Geometric algebra
The geometric algebra (GA) of a vector space is an algebraic structure, noted for its multiplication operation called the geometric product on a space of elements called multivectors, which is a superset of both the scalars and the vector space . Mathematically, a geometric algebra is defined as the Clifford algebra of a real vector space with a quadratic form. In practice, several derived operations are generally defined, and together these allow a correspondence of elements, subspaces and operations of the algebra with physical interpretations. A derived operation, the exterior product, defines an exterior algebra on the same space and provides many of the interpretations of its elements, as well as demonstrating that a GA is basis-independent.
The scalars and vectors have their usual interpretation, and make up distinct subspaces of a GA. Bivectors provide a more natural representation of pseudovector quantities in vector algebra such as oriented area, oriented angle of rotation, torque, angular momentum, electromagnetic field and the Poynting vector. A trivector can represent an oriented volume, and so on. An element called a blade may be used to represent a subspace of and orthogonal projections onto that subspace. Rotations and reflections are represented as elements. Unlike vector algebra, a GA naturally accommodates any number of dimensions and any quadratic form such as in relativity. However, a direct representation within the algebra has not been found for all physical and geometric operations, including general linear transforms of , which are represented as a class of linear function named outermorphisms, as well as other quantities such as the stress–energy tensor or Ricci curvature, in contrast with the more universal tensor algebra.
Specific examples of geometric algebras applied in physics include the algebra of physical space, the spacetime algebra, and the conformal geometric algebra. Geometric calculus, an extension of GA that incorporates differentiation and integration, can be used to formulate other theories such as complex analysis, differential geometry, e.g. by using the Clifford algebra instead of differential forms. Geometric algebra has been advocated, most notably by David Hestenes[1] and Chris Doran,[2] as the preferred mathematical framework for physics. Proponents claim that it provides compact and intuitive descriptions in many areas including classical and quantum mechanics, electromagnetic theory and relativity.[3] GA has also found use as a computational tool in computer graphics[4] and robotics.
The geometric product was first briefly mentioned by Hermann Grassmann, who was chiefly interested in developing the closely related exterior algebra, which is the geometric algebra of the trivial quadratic form. In 1878, William Kingdon Clifford greatly expanded on Grassmann's work to form what are now usually called Clifford algebras in his honor (although Clifford himself chose to call them "geometric algebras"). For several decades, geometric algebras went somewhat ignored, greatly eclipsed by the vector calculus then newly developed to describe electromagnetism. The term "geometric algebra" was repopularized by Hestenes in the 1960s, who advocated its importance to relativistic physics.[5]
Definition and notation
Given a finite-dimensional real quadratic space with a symmetric bilinear form (e.g. the Euclidean or Lorentzian metric) , the geometric algebra for this quadratic space is the Clifford algebra .
The algebra product is called the geometric product. It is standard to denote the geometric product by juxtaposition (i.e., suppressing any explicit multiplication symbol). The above definition of the geometric algebra is abstract, so we summarize the properties of the geometric product by the following set of axioms. The geometric product has the following properties:
- , where is the unit and any element of the algebra (existence of an identity element)
- , where , and are any elements of the algebra (associativity)
- and , where , and are any elements of the algebra (distributivity)
- , where is any element of the subspace of the algebra.
Note that in the final property above, the real number need not be nonnegative if is not positive-definite. An important property of the geometric product is the existence of elements having a multiplicative inverse. If for some vector , then exists and is equal to . A nonzero element of the algebra does not necessarily have a multiplicative inverse. For example, if is a vector in such that , the element is both a nontrivial idempotent element and a nonzero zero divisor, and thus has no inverse.[lower-alpha 1]
It is usual to identify with , with associated natural embeddings and . For the remainder of this article, this identification is assumed. Throughout, the term vector refers to an element of (and its image under this embedding), and is synonymous with -vector.
Inner and exterior product of vectors



For vectors and , we may write the geometric product of any two vectors and as the sum of a symmetric product and an antisymmetric product:
Thus we can define the inner product of vectors as
so that the symmetric product can be written as
Conversely, is completely determined by the algebra. The antisymmetric part is the exterior product (also called the outer product) of the two vectors, the product of the contained exterior algebra:
The inner and exterior products are associated with familiar concepts from standard vector algebra. Geometrically, and are parallel if their geometric product is equal to their inner product, whereas and are perpendicular if their geometric product is equal to their exterior product. In a geometric algebra for which the square of any nonzero vector is positive, the inner product of two vectors can be identified with the dot product of standard vector algebra. The exterior product of two vectors can be identified with the signed area enclosed by a parallelogram the sides of which are the vectors. The cross product of two vectors in dimensions with positive-definite quadratic form is closely related to their exterior product.
Most instances of geometric algebras of interest have a nondegenerate quadratic form. If the quadratic form is fully degenerate, the inner product of any two vectors is always zero, and the geometric algebra is then simply an exterior algebra. Unless otherwise stated, this article will treat only nondegenerate geometric algebras.
