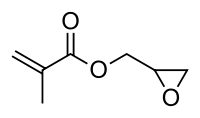
Glycidyl methacrylate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
oxiran-2-ylmethyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate | |
| Other names
glycidyl methacrylate, 2,3-epoxypropyl methacrylate, 2-((Methacryloxy)methyl)oxirane | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.130 |
| PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 142.1546 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear liquid |
| Density | 1.07 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 189.0 °C (372.2 °F; 462.1 K) |
| ca 50g/l | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 76.0 °C (168.8 °F; 349.1 K) |
| 389.0 °C (732.2 °F; 662.1 K) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) is an ester of methacrylic acid and glycidol, it is a common monomer used in the creation of epoxy resins. While typical home epoxies contain diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A (DGEBA), glycidyl methacrylate is instead used to provide epoxy functionalization to polyolefins and other acrylate resins. Glycidyl methacrylate is produced by several companies worldwide, including Dow Chemical.[2]
See also
References
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.