Groningen
| Groningen | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City and Municipality | |||
|
Top row: Gasunie Building and Grote Markt Square; middle row: Groningen City Theater/Korenbeurs and Aa Church, Martini Tower and Goudkantoor; bottom row: Groninger Museum. | |||
| |||
.svg.png) Location in Groningen | |||
| Coordinates: 53°13′N 6°34′E / 53.217°N 6.567°ECoordinates: 53°13′N 6°34′E / 53.217°N 6.567°E | |||
| Country | Netherlands | ||
| Province | Groningen | ||
| Government[1] | |||
| • Body | Municipal council | ||
| • Mayor | Peter den Oudsten (PvdA) | ||
| Area[2] | |||
| • Municipality | 83.75 km2 (32.34 sq mi) | ||
| • Land | 78.05 km2 (30.14 sq mi) | ||
| • Water | 5.70 km2 (2.20 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation[3] | 7 m (23 ft) | ||
| Population (Municipality, February 2017; Urban and Metro, May 2014)[4][5] | |||
| • Municipality | 197,823 | ||
| • Density | 2,535/km2 (6,570/sq mi) | ||
| • Urban | 216,655 | ||
| • Metro | 360,748 | ||
| Demonym(s) | Groninger | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| Postcode | 9700–9747 | ||
| Area code | 050 | ||
| Website |
gemeente | ||
Groningen (Dutch pronunciation: [ˈɣroːnɪŋə(n)]; Gronings: Grunnen) is the main municipality as well as the capital city of the eponymous province in the Netherlands. With a population of 202,567 as of 2017,[6] it is the largest city in the north of the Netherlands. An old city, Groningen was the regional power of the northern Netherlands, a semi-independent city-state and member of the German Hanseatic League. Groningen is a university city: it houses the University of Groningen (with about 30,000 students) and the Hanze University of Applied Sciences (with about 25,000 students).
History
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1400 | 5,000 | — |
| 1560 | 12,500 | +0.57% |
| 1600 | 16,600 | +0.71% |
| 1721 | 20,680 | +0.18% |
| 1770 | 23,296 | +0.24% |
| 1787 | 22,000 | −0.34% |
| 1795 | 23,770 | +0.97% |
| Source: Lourens & Lucassen 1997, pp. 30–31 | ||

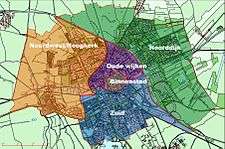







The city was founded on the northernmost point of the Hondsrug area. The oldest document referring to Groningen's existence dates from 1040. However, the city already existed long before then: the oldest archaeological traces found are believed to stem from the years 3950–3720 BC, although the first major settlement in Groningen has been traced back to the 3rd century AD.
In the 13th century, when Groningen was an important trade centre, its inhabitants built a city wall to underline its authority. The city had a strong influence on the surrounding lands and made its dialect a common tongue. The most influential period of the city was the end of the 15th century, when the nearby province of Friesland was administered from Groningen. During these years, the Martinitoren was built, which loomed over the city (then) at 127 metres (417 feet) tall. The city's independence came to an end when in 1536, it chose to accept Emperor Charles V, the Habsburg ruler of the other Netherlands, as its overlord. Later, it joined the Republic of the Seven United Provinces.
In 1614, the University of Groningen was founded, initially only for religious education. In the same period the city expanded rapidly and a new city wall was built. That same city wall was tested during the Third Anglo-Dutch War in 1672, when the city was attacked fiercely by the bishop of Münster, Bernhard von Galen. The city walls resisted, an event that is still celebrated with music and fireworks on August the 28th (as "Gronings Ontzet" or "Bommen Berend").
The city did not escape the devastation of World War II. In particular, the main square, the Grote Markt, was largely destroyed in April 1945 in the Battle of Groningen. However, the Martinitoren, its church, the Goudkantoor, and the city hall were not damaged. The battle lasted several days.
