George Viner Ellis
George Viner Ellis FRS (25 September 1812 Minsterworth - 25 April 1900 Minsterworth) was Professor of Anatomy at University College London and one of the foremost anatomists of his time.[1][2]
George Viner was the second son of Viner Ellis of Duni House, Minsterworth, near Gloucester, his family having been landowners in the area for many years. His education was at the Crypt Grammar School from where he went to the Cathedral Grammar School, and later was apprenticed to a Dr Buchanan of Gloucester. His uncle, Daniel Ellis, a member of the Royal Society Edinburgh, suggested that he enrol as a medical student at the newly founded University College London. In his vacations he studied in Paris and attended lectures and worked at anatomy in Berlin.
Ellis was Demonstrator of Anatomy under Professor Richard Quain, and succeeded him in the Chair of Anatomy in 1850, retiring as Emeritus Professor in 1877, but always aloof from the professional world. He was succeeded by Sir George Dancer Thane (1850-1930).[3] Ellis was one of the great names of the world of anatomy in England, having given all his working life to the study and teaching of this discipline, and was held in the highest respect. His lectures were conscientiously precise and lucid, so that his students always paid close attention.
In 1840 he published "Demonstrations of Anatomy: being a Guide to the Knowledge of the Human Body by Dissections", his name becoming a household word among medical students, and his work becoming the standard textbook in England and the United States. The 11th edition of his book was published in 1890.
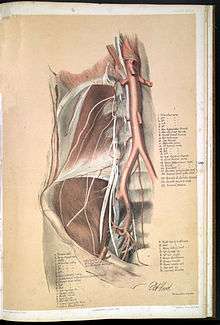
University College London in its first thirty-five years of existence, published an extraordinary number of anatomical atlases. Ellis carried on this tradition by collaborating with the South African natural history illustrator, George Henry Ford, to produce some of the best anatomical artwork ever published. They used the relatively new technique of chromolithography for their imperial folio atlas of fifty-eight plates, "Illustrations of Dissections in a Series of Original Coloured Plates the Size of Life". The plates were done between 1863 and 1867, with from four to seven completed each year. These plates are considered exceptionally clear and accurate, with an aesthetic depiction of the cadavers, printed by Mintern Bros., and published by James Walton.[4]
During Ellis' tenure the University College London was regarded as the pre-eminent centre for the study of anatomy, its spacious and well-lit dissecting room approved of by both staff and students. The College was fortunate in acquiring and retaining the services of an anatomist of Ellis' stature - his culture, zeal, and energy were legendary - receiving only a moderate salary and with no prospect of career improvement. In Ellis' day cadavers were not treated with any preservatives, so that they were often in an advanced state of putrefaction, limiting dissection to the winter months. Several times he acted as Examiner in Anatomy at the University of London, but declined to join the Court of Examiners of the Royal College of Surgeons.
On his retirement Ellis came into a small fortune left him by a relative, built himself a house at Minsterworth, 'Severn Bank', and lived there quietly with his younger sister, devoting himself to gardening and apple-growing. He also ran night classes for the older boys of the parish. A few years before his death he became blind and was tended by his sister.[5]
"Ellis' muscle", the Corrugator cutis ani muscle, is named after him.[6]
Publications
- "Demonstrations of anatomy : being a guide to the knowledge of the human body by dissection" - George Viner Ellis (London : J. Walton, 1840)
- "Illustrations of dissections in a series of original coloured plates : the size of life, representing the dissection of the human body" - George Viner Ellis and G. H. Ford. (London : Walton, 1867)
Ellis wrote the greater part of the description of the nerves in Sharpey's edition of Jones Quain's "Elements of Anatomy", 6th ed., 1856, and contributed several papers on scientific subjects to the London Medical Gazette.
References
- ↑ "George Viner Ellis, F.R.C.S". The British Medical Journal. 1 (2053): 1132. 1900. PMC 2506159
 . doi:10.1136/bmj.1.2053.1132.
. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.2053.1132. - ↑ "Ellis, George Viner - Biographical entry - Plarr's Lives of the Fellows Online". rcseng.ac.uk.
- ↑ http://www.ucl.ac.uk/cdb/about/history/thane_obiturary.pdf
- ↑ Christie?s. "ELLIS, George Viner (1812-1900) and George Henry FORD (1809-1876). Illustrations of Dissections in a Series of Original Coloured Plates the Size of Life. London: James Walton, 1867.". christies.com.
- ↑ "Erratum" (PDF). British Medical Journal. 1 (2057): 1392. PMC 2506507
 . doi:10.1136/bmj.1.2057.1392.
. doi:10.1136/bmj.1.2057.1392. - ↑ "Glossary of Eponyms". dartmouth.edu.