Government-owned and controlled corporation
A The Government-owned and controlled corporation (GOCC), sometimes with an "and/or",[1] is a term in the Philippines used to describe government-owned corporations that conduct both commercial and non-commercial activity. Examples of the latter would be the Government Service Insurance System, a social security system for government employees. There are over 200 GOCCs.[2] GOCCs both receive subsidies and pay dividends to the national government.
Under the GOCC Governance Act (Republic Act 10149; Government Owned and Controlled Corporations (GOCC) Governance Act of 2011), GOCCs are overseen by the Governance Commission for Government-Owned or Controlled Corporations (GCG).[3] The Governance Commission is the "government’s central advisory and oversight body over the public corporate sector" according to the Official Gazette of the Philippine government.[4] The Governance Commission among other duties prepares for the President of the Philippines a shortlist of candidates for appointment by the president to GOCC boards.[3]
Many but not all GOCCs have their own charter or law outlining its responsibilities and governance.[5]
Finances
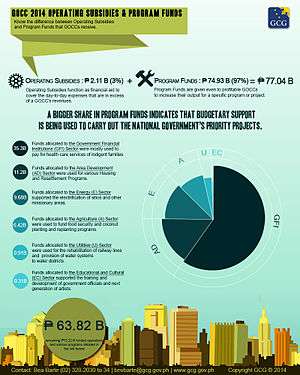
GOCCs receive from the government "subsidies" and "program funds".[6] Subsidies cover the day-to-day operations of the GOCCs when revenues are insufficient while program funds are given to profitable GOCCs to pay for a specific program or project.[6]
Subsidies from the National Government in 2011 amounted to 21 billion Philippine pesos.[7] In the 2013 fiscal year, the national government gave P71.9 billion pesos to GOCCs in subsidies, nearly twice the 44.7 billion pesos that was programmed in the budget.[2] In 2014, 77.04 billion pesos was spent on GOCCs by the national government, 3% of which was classified as subsidies and 97% was classified as program funds.[6]
In 2013, on "GOCC Dividend Day", the Philippine government received 28-billion Philippine pesos in dividends and other forms of remittances from the 2012 operations of 38 GOCCs.[8] Eight GOCCs remitted 1 billion pesos each: Philippine Reclamation Authority (PRA)(P1 billion pesos), Philippine Ports Authority (PPA)(1.03-billion), Manila International Airport Authority (MIAA)(P1.54-billion), Philippine Amusement and Gaming Corporation (PAGCOR) (P7.18-billion), Power Sector Assets and Liabilities Management Corporation (PSALM)(P2-billion), Bases Conversion Development Authority (BCDA)(P2.30-billion), Development Bank of the Philippines (DBP) (P3.16-billion) and Land Bank of the Philippines (LBP) (P6.24-billion). Under Republic Act No. 7656, all GOCCs are required to “declare and remit at least 50% of their annual net earnings as cash, stock or property dividends to the National Government."[8] The Commission on Audit reports that in 2013 of the 219 profitable GOCCs, only 45 remitted a full 50% share of their dividends to the national treasury, leaving 174 others with unremitted government shares, amounting to more than P50 billion.[2] Dividends remitted were only one-tenth (1/10) of the total required by law according to the Commission.[2]
In 2014, on "GOCC Dividend Day", the Philippine government received 32.31 billion Philippine pesos worth of dividends and other remittances from 50 GOCCs.[9] Seven GOCCs submitted over a billion pesos each: Development Bank of the Philippines (DBP) with P3.616 billion; Power Sector Assets and Liabilities Management Corporation (PSALM) with P2.5 billion; Bases Conversion Development Authority (BCDA) with P2.107 billion; Manila International Airport Authority (MIAA) with P1.577 billion; Philippine National Oil Company-Exploration Corporation (PNOC-EC) with P1.5 billion; Philippine Ports Authority (PPA) with P1.422 billion; and Philippine Deposit Insurance Corporation (PDIC) with P1.05 billion.[9]
List of Government-owned and controlled corporations
See also: Category:Government-owned and controlled corporations
There are over 200 GOCCs.[2] Below is a partial list of GOCCs:[7][10]
- Al-Amanah Islamic Investment Bank of the Philippines (AAIIBP)
