noord, 2011. Retrieved on 14 April 2014.
- ↑ Rafael Sandrea, Global Natural Gas Reserves – A Heuristic Viewpoint, IPC Petroleum Consultants, 2005. Retrieved on 14 April 2014.
- 1 2 (in Dutch) Aardbevingen door gaswinning in Noord-Nederland, Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute, 2013. Retrieved on 27 January 2014.
- ↑ The Wadden Sea, UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved on 14 April 2014.
- ↑ Bernardus Mourik, Staatkundige historie van Holland, 1768, vol. 25, pp. 7–9. Retrieved on 2 June 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Indeling van Nederland in 40 COROP-gebieden, Statistics Netherlands. Retrieved on 25 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Grenzeloos Gunnen, Province of Groningen, 2013. Retrieved on 14 April 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Makelaar helpt gemeenten en provincie bij gemeentelijke herindeling, Province of Groningen, 2013. Retrieved on 14 April 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 "Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand" [Population growth; regions per month]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 7 April 2017. Retrieved 7 April 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Kerncijfers wijken en buurten" [Key figures for neighbourhoods]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 2 July 2013. Retrieved 12 March 2014.
- ↑ About us, Groningen-Assen Region. Retrieved on 6 April 2014.
- ↑ (in German) Die Mitglieder der EDR, Ems Dollart Region. Retrieved on 6 April 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Nieuw Beerta, langjarige gemiddelden, tijdvak 1981-2010, Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute. Retrieved on 25 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Volkstelling 1899; algemene uitkomsten per gemeente, Statistics Netherlands, 1999. Retrieved on 25 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Volkstelling 1930; bewoners naar geslacht en geboorteplaats, Statistics Netherlands, 2006. Retrieved on 25 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Bevolkingsontwikkeling; levendgeborenen, overledenen en migratie per regio, Statistics Netherlands, 2013. Retrieved on 12 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Bevolking op 1 januari; leeftijd, geboorteland en regio, Statistics Netherlands, 2013. Retrieved on 25 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Kerkelijke gezindte per provincie vanaf 1849, Statistics Netherlands, 2001. Retrieved on 25 March 2014.
- 1 2 3 (in Dutch) Algemeen, Economie.groningen.nl. Retrieved on 8 April 2014.
- ↑ Facts and figures, University Medical Center Groningen, 2015. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- ↑ Key figures, University of Groningen, 2016. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- ↑ Concern en burgercontacten (in Dutch), Municipality of Groningen. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- ↑ "Slechts 10 deelenemers aan cursus hoogtevrees DUO" (in Dutch), RTV Noord, 2011. Retrieved on 8 April 2014.
- ↑ About us, Gasunie. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- ↑ The ports, Groningen Seaports. Retrieved on 27 January 2014.
- ↑ Facts & Figures 2015, Groningen Seaports. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Over Chemie Park, Chemie Park Delfzijl. Retrieved on 8 April 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Eemscentrale, GDF Suez. Retrieved on 8 April 2014.
- ↑ Gasgestookte centrales, Nuon. Retrieved on 8 April 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Eemshavencentrale, Essent. Retrieved on 16 April 2014.
- ↑ Jane Whaley, "The Groningen Gas Field", GEO ExPro Magazine, 2009. Retrieved on 27 January 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Beroepsbevolking; kerncijfers provincie, Statistics Netherlands, 2014. Retrieved on 26 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Over ons, Museumhuis Groningen. Retrieved on 18 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Aangesloten organisaties Museumhuis Groningen februari 2014, Museumhuis Groningen, 2014. Retrieved on 18 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Bezoekcijfers erfgoedinstellingen Groningen, Stichting Erfgoedpartners, 2016. Retrieved 14 May 2016.
