Goniopholis
| Goniopholis Temporal range: Late Jurassic - Early Cretaceous, 155–139.8 Ma | |
|---|---|
 | |
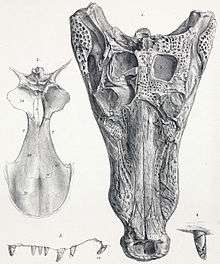
| Skull of the "Swanage Crocodile", G. kiplingi. Berriasian age (earliest Cretaceous) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Family: | †Goniopholididae |
| Genus: | †Goniopholis Owen, 1841 |
| Type species | |
| †Goniopholis crassidens Owen, 1841 | |
| Species | |
Goniopholis is an extinct genus of goniopholidid crocodyliform that lived in Europe and Africa during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous.[1][2] Being semi-aquatic it is very similar to modern crocodiles. It ranged from 2–4 metres in length, and would have had a very similar lifestyle to the American alligator or Nile crocodile.
Discovery and species

Through the years, many species of Goniopholididae have been referred to Goniopholis. Most of these species are no longer considered to belong to this genus. Two species were referred to Goniopholis from Brazil. Goniopholis hartti (Marsh, 1869) from the Lower Cretaceous of Brazil is in fact a member of the genus Sarcosuchus, while G. paulistanus (Roxo, 1936), known only from two tooth crowns and a fragment of the right tibia from the Upper Cretaceous Bauru Group, is a nomen dubium referable only to Neosuchia incertae sedis.[1]
From North America, G. lucasii and G. kirtlandicus are currently placed in their own genera Amphicotylus and Denazinosuchus, respectively,[1] while G. felix, G. gilmorei (Holland, 1905) and G. stovalli (Mook, 1964), all from the Morrison Formation, are referable to Amphicotylus and closely related to Eutretauranosuchus which are known from the same formation.[3][4][5]
G. phuwiangensis (Buffetaut & Ingavat, 1983) is known from NE Thailand, but this species is fragmentary and was recently reassigned to Sunosuchus. Nannosuchus from the Early Cretaceous (Berriasian stage) of England and Spain currently considered to be valid, was referred to as G. gracilidens by some authors.[1] Willett’s / Hulke’s, Hooley’s and Dollo’s goniopholidids represent several complete specimens previously classified as either G. simus or G. crassidens,[1] and one of them was recently re-described as the new species, G. willetti (Salisbury & Naish, 2011). More recently these specimens were removed from Goniopholis, and two of the, Hooley’s and Hulke’s goniopholidids, have been already reassigned to their own genera Anteophthalmosuchus and Hulkepholis, respectively.[2][6] Dollo's goniopholidid has also been assigned to Anteophthalmosuchus.[7]

The type species of the genus, G. crassidens which is known from the Berriasian of England, and the referable species G simus from the Berriasian of NW Germany, might be conspecific. Other species that are referable to Goniopholis include G. kiplingi from the Berriasian of England, and G. baryglyphaeus from the Late Jurassic (Kimmeridgian) of Portugal making it the oldest known Goniopholis species.[1][2] The species G. kiplingi honors the author Rudyard Kipling, "in recognition for his enthusiasm for natural sciences".[8]
Eggs attributed to Goniopholis were found in the Late Jurassic of Portugal.[9]
Classification
Below is a cladogram including several Goniopholis species:[1]
| Neosuchia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 De Andrade, M. B.; Edmonds, R.; Benton, M. J.; Schouten, R. (2011). "A new Berriasian species of Goniopholis (Mesoeucrocodylia, Neosuchia) from England, and a review of the genus". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 163: S66. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2011.00709.x.
- 1 2 3 Buscalioni, A.D.; Alcalá, L.; Espílez, E.; Mampel, L. (2013). "European Goniopholididae from the Early Albian Escucha Formation in Ariño (Teruel, Aragón, España)". Spanish Journal of Palaeontology. 28 (1): 103–122.
- ↑ Allen, Eric (2010). "Phylogenetic analysis of goniopholidid crocodyliforms of the Morrison Formation". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 30 (Supp. 1): 52A. doi:10.1080/02724634.2010.10411819.
- ↑ Pol, D.; Leardi, J. M.; Lecuona, A.; Krause, M. (2012). "Postcranial anatomy of Sebecus icaeorhinus (Crocodyliformes, Sebecidae) from the Eocene of Patagonia". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 32 (2): 328. doi:10.1080/02724634.2012.646833.
- ↑ Pritchard, A. C.; Turner, A. H.; Allen, E. R.; Norell, M. A. (2013). "Osteology of a North American Goniopholidid (Eutretauranosuchus delfsi) and Palate Evolution in Neosuchia". American Museum Novitates. 3783 (3783): 1. doi:10.1206/3783.2.
- ↑ Steven W. Salisbury; Darren Naish (2011). "Crocodilians". In Batten, D. J. English Wealden Fossils. The Palaeontological Association (London). pp. 305–369.
- ↑ Martin, J.E.; Delfino, M.; Smith, T. (2016). "Osteology and affinities of Dollo's goniopholidid (Mesoeucrocodylia) from the Early Cretaceous of Bernissart, Belgium". Journal of Vertebrate Palaeontology. doi:10.1080/02724634.2016.1222534.
- ↑ "BBC News - Rudyard Kipling inspires naming of prehistoric crocodile". BBC Online. 2011-03-20. Retrieved 20 March 2012.
- ↑ Russo, J., Mateus O., Marzola M., & Balbino A. (2017). Two new ootaxa from the late Jurassic: The oldest record of crocodylomorph eggs, from the Lourinhã Formation, Portugal. PLOS ONE. 12, 1-23.
Sources
- Buffetaut, E; Ingavat, R (1983). "Goniopholis phuwiangensis nov. sp., a new mesosuchian crocodile from the Mesozoic of North-eastern Thailand". Geobios. 16 (1): 79–91. doi:10.1016/S0016-6995(83)80048-5.
- Holland, W. J. (1905). "A new crocodile from the Jurassic of Wyoming". Annals of the Carnegie Museum. 3 (3): 431–434. ISSN 0097-4463.
- Mook, C. C. (1964). "New species of Goniopholis from the Morrison of Oklahoma". Oklahoma Geology Notes. 24: 283–287. ISSN 0030-1736.
- Owen, R. 1878. Monograph on The Fossil Reptilia of the Wealden and Purbeck Formations, Supplement no. VII. Crocodilia (Goniopholis, Pterosuchus, and Suchosaurus). Palaeontological Society Monograph, p. 1-15.
- Owen, R. (1879). "On the Association of dwarf crocodiles (Nanosuchus and Theriosuchus pusilus, e. g.) with the diminutive mammals of the Purbeck Shales". Quarterly Journal of the Geological Society of London. 35: 148–155. doi:10.1144/GSL.JGS.1879.035.01-04.02.
- Salisbury, S. W., Willis, P. M. A., Peitz, S. & Sander, P. M. (December 1999). "The crocodilian Goniopholis simus from the Lower Cretaceous of north-western Germany". Special Papers in Palaeontology. 60: 121–148. ISBN 978-0-901702-67-8.
- Schwarz, Daniela (2002). "A new species of Goniopholis from the Upper Jurassic of Portugal". Palaeontology. 45 (1): 185–208. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00233.