- APO Production Unit, Inc. (APO-PUI)
- Aurora Pacific Economic Zone and Freeport Authority
- Authority of the Freeport of Bataan (AFAB)
- Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP)
- Bases Conversion and Development Authority (BCDA)
- Batangas Land Company, Inc. (BLCI)
- BCDA Management and Holdings, Inc. (BMHI)
- Bukidnon Forest, Inc. (BFI)
- Cagayan Economic Zone Authority
- Cebu Port Authority (CPA)
- Center for International Trade Expositions and Missions (CITEM)
- Central Bank-Board of Liquidators
- Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines (CAAP)
- Clark Development Corporation (CDC)
- Clark International Airport Corporation (CIAC)
- Corregidor Foundation, Inc. (CFI)
- Cottage Industry Technology Center (CITC)
- Credit Information Corporation (CIC)
- Cultural Center of the Philippines (CCP)
- DBP Data Center, Inc. (DDCI)
- DBP Leasing Corporation (DBP-LC)
- Development Academy of the Philippines (DAP)
- Development Bank of the Philippines (DBP)
- Duty Free Philippines Corporation (DFPC)
- Employees Compensation Commission (ECC)
- Fiber Industry Development Authority (FIDA)
- First Cavite Industrial Estate, Inc. (FCIEI)
- Fisheries Development Authority
- Food Terminal, Inc. (FTI)
- G.Y. Real Estate, Inc. (GYREI)
- Government Service Insurance System (GSIS)
- GSIS Family Bank (GSIS-FB)
- Home Development Mutual Fund (HDMF / Pag-IBIG)
- Home Guaranty Corporation (HGC)
- Human Settlements Development Corporation
- Instructional Materials Corporation
- Intercontinental Broadcasting Corporation (IBC-13) (PCGG)
- John Hay Management Corporation (JHMC)
- Kamayan Realty Corporation (KRC)
- Laguna Lake Development Authority (LLDA)
- Land Bank Countryside Development Foundation, Inc. (LCDFI)
- Land Bank of the Philippines (LBP)
- LBP Insurance Brokerage, Inc. (LIBI)
- LBP Leasing and Finance Corporation (LBP-LFC)
- LBP Resources and Development Corporation (LBRDC)
- Light Rail Transit Authority (LRTA)
- Local Water Utilities Administration (LWUA)
- Lung Center of the Philippines
- Mactan-Cebu International Airport Authority (MCIAA)
- Manila International Airport Authority (MIAA)
- Marawi Resort Hotel, Inc. (MRHI)
- Masaganang Sakahan, Inc. (MSI)
- Metro Manila Development Authority (MMDA)
- Metropolitan Waterworks and Sewerage System (MWSS)
- Metropolitan Waterworks and Sewerage System-Corporate Office
- Metropolitan Waterworks and Sewerage System-Regulatory
- National Dairy Authority (NDA)
- National Development Company (NDC)
- National Electrification Administration (NEA)
- National Food Authority (NFA)
- National Home Mortgage Finance Corporation (NHMFC)
- National Housing Authority (NHA)
- National Irrigation Administration (NIA)
- National Kidney and Transplant Institute
- National Livelihood Development Corporation (NLDC)
- National Power Corporation (NPC/NAPOCOR)
- National Research Council of the Philippines (NRCP)
- National Tobacco Administration (NTA)
- National Transmission Corporation (TransCo)
- Natural Resources Development Corporation (NRDC)
- Nayong Pilipino Foundation, Inc. (NPF)
- NDC-Philippine Infrastructure Corporation (NDC-PIC)
- North Luzon Railway Corporation (NorthRail)
- Northern Foods Corporation (NFC)
- Occupational Safety and Health Center
- Palacio del Gobernador Condominium Corporation (PDGCC)
- Panay Railways
- Partido Development Administration
- People's Credit and Finance Corporation (PCFC)
- People's Television Network, Inc. (PTV-4)
- Philippine Aerospace Development Corporation (PADC)
- Philippine Amusement and Gaming Corporation (PAGCOR)
- Philippine Center for Economic Development
- Philippine Charity Sweepstakes Office (PCSO)
- Philippine Children's Medical Center
- Philippine Coconut Authority (PCA)
- Philippine Cotton Corporation
- Philippine Crop Insurance Corporation (PCIC)
- Philippine Dairy Corporation (PDC)
- Philippine Deposit Insurance Corporation (PDIC)
- Philippine Economic Zone Authority (PEZA)
- Philippine Export and Foreign Loan Guarantee Corporation
- Philippine Export-Import Credit Agency (PHILEXIM)
- Philippine Fisheries Development Authority (PFDA)