The exterior product is naturally extended as an associative bilinear binary operator between any two elements of the algebra, satisfying the identities
where the sum is over all permutations of the indices, with the sign of the permutation, and are vectors (not general elements of the algebra). Since every element of the algebra can be expressed as the sum of products of this form, this defines the exterior product for every pair of elements of the algebra. It follows from the definition that the exterior product forms an alternating algebra.
Blades, grades, and canonical basis
A multivector that is the exterior product of independent vectors () is called a blade, and the blade is said to be a multivector of grade . From the axioms, with closure, every multivector of the geometric algebra is a sum of blades.
Consider a set of independent vectors spanning an -dimensional subspace of the vector space. With these, we can define a real symmetric matrix
By the spectral theorem, can be diagonalized to diagonal matrix by an orthogonal matrix via
Define a new set of vectors , known as orthogonal basis vectors, to be those transformed by the orthogonal matrix:
Since orthogonal transformations preserve inner products, it follows that and thus the are perpendicular. In other words, the geometric product of two distinct vectors is completely specified by their exterior product, or more generally
Therefore, every blade of grade can be written as a geometric product of vectors. More generally, if a degenerate geometric algebra is allowed, then the orthogonal matrix is replaced by a block matrix that is orthogonal in the nondegenerate block, and the diagonal matrix has zero-valued entries along the degenerate dimensions. If the new vectors of the nondegenerate subspace are normalized according to
then these normalized vectors must square to or . By Sylvester's law of inertia, the total number of s and the total number of s along the diagonal matrix is invariant. By extension, the total number of these vectors that square to and the total number that square to is invariant. (If the degenerate case is allowed, then the total number of basis vectors that square to zero is also invariant.) We denote this algebra . For example, models -dimensional Euclidean space, relativistic spacetime and a conformal geometric algebra of a -dimensional space.
The set of all possible products of orthogonal basis vectors with indices in increasing order, including as the empty product, forms a basis for the entire geometric algebra (an analogue of the PBW theorem). For example, the following is a basis for the geometric algebra :
A basis formed this way is called a canonical basis for the geometric algebra, and any other orthogonal basis for will produce another canonical basis. Each canonical basis consists of elements. Every multivector of the geometric algebra can be expressed as a linear combination of the canonical basis elements. If the canonical basis elements are with being an index set, then the geometric product of any two multivectors is
Grade projection
Using an orthogonal basis, a graded vector space structure can be established. Elements of the geometric algebra that are scalar multiples of are grade- blades and are called scalars. Multivectors that are in the span of are grade- blades and are the ordinary vectors. Multivectors in the span of are grade- blades and are the bivectors. This terminology continues through to the last grade of -vectors. Alternatively, grade- blades are called pseudoscalars, grade- blades pseudovectors, etc. Many of the elements of the algebra are not graded by this scheme since they are sums of elements of differing grade. Such elements are said to be of mixed grade. The grading of multivectors is independent of the basis chosen originally.
A multivector may be decomposed with the grade-projection operator , which outputs the grade- portion of . As a result:
As an example, the geometric product of two vectors since and and , for other than and .
The decomposition of a multivector may also be split into those components that are even and those that are odd:
This makes the algebra a -graded algebra or superalgebra with the geometric product. Since the geometric product of two even multivectors is an even multivector, they define an even subalgebra. The even subalgebra of an -dimensional geometric algebra is isomorphic to a full geometric algebra of dimensions. Examples include and .
Representation of subspaces
Geometric algebra represents subspaces of as blades, and so they coexist in the same algebra with vectors from . A -dimensional subspace of is represented by taking an orthogonal basis and using the geometric product to form the blade . There are multiple blades representing ; all those representing are scalar multiples of . These blades can be separated into two sets: positive multiples of and negative multiples of . The positive multiples of are said to have the same orientation as , and the negative multiples the opposite orientation.
Blades are important since geometric operations such as projections, rotations and reflections depend on the factorability via the exterior product that (the restricted class of) -blades provide but that (the generalized class of) grade- multivectors do not when .
Unit pseudoscalars
Unit pseudoscalars are blades that play important roles in GA. A unit pseudoscalar for a non-degenerate subspace of is a blade that is the product of the members of an orthonormal basis for . It can be shown that if and are both unit pseudoscalars for , then and .
Suppose the geometric algebra with the familiar positive definite inner product on is formed. Given a plane (-dimensional subspace) of , one can find an orthonormal basis spanning the plane, and thus find a unit pseudoscalar representing this plane. The geometric product of any two vectors in the span of and lies in , that is, it is the sum of a -vector and a -vector.
By the properties of the geometric product, . The resemblance to the imaginary unit is not incidental: the subspace is -algebra isomorphic to the complex numbers. In this way, a copy of the complex numbers is embedded in the geometric algebra for each 2-dimensional subspace of on which the quadratic form is definite