University of Groningen
The University of Groningen (in Dutch: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen) has a rich academic tradition that dates back to 1614. After the University of Leiden, it is the second oldest Dutch university. The university educated the first female student, Aletta Jacobs, the first Dutch national astronaut, Wubbo Ockels, the first president of the European Central Bank, Wim Duisenberg and two Nobel prize winners, Heike Kamerlingh Onnes and Ben Feringa. 200,000 people were either students, teachers or researchers at the university. Groningen has the highest percentage of students by total population, approximately 25 percent.
Art, culture and nightlife
The city is nationally known as the "Metropolis of the North" and as "Martinistad" referring to the tower of the Martinitoren, named after its patron saint Martin of Tours.
Although Groningen is not a very large city, it does have an important role as the main urban centre of this part of the country, particularly in the fields of music and other arts, education, and business. The large number of students living in Groningen also contributes to a diverse cultural scene for a city of its size.
Museums
The most important and most famous museum in Groningen is the Groninger Museum. With the construction of its current building, designed by Alessandro Mendini, the museum has been transformed into one of the most modern and innovative of its kind in the Netherlands. In addition, the city has a maritime museum, a university museum, a comics museum and a graphics museum. Groningen is also home of Noorderlicht, an international photographic platform that runs a photo gallery and organizes an international photo festival.
Theatre and music
Groningen has a city theatre (Stadsschouwburg), located on the Turfsingel; a big theatre and concert venue called Martini Plaza; and another major cultural venue on the Trompsingel, called the Oosterpoort. Vera is located on the Oosterstraat, the Grand Theatre on the Grote Markt, and Simplon on the Boterdiep. Several cafés feature live music, a few of which specialize in jazz music, including Jazzcafe De Spieghel on the Peperstraat. The jazz music students from the Prince Claus Conservatoire have been known to hold regular jam sessions in cafés such as Peter Pan on the Voor Het Voormalige Klein Poortje and café De Smederij on the Tuinstraat 2–4. Groningen is also the host city for Eurosonic Noorderslag, an annual music showcase event for over a hundred bands from all over Europe.
Nightlife
Groningen's nightlife depends largely on its student population. Its cultural scene is vibrant and remarkable for a city its size. In particular, the Grote Markt, the Vismarkt, the Poelestraat and Peperstraat are crowded every night of the week, and most bars do not close until 5 in the morning. Between 2005 and 2007, Groningen was elected "best city centre" of the Netherlands.[7] Groningen has a red-light district, called Nieuwstad. A second one in the A-kwartier (an area) has been closed as of late 2015. Both areas are in or near the city centre.
Other
In 2014 a 3D Dome theatre, known as Infoversum, opened in Groningen. This is housed in an unusual dome shaped building made out of steel. It shows special dome films and also presents performing arts events. The Infoversum went bankrupt in 2015. It has since been bought by an independent company and transformed into a restaurant.
International relations
Groningen is twinned with the following cities:[8]
|
Politics
The city council has 39 members. With 9 seats, the social-liberal D66 is the largest party on the council. The social-democratic PvdA has 6 seats, as does the Socialist Party. The centre-right VVD has 3 seats. GroenLinks holds 4 seats, and the local party Stadspartij 2 seats. The CDA and ChristenUnie are represented by 3 and 2 councilors, respectively. The Students and City (Student en Stad) holds 2 seats, and the Party for the Animals and 100% Groningen both hold one seat.[11]
Religion
The largest religion in Groningen is Christianity with 25,1% of the population that is Christian.
Religions in Groningen (2013)[12]
Economy
Until recently, two large sugar refineries were inside the city boundaries. The Suiker Unie plant was originally outside Groningen, but it was completely swallowed by the expansion of the city. After a campaign to close the factory, it was finally shut down in 2008/2009. Before closing down, the sugar production amounted to 250,000 tonnes of beet sugar, with 250 employees (2005 figures). The only remaining sugar factory is CSM Vierverlaten in Hoogkerk, which produces 235,000 tonnes of beet sugar, with 283 employees.
Nowadays, well known companies from Groningen are a publishing company Noordhoff Uitgevers, a tobacco company Royal Theodorus Niemeyer, a health insurance company Menzis, a distillery Hooghoudt and the natural gas companies GasUnie and GasTerra. There is an increased focus on business services; specifically ICT, Life Sciences, Tourism, Energy and Environment.