- Philippine Health Insurance Corporation (PhilHealth)
- Philippine Heart Center (PHC)
- Philippine Institute for Development Studies (PIDS)
- Philippine Institute of Traditional and Alternative Health Care
- Philippine International Trading Corporation (PITC)
- Philippine Mining Development Corporation (PMDC)
- Philippine National Construction Corporation (PNCC)
- Philippine National Oil Company (PNOC)
- Philippine National Railways (PNR)
- Philippine Pharma Procurement Inc. (PPPI)
- Philippine Phosphate Fertilizer Corporation (PHILPOS)
- Philippine Ports Authority (PPA)
- Philippine Postal Corporation (PHLPost)
- Philippine Postal Savings Bank (Postbank)
- Philippine Racing Commission
- Philippine Reclamation Authority (PRA)
- Philippine Retirement Authority (PRA)
- Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice)
- Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA)
- Philippine Sugar Corporation (PHILSUCOR)
- Philippine Veterans Investment Development Corporation (PHIVIDEC) Industrial Authority
- Pinagkaisa Realty Corporation (PRC)
- PNOC Exploration Corporation (PNOC-EC)
- PNOC Renewables Corporation (PNOC-RC)
- Poro Point Management Corporation (PPMC)
- Power Sector Assets and Liabilities Management Corporation (PSALM)
- Quedan and Rural Credit Guarantee Corporation (Quedancor)
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
- Small Business Corporation (SBC)
- Social Housing Finance Corporation (SHFC)
- Social Security System (SSS)
- Southern Philippines Development Authority
- Southern Utility Management and Services, Inc. (SUMSI)
- Subic Bay Metropolitan Authority
- Sugar Regulatory Administration (SRA)
- Technology Resource Center (TRC)
- Tourism Infrastructure and Enterprise Zone Authority (TIEZA)
- Tourism Promotions Board (TPB)
- Trade Investment Development Corporation of the Philippines
- United Coconut Planters Bank (UCPB)
- Zamboanga City Special Economic Zone Authority
See also
References
- ↑ "Government-Owned and/or Controlled Corporations". Official Gazette. Republic of the Philippines. Archived from the original on 26 May 2015. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Lopez, Melissa Luz T. (May 25, 2015). "State-run corporations only remitted a tenth of dividends". BusinessWorld. Retrieved July 29, 2017.
- 1 2 Cayabyab, Marc Jayson (May 25, 2015). "House passes DBP, LBP merger bill". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ↑ "President Aquino approves closure of 7 nonperforming GOCCs". Official Gazette. October 22, 2014. Archived from the original on October 24, 2014. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ↑ "GCG marks third year as overseer of GOCC sector". Official Gazette. June 6, 2014. Archived from the original on June 18, 2014. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- 1 2 3 "GOCC 2014 OPERATING SUBSIDIES AND PROGRAM FUNDS". Governance Commission for GOCCs. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- 1 2 Cabuag, V.S. (8 March 2012). "Government subsidies to GOCCs grew by 155% in 2011". Business Mirror. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
- 1 2 "President Aquino receives P28-billion representing dividend contributions from 38 Government-Owned and Controlled Corporation in Malacañang". Office of the President of the Philippines. June 3, 2013. Archived from the original on August 6, 2013. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- 1 2 "GOCCs remit P32.31B to National Treasury". Philippine national government. Official Gazette. June 9, 2014. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ↑ Cabuag, V. S. (1 July 2012). "Subsidies to GOCCs declined in May". Business Mirror. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 5 July 2012.
External links
- Official website of the Governance Commission of GOCCs
- List of GOCCs from the Official Gazette of the Philippine national government
- List of GOCCs from the Department of Budget and Management
- Directory of 67 GOCCs' websites from the Department of Science and Technology
- Governance Commission for Government-Owned or -Controlled Corporations on Legal Wiki of LawCenter.ph.