- ↑ (in Dutch) "Stand Eredivisie 2013/2014", Voetbal International, 2014. Retrieved on 13 April 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Stadion Euroborg, FC Groningen. Retrieved on 13 April 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) "Stand Eredivisie 2012/2013", Voetbal International, 2013. Retrieved on 13 April 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) "Reddingsactie niet gelukt; SC Veendam definitief failliet", Algemeen Dagblad, 2013. Retrieved on 13 April 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Home, Energy Valley Topclub. Retrieved on 13 April 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) "Dit weekend NK Sprint Kardinge", OOG Radio en TV, 2013. Retrieved on 13 April 2014.
- 1 2 Provincial Council and Provincial Executive, Province of Groningen. Retrieved on 28 January 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Over Gedeputeerde Staten, Province of Groningen. Retrieved on 28 January 2014.
- ↑ Mr.Drs. F.J. (René) Paas (in Dutch), Parlement & Politiek, 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Verkiezingsuitslagen Provinciale Staten 1918 - heden, Electoral Council. Retrieved on 27 January 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) "Lijsttrekker breekt met Partij voor het Noorden", Dagblad van het Noorden, 2011. Retrieved on 16 June 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Fracties, Province of Groningen. Retrieved on 16 June 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Provinciale staten, Kiesraad. Retrieved on 3 June 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Collegeprogramma 2011-2015, Province of Groningen. Retrieved on 28 January 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Henk Staghouwer nieuwe gedeputeerde in Groningen: ChristenUnie vervangt GroenLinks, Groninger Internet Courant, 2013. Retrieved on 27 January 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Leden Gedeputeerde Staten, Province of Groningen. Retrieved on 16 June 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Verkiezingsuitslagen Provinciale Staten 1918 - heden, Electoral Council. Retrieved 19 June 2016.
- 1 2 (in Dutch) Wat voor wegen zijn er in Nederland en wie is de wegbeheerder?, Rijksoverheid. Retrieved on 15 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Wegenoverzicht Archived 15 March 2014 at the Wayback Machine., Rijkswaterstaat. Retrieved on 15 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) A7, Rijkswaterstaat. Retrieved on 15 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) A28, Rijkswaterstaat. Retrieved on 15 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) N33, Rijkswaterstaat. Retrieved on 15 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch), Openbaar vervoer, Province of Groningen. Retrieved on 17 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Wat doet ProRail, ProRail. Retrieved on 17 March 2014.
- 1 2 (in Dutch) Leeuwarden - Groningen, Sporenplan. Retrieved on 8 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Bestuur & Management Team, Groningen Airport Eelde. Retrieved on 17 March 2014.
- ↑ Destinations, Groningen Airport Eelde. Retrieved on 8 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) "Airport Eelde krijgt vlucht naar Londen", Dagblad van het Noorden, 2014. Retrieved on 3 April 2014.
- ↑ Home, Oostwold Airport. Retrieved on 8 March 2014.
- ↑ (in Dutch) Vliegveld Stadskanaal, Stadskanaal Airfield. Retrieved on 8 March 2014.
- ↑ Who are we?, University of Groningen, 2013. Retrieved on 28 January 2014.
- ↑ Key Figures, University of Groningen, 2014. Retrieved on 6 April 2014.
- ↑ Faculties, University of Groningen. Retrieved on 6 April 2014.
- ↑ "Dagblad van het Noorden" (in Dutch), Trouw, 2001. Retrieved on 14 April 2014.
- ↑ Abonneeverlies Dagblad van het Noorden vlakt af (in Dutch), RTV Noord, 2016 Retrieved 3 June 2016.
- ↑ Jaarverslag 2012 (in Dutch), RTV Noord, 2013. Retrieved on 13 April 2014.
- ↑ RTV Noord (in Dutch), Omroep Reclame Nederland. Retrieved on 2 September 2014.
- ↑ Bereik regionale omroepen blijft dalen (in Dutch), Nu.nl, 2013. Retrieved on 2 September 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Groningen (province). |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Groningen (province). |
- Province of Groningen, official government website
- Nothing Tops Groningen, official tourism website
 Texts on Wikisource:
Texts on Wikisource:
- Groningen in Holland and its People (1874)
- Groningen (province) in The New International Encyclopædia (1905)