Moreover, the Hotel and Catering Industry form a significant part of the economy of Groningen.
Topography
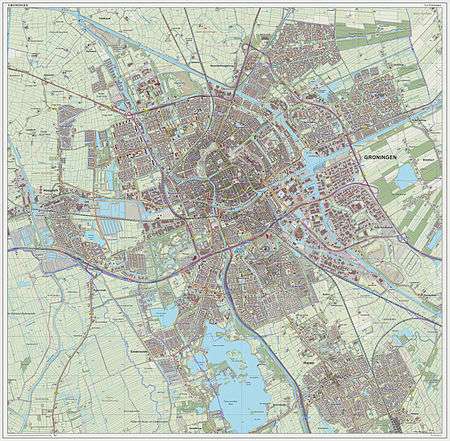
Transport
Cycling and walking
Groningen has been called the "World Cycling City" because 57% of journeys within the city are made by bicycle.[13] Like most Dutch cities, Groningen is well adapted to the high number of cyclists. A large network of bike paths makes it convenient to cycle to various destinations and within the town the bike is the most popular means of transportation. In 2000, Groningen was chosen as Fietsstad 2002 — top BikeCity of the Netherlands for 2002.
The city is very much adapted to the wishes of those who want to get around without a car, as it has an extensive network of segregated cycle-paths, good public transport, and a large pedestrianised zone in the city centre. The transformation of the historic centre into a pedestrian priority zone enables and invites walking and biking by making these active modes of transport comfortable, safe and enjoyable.
These attributes are accomplished by applying the principle of "filtered permeability". It means that the network configuration favours active transportation and selectively "filters out" the car by reducing the number of streets that run through the centre. While certain streets are discontinuous for cars, they connect to a network of pedestrian and bike paths which permeate the entire centre. In addition, these paths go through public squares and open spaces, increasing the enjoyment of the trip (see image). The logic of filtering a mode of transport is fully expressed in a comprehensive model for laying out neighbourhoods and districts – the Fused Grid. In the Italian TV programme of investigative journalism "Report" appeared a short film,[14] considering the use of bikes in Groningen a good practice to emulate in Italy.
Rail
There are three stations in Groningen:
The main train station (served by the Nederlandse Spoorwegen and Arriva) has regular services to most of the major cities in the Netherlands.
The following services operated by the Nederlandse Spoorwegen call at Groningen:
- 1x per hour intercity service Rotterdam - Gouda - Utrecht - Amersfoort - Zwolle - Assen - Groningen
- 1x per hour intercity service The Hague - Leiden - Schiphol - Amsterdam Zuid - Almere - Lelystad - Zwolle - Assen - Groningen
- 2x per hour local service (sprinter) Zwolle - Meppel - Assen - Groningen
The following services operated by Arriva call at Groningen:
- 1x per hour express service (sneltrein) Leeuwarden - Buitenpost - Groningen
- 2x per hour local service (stoptrein) Leeuwarden - Buitenpost - Groningen
- 2x per hour local service (stoptrein) Groningen - Zuidbroek - Veendam
- 1x per hour local service (stoptrein) Groningen - Zuidbroek - Winschoten - Bad Nieuweschans - Leer
- 1x per hour local service (stoptrein) Groningen - Zuidbroek - Winschoten
- 2x per hour local service (stoptrein) Groningen - Sauwerd - Roodeschool
- 2x per hour local service (stoptrein) Groningen - Sauwerd - Delfzijl
As of 2017, the hourly train to Leer only runs to Weener due to a damaged rail bridge. Travellers can either take the bi-hourly direct bus connection from Groningen to Leer, or change to a local bus at Weener.
Road
The A28 motorway connects the city of Groningen to Utrecht (via Zwolle and Amersfoort). The A7 motorway connects Groningen to Friesland and Amsterdam (South-West) and Winschoten and the direction of Bremen in the East.
