Georgian nationality law
Georgian nationality law is the law governing the acquisition, transmission and loss of Georgian citizenship.
Naturalization as a Georgian
Anyone who has stayed in Georgia for a total period of five years may apply for a Georgian nationality. The applicant will be asked to undergo a language proficiency test which will also test the G.K. (general knowledge) of the applicant about the history and the heritage of Georgia.
Nationality through marriage
The Georgian nationality may be applied after the first marriage anniversary. The couple should still be together and having a child would strengthen the case.
Temporary Residence permit
Anyone who enters the Georgian states with a valid passport (or ID card for EU/Turkish citizens) and visa (where required) may ask for a temporary residence permit which may extend up to a period of 6 years. The decision of giving the residence permit is totally up to the City Hall of the corresponding area. Generally people who come for medical treatment or business are warmly welcomed.
Permanent residence permit
Anyone who has stayed a period of 6 years in Georgia with a temporary residence permit may apply for a permanent residence permit.
Visas and Residence permit
Foreign staff of diplomatic missions and consular posts, as well as similar representations accredited to Georgia need visas for their first entry to the territory of Georgia. During their accreditation period they stay in the country and cross the border on the basis of an accreditation card issued according to the determined rule of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Georgia, if other is not provided by international obligation.
In cases determined by the Georgian legislation a visa/entry permit for up 90 days (visa fee 50 GEL) or for 360 days (visa fee 100 GEL) can be issued by the Patrol Police of Georgia (sub-divisional institution of the Ministry of Internal Affairs) at border crossing points situated at the Georgian State Border.
The basis for the stay of an alien in Georgia is a visa or residence permit (permanent or temporary) if other is not provided by this law and international treaties of Georgia.
Visa requirements for entering the Georgian territory
The citizens of Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and foreign nationals, who permanently reside in the United States, the Republic of Lithuania, Swiss Confederation, Germany, Republic of Korea, Czech Republic, Republic of Hungary, Republic of Poland, Republic of Slovenia, Kingdom of Denmark, Republic of Ireland, Kingdom of Norway, Kingdom of Sweden, Kingdom of Spain, Republic of Bulgaria, Slovak Republic, Republic of Romania, United Mexican States, Republic of Estonia and the Republic of Latvia and possess a document certifying permanent residence in one of these countries, do not need a visa to enter and stay in the territory of Georgia up to 360 days.
Foreign nationals, who have temporary residence document and reside in the territory of Qatar, Sultanate of Oman, Kingdom of Bahrain and State of Kuwait do not need a visa to enter and stay in the territory of Georgia up to 360 days. The citizens of Russian Federation and foreign nationals residing in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia having valid resident permit do not need a visa to enter and stay in the territory of Georgia up to 90 days.
Georgian, Turkish and EU citizens can enter Georgia on a national ID card.
Foreign nationals who are holders of the United Nations', or its specialized agencies', travel documents (Laissez-Passer), can enter or stay in the territory of Georgia without a visa up to 90 days.
Special Nationality
An application is to be written to the president of Georgia. He has the right to grant the Georgian nationality to anyone. The president of Georgia can grant nationality to a national of a foreign country, dual nationality, if he finds him important to the national interest of the state of Georgia. Thus, by decree of the president of Georgia, the foreign nationality who had been granted the nationality of Georgia by declaration of the president will keep his foreign nationality, dual nationality, that was allowed for Georgians only in this specific case. This way of granting Georgian nationality also became a way for the president to enable ethnic Georgians in the past, who left Georgia during the Soviet era, and their descendants who had been born out of Georgia, to reunite with their homestate and be naturalized Georgians in order to reconnect with their ancestral homeland, which was also considered as a national goal and the state interest.
Keeping in consideration that granting the nationality to a particular person is beneficial for Georgia, such special nationality is granted without the need of fulfilling the 'residence and language' requirements.
Travel freedom
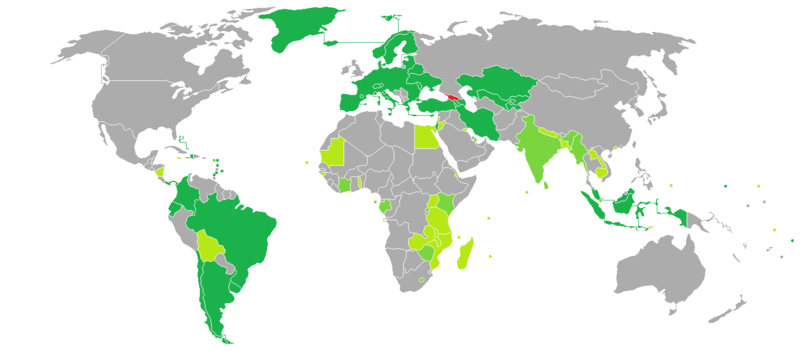
A Georgian citizen may travel visa-free to 69 countries (as of 01.01.2017), although the EU/Schengen states are not among these 69, Georgian nationals are granted to travel visa-free to the EU and the Schengen area (except for the UK and Ireland). This regulation entered into force on 28 March 2017.
In 2016, Georgian citizens had visa-free or visa on arrival access to 67 countries and territories, ranking the Georgian passport 71st in the world according to the Visa Restrictions Index.