Goldstone Solar System Radar
|
Goldstone Deep Space Network | |
| Organization | NASA / JPL / Caltech |
|---|---|
| Location | Mojave Desert (near Barstow, California) |
| Coordinates | 35°25′36″N 116°53′24″W / 35.42667°N 116.89000°WCoordinates: 35°25′36″N 116°53′24″W / 35.42667°N 116.89000°W |
| Altitude | 2950 ft |
| Established | 1985 |
| Website | Asteroid Radar Research |
The Goldstone Solar System Radar, or GSSR, is a large radar system used for investigating objects in the Solar system. Located in the desert near Barstow, California, it comprises a 500-kW X-band (8500 MHz) transmitter and a low-noise receiver on the 70-m DSS 14 antenna at the Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex. It has been used to investigate Mercury, Venus, Mars, the asteroids, and moons of Jupiter and Saturn. The most comparable facility is the radar at Arecibo Observatory.[1]
Planetary observations
GSSR can work in two different modes. In the monostatic radar mode, GSSR both transmits and receives. In bistatic mode, GSSR transmits and other radio astronomy facilities receive. Although more difficult to schedule, this offers two advantages - the transmitter does not need to turn off to allow the receiver to listen, and it allows the use of interferometry to extract more information from the reflected signal.
Bodies that have been investigated using GSSR include:
- Mercury: In particular, by watching specific reflected features of Mercury sweep across the Earth's surface (using spatially separated receivers), GSSR enables the pole position to be computed quite accurately. The measured librations show Mercury has a liquid core.
- Venus
- Mars: GSSR was used extensively to characterize sites for Mars landers.
- Asteroids: Asteroids appear only as unresolved points of light in ground-based optical telescopes. Radar, however, can image near-Earth asteroids and comets with a resolution of several meters. For example, the asteroid 4179 Toutatis was imaged in 1992, 1996, 2000, 2004, 2008, and 2012. Although spacecraft such as Dawn can image particular asteroids in much finer detail, radar astronomy can investigate many more asteroids of different characteristics. For example, all existing images of binary asteroids were obtained through radar astronomy.
- Moons of Jupiter
- Rings and moons of Saturn
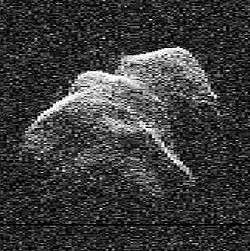 4179 Toutatis in 1996
4179 Toutatis in 1996 (53319) 1999 JM8 in 1999
(53319) 1999 JM8 in 1999 (308635) 2005 YU55 in 2011
(308635) 2005 YU55 in 2011
Other scientific uses
- Recovery of the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory after loss of attitude control.
- Investigation of orbital debris around Earth.
References
- ↑ Slade, Martin, Lance AM Benner, and Arnold Silva (2011). "Goldstone solar system radar observatory: Earth-based planetary mission support and unique science results." (PDF). Proceedings of the IEEE (99.5): 757–769.