Bus
Qbuzz runs several city buses and regional buses. The main routes are:
- 1: Zuidhorn-Zernike-Groningen Noord-city centre-main station
- 2: Groningen Noord-city centre-main station-Martini Hospital-Eelde-De Punt
- 3: Lewenborg-city centre-main station-Leek
- 4: Beijum-centre-main station-Hoogkerk-Roden
- 5: Groningen Europapark-city centre-main station-Haren-Zuidlaren-Annen
- 6: Groningen Noord-city centre-main station-Hoornsemeer
- 7: Groningen Noord-Korrewegwijk-main station
- 8: Hoogkerk-main station-Corpus den Hoorn-Martini Hospital
- 9: Main station-city centre-Paddepoel-Selwerd-Groningen Noord
- 15: Zernike-main station
- 35: Groningen-Oldehove
- 39/133: Groningen-Surhuisterveen
- 40/140: Groningen-Appingedam-Delfzijl
- 50: Groningen-Assen
- 58: Groningen-Zuidlaren-Assen
- 61: Groningen-Bedum-Uithuizen-Delfzijl
- 65: Groningen-Winsum-Zoutkamp
- 73: Groningen-Stadskanaal-Emmen
- 78: Groningen-Siddeburen
- 85: Groningen-Oosterwolde
- 163: Groningen-Lauwersoog (connecting the ferry to Schiermonnikoog)
- 300/305: Groningen-Gieten-Borger-Emmen-Klazienaveen
- 304/314: Groningen-Drachten
- 309: Groningen-Assen
- 315: Groningen-Heereveen-Emmeloord
There are also direct buses between Groningen and Bremen, Hamburg and Berlin in Germany, run by Flixbus and between Groningen and Munich run by ADAC Postbus.
Groningen planned to build a tram route connecting the main station, via the university hospital with the university complex (Zernike), and the central station via the city center with the Park & Ride and sportscenter at Kardinge . However, in October 2012 the city council decided not to build the tramlines due to the high costs.
Air
Groningen Airport Eelde is located 10 kilometres (6 miles) south of the centre of Groningen, with scheduled services to Gdansk, Copenhagen, and London Southend, and several seasonal holiday charter services to other European destinations.
Climate
Groningen has an oceanic temperate climate, like all of the Netherlands, although slightly colder in winter than other major cities in the Netherlands due to its northeasterly position. Weather is influenced by the North Sea to the north-west and its prevailing north-western winds and gales. Winter temperatures are cool: on average above freezing, although frosts are common during spells of easterly winds blowing in from the inner European continent, i. e., Germany, Russia and even Siberia. Night-time temperatures of −10 °C (14 °F) or lower are not uncommon during cold winter periods. The lowest temperature ever recorded is −26.8 °C (−16.2 °F) on February 16, 1956. Snow often falls, but rarely stays long due to warmer daytime temperatures, although white snowy days happen every winter. Summers are somewhat warm and humid. Temperatures of 30 °C (86 °F) or higher occur sporadically, most average daytime highs are around 22 °C (72 °F). Very rainy periods are common, especially in spring and summer. Average annual precipitation is about 800 mm (31 in). Sunshine hours vary, but are usually below 1600 hours, giving much cloud cover similar to most of the Netherlands. Climate in this area has mild differences between highs and lows, and there is adequate rainfall year-round. The Köppen Climate Classification subtype for this climate is "Cfb". (Marine West Coast Climate/Oceanic climate).[15]
| Climate data for Groningen Airport Eelde | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 14.5 (58.1) |
16.1 (61) |
24.0 (75.2) |
28.8 (83.8) |
32.8 (91) |
33.8 (92.8) |
34.9 (94.8) |
36.3 (97.3) |
32.6 (90.7) |
27.4 (81.3) |
18.0 (64.4) |
15.4 (59.7) |
36.3 (97.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 4.7 (40.5) |
5.4 (41.7) |
9.0 (48.2) |
13.4 (56.1) |
17.4 (63.3) |
19.9 (67.8) |
22.2 (72) |
22.1 (71.8) |
18.6 (65.5) |
13.9 (57) |
8.7 (47.7) |
5.2 (41.4) |
13.4 (56.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.4 (36.3) |
2.4 (36.3) |
5.2 (41.4) |
8.4 (47.1) |
12.3 (54.1) |
14.9 (58.8) |
17.1 (62.8) |
16.9 (62.4) |
13.8 (56.8) |
10.0 (50) |
6.0 (42.8) |
2.9 (37.2) |
9.3 (48.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −0.4 (31.3) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
1.4 (34.5) |
3.4 (38.1) |
6.9 (44.4) |
9.5 (49.1) |
11.9 (53.4) |
11.6 (52.9) |
9.3 (48.7) |
6.2 (43.2) |
2.9 (37.2) |
0.1 (32.2) |
5.2 (41.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −22.0 (−7.6) |
−22.9 (−9.2) |
−18.4 (−1.1) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
0.1 (32.2) |
2.5 (36.5) |
3.2 (37.8) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
−6.9 (19.6) |
−13.6 (7.5) |
−22.0 (−7.6) |
−22.9 (−9.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 74.2 (2.921) |
51.4 (2.024) |
64.3 (2.531) |
42.1 (1.657) |
58.0 (2.283) |
71.2 (2.803) |
79.4 (3.126) |
70.9 (2.791) |
78.3 (3.083) |
74.0 (2.913) |
75.0 (2.953) |
73.4 (2.89) |
812.1 (31.972) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1 mm) | 13 | 10 | 12 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 137 |
| Average snowy days | 8 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 33 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 90 | 88 | 85 | 79 | 79 | 81 | 82 | 83 | 86 | 89 | 91 | 92 | 85.4 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 54.2 | 78.7 | 117.2 | 171.6 | 210.0 | 187.0 | 199.1 | 183.9 | 137.0 | 107.2 | 56.5 | 47.5 | 1,550 |
| Source #1: Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (1981−2010 normals, snowy days normals for 1971−2000)[16] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (1906−2015 extremes)[17] | |||||||||||||
Sport
Sports clubs
The local football club is FC Groningen, founded in 1971. Currently it is playing in the Dutch top football league, called the Eredivisie. Winners of the KNVB cup in 2014/15, their best league result was in the Eredivisie during the 1990/91 season when they finished third. The current stadium of FC Groningen, which opened in January 2006, is called Noordlease stadium (before the 2015-2016 season it was called the Euroborg stadium) and has 22,550 seats.[18] There are plans to expand the stadium to a capacity of 35- or 40,000.
Donar is a professional basketball club, playing in the Dutch Basketball League. The home arena is Martiniplaza. The club won the national championship five times: in 1982, 2004, 2010, 2014 and 2016. In 2005, 2011 and 2014 they won the NBB Cup.
Each year, the second Sunday of October, the 4 Mile of Groningen takes place. This is one of the biggest running events of the Netherlands; in the year 2013, there were places for 21,000 participants: this was 1000 more than in 2012, when there were 20,000 starting spots.[19]
Also the sport American Football is represented in the city of Groningen, which is at the highest level in the Netherlands. The Groningen Giants , founded in 2000, play their home games at Sportpark Corpus den Hoorn.
Cycling
The 2002 Giro d'Italia started in Groningen, including the prologue and the start of stage 1. The city also hosted the start and finish of stage 5 of the 2013 Energiewacht Tour.
Notable people from Groningen






.jpg)





.jpg)

early times to 1750
- Wessel Gansfort (1419–1489) theologian and early humanist of the northern Low Countries
- Volcher Coiter (1534–1576) anatomist, founder of comparative osteology and first to identify cerebrospinal meningitis
- Christiaan Coevershoff (1595-1659) Dutch Golden Age painter
- Egbert Bartholomeusz Kortenaer (1604–1665) Dutch admiral, killed in the Battle of Lowestoft
- Albert Eckhout (c.1610–1665) portrait and still life painter
- Roche Braziliano (c.1630–c.1671) pirate long exile in Brazil
- Joris Andringa (1635–1676) naval officer
- Tiberius Hemsterhuis (1685–1766) was philologist and critic
- Albert Schultens (1686–1750) philologist
- Daniel Bernoulli (1700–1782) mathematician and physicist
- Johannes Antiquus (1702–1750) painter.
- Bernard II van Risamburgh (c.1710—c.1767) cabinetmaker in the Rococo style
- Willem Arnold Alting (1724–1800) Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies from 1780 until 1797
- Elisabeth Geertruida Wassenbergh (1729–1781) painter from the Northern Netherlands.
- Etta Palm d'Aelders (1743–1799) early feminist and spy
- Egbert Benson (1746–1833) lawyer, jurist, politician one of the Founding Fathers of the USA
- Leopold Friedrich Günther von Goeckingk (1748–1828) German lyric poet, journalist and Prussian official.
- Johann August Just (c.1750–c.1791) keyboard player, violinist and composer
1750 to 1870
- John Goodricke (1764–1786) astronomer observed the variable star Algol
- Jonkheer Albert Dominicus Trip van Zoudtlandt (1776—1835) lieutenant-general of cavalry who headed the Dutch-Belgian heavy cavalry brigade at the Battle of Waterloo
- Petrus Hofman Peerlkamp (1786-1865) classical scholar and critic.
- Geert Adriaans Boomgaard (1788-1899), first validated supercentenarian and last living veteran of Napoleon's Grande Armée
- Schelto van Heemstra Baron of Heemstra (1807–1864) politician, Prime Minister 1861/2.
- Jozef Israëls (1824–1911) painter of the Hague School
- Joseph Ascher (1829–1869) composer and pianist
- Hendrik Willem Mesdag (1831–1915) marine art painter
- Samuel van Houten (1837–1930) politician, cabinet minister, founder of the Netherlands Liberal Party
- Jonkheer Alexander de Savornin Lohman (1837–1924) politician, leader of the Christian Historical Union
- Otto Eerelman (1839-1926) painter, known for his depictions of dogs and horses
- Klaas Plantinga (1846–1922) distiller, founded the Plantinga Distillery in Bolsward, Friesland province
- Heike Kamerlingh Onnes (1853–1926) was Nobel laureate physicist who pioneered refrigeration and superconductivity
- Gerard Bolland (1854–1922) autodidact, linguist, philosopher, biblical scholar and lecturer
- René de Marees van Swinderen (1860–1955) diplomat and politician.
- Barbara Elisabeth van Houten (1863–1950) painter
- Gerrit van Houten (1866–1934) painter and artist.
- Jonkheer Dirk Jan de Geer (1870–1960) statesman and Dutch Prime Minister (1926/29, 1939/40), advocated peace settlement between the Netherlands and Nazi Germany in 1940
1870 to 1900
- Jantina Tammes (1871–1947) botanist and geneticist, first professor of genetics in the Netherlands.
- Johan Huizinga (1872–1945) historian one of the founders of modern cultural history
- Bert Nienhuis (1873–1960) ceramist, designer and jewelry designer
- Gerrit David Gratama (1874–1965) artist, writer, and director of the Frans Hals Museum
- Jan Gratama (1877–1947) architect
- Albert Hahn (1877-1918) political cartoonist, poster artist and book cover designer
- C. U. Ariëns Kappers (1877-1946) neurologist and anatomist
- Dr. Herman de Vries de Heekelingen (1880–1942) scholar and author, professor of palaeography at the University of Nijmegen
- Julia Culp (1880–1970), the mezzo-soprano, the "Dutch nightingale"
- Jonny Heykens (1884–1945) composer of light classical music
- Wilhelm Baehrens (1885–1929) classical scholar
- Pieter Korteweg (1888–1970) philatelist
- A.W.L. Tjarda van Starkenborgh Stachouwer (1888–1978) last colonial Governor-General of the Netherlands East Indies
- Jaap Kunst (1891–1960) ethnomusicologist
- Michel Velleman (1895–1943) Jewish magician, killed in World War II
- Hendrik de Vries (1896–1989) poet and painter, an early surrealist
- Paul Schuitema (1897-1973) graphic artist, he designed furniture and expositions
1900 to 1930
- Ulbo de Sitter (1902–1980) geologist at Leiden University, founded the school of structural geology
- Jan Wolthuis (1903–1983) lawyer and Dutch Nazi collaborator, active in far-right politics after WWII
- Hans Dirk de Vries Reilingh (1908-2001) geographer and professor
- Elie Aron Cohen (1909–1993) Jewish doctor, survived the Auschwitz concentration camp
- Theodoor Overbeek (1911–2007) professor of physical chemistry at Utrecht University
- Pieter Meindert Schreuder (1912–1945) resistance leader in the occupied Netherlands during WWII
- Lucas Hoving (1912–2000) modern dancer, choreographer and teacher
- Jacob B. Bakema (1914–1981) modernist architect
- Anno Smith (1915-1990) artist, ceramist, painter, sculptor and art teacher
- Jan C. Uiterwijk (1915-2005) entrepreneur and shipping line owner in the USA
- Dirk Boonstra (1920-1944) active in the WWII resistance movement, caught and executed
- Poppe Damave (1921–1988) painter.
- Selma Engel-Wijnberg (born 1922) is a Dutch Jewish Holocaust survivor
- Henk Visser (1923–2006) arms and armory collector
- Jan Drenth (born 1925) chemist, was professor of structural chemistry at the University of Groningen
- Cor Edskes (1925–2015) important authority on the history of organ music and building
- Wim Crouwel (born 1928) graphic designer, type designer and typographer.
- Maarten Schmidt (born 1929) astronomer named and optically identified a quasar
- Jan Borgman (born 1929) astronomer and university administrator
- Dirk Bolt (born 1930), architect and town planner in Australia
1930 to 1950
- Ida Vos (1931–2006) writer and poet
- Arie van Deursen (1931–2011) historian whose focus was the early modern period
- Nico Habermann (1932–1993) computer scientist
- Gerrit Krol (1934−2013) author, essayist and writer
- Ad van Luyn (born 1935) Roman Catholic bishop.
- Bert de Vries (born 1938) retired Dutch politician
- Wim T. Schippers (born 1942) artist, comedian, television director and voice actor
- Driek van Wissen (1943–2010) poet
- Chas Gerretsen (born 1943) war photographer, photojournalist and film advertising photographer
- Joanna Gash (born 1944), Australian politician, emigrated aged six to New South Wales
- Jan Sloot (1945–1999) inventor, claimed to have invented a revolutionary data compression technique
- Andy Anstett (born 1946) former politician in Manitoba, Canada
- Wubbo Ockels (1946–2014) physicist and astronaut of the European Space Agency
- Alphons Orie (born 1947) former lawyer specialising in criminal law
- Alfred Lagarde (1948–1998) voice actor
- Diederik Grit (1949–2012) translator and translation scholar
- Sierd Cloetingh (born 1950) Professor of Earth Sciences at Utrecht University
1950 to modern times
- Pete Hoekstra (born 1953) American Republican member of Congress representing Michigan's 2nd congressional district
- Ellen van Wolde (born 1954) biblical scholar
- Rob Nanninga (1955–2014) skeptic, writer, board member of Stichting Skepsis
- Bert Meijer (born 1955) organic chemist, works on supramolecular chemistry, materials chemistry and polymer chemistry
- Gerard de Korte (born 1955) Roman Catholic bishop
- Joep Franssens (born 1955) composer, regarded as a representative of New Spirituality in the Netherlands
- Jan van der Kooi (born 1957) painter and drawer in the style of figurative art
- Anita Buma (born 1958) pioneer Antarctic researcher, worked on ecophysiology of marine microalgae
- Tjibbe Veldkamp (born 1962) author of children's books
- Wilma Mansveld (born 1962) politician
- Aernout Mik (born 1962) artist, known for his installations and films.
- Harm Peter Hofstee (born 1962) physicist and computer scientist
- Hans van den Hende (born 1964) Roman Catholic bishop
- Didy Veldman (born 1967) choreographer
- J. Maarten Troost (born 1969), travel writer
- Sharon Dijksma (born 1971) politician
- Diederik Samsom (born 1971) politician
- Michiel van Veen (born 1971) politician
- Attje Kuiken (born 1977) politician and former civil servant
- Rudmer Heerema (born 1978) politician
- Henk Nijboer (born 1983) politician
- Kim Feenstra (born 1985) model
- Manja Smits (born 1985) politician
- Dope D.O.D. Hardcore hip hop group (founded 2001), made up of Skits Vicious, Jay Reaper and DJ Dr. Diggles
- Noisia, Electronic Music trio (founded 2003), made up of Nik Roos, Thijs de Vlieger and Martijn van Sonderen
- Vicetone DJ and production duo (formed in 2012) by Ruben Den Boer and Victor Pool
Sport
- Jaap Eden (1873–1925) only male athlete to have won world championships in both speed skating and cycling
- Dirk Janssen (1881–1986) was gymnast in the 1908 Summer Olympics who was 105 at the time of his death, making him the longest-lived Olympic competitor
- Jan Janssen (1885–1953) gymnast, competed in the 1908 Summer Olympics
- Corrie Winkel (born 1944) backstroke swimmer and silver medalist 1964 Summer Olympics
- Gerard Kemkers (born 1967), speed skating bronze medalist at 1988 Winter Olympics
- Stephan Veen (born 1970) field hockey player in the 1996 and 2000 Summer Olympics
- Rutger Smith (born 1981), track and field athlete competing in shot put and discus throw, winning medals in both events
- Sophie Polkamp (born 1984) field hockey athlete, 2 time Olympic champion
- Marijn Nijman (born 1985) former international cricketer
- Bauke Mollema (born 1986), cyclist
- Lorena Klijn (born 1987), kickboxer
- Tom-Jelte Slagter (born 1989) professional road racing cyclist
- Lois Abbingh (1992) handball player
See also
References
- ↑ "Burgemeester" [Mayor] (in Dutch). Gemeente Groningen. Retrieved 22 December 2013.
- ↑ "Kerncijfers wijken en buurten" [Key figures for neighbourhoods]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 2 July 2013. Retrieved 12 March 2014.
- ↑ "Postcodetool for 9712HW". Actueel Hoogtebestand Nederland (in Dutch). Het Waterschapshuis. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 22 December 2013.
- ↑ "Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand" [Population growth; regions per month]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 7 April 2017. Retrieved 7 April 2017.
- ↑ "Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand" [Population growth; regions per month]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 26 June 2014. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ↑ "province of Groningen". Retrieved 24 April 2017.
- ↑ "Winnaars 2005 - 2007 -- Verkiezing Beste Binnenstad" [Winners 2005 - 2007 -- Election Best City Centre] (in Dutch). www.debestebinnenstad.nl. Retrieved 15 February 2012.
- ↑ "Groningen – Partner Cities". 2008 Gemeente Groningen, Kreupelstraat 1,9712 HW Groningen. Retrieved 8 December 2008.
- ↑ "Twin Towns – Graz Online – English Version". www.graz.at. Archived from the original on 8 November 2009. Retrieved 5 January 2010.
- ↑ "Kaliningrad – Partner Cities". 2000–2006 Kaliningrad City Hall. Archived from the original on 11 December 2008. Retrieved 8 December 2008.
- ↑ "Samenstelling gemeenteraad". Gemeente Gronignen. Retrieved 19 June 2016.
- ↑ "Kerkelijkheid en kerkbezoek, 2010/2013". Centraal Bureau voor de Statistiek.
- ↑ "global ideas bank". globalideasbank.org. 15 October 2007. Retrieved 14 July 2009.
- ↑ "Rai.tv". Rai.tv. 15 October 2007. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ↑ Climate Summary for Groningen
- ↑ "Klimaattabel Eelde, langjarige gemiddelden, tijdvak 1981–2010" (PDF). Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute. Retrieved 9 September 2013.
- ↑ "Eelde, gehomogeniseerde langjarige extremen, tijdvak 1906–2015". Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute.
- ↑ FC Groningen: Club Info
- ↑ 4 Mijl.
Literature
- Lourens, Piet; Lucassen, Jan (1997). Inwonertallen van Nederlandse steden ca. 1300–1800. Amsterdam: NEHA. ISBN 9057420082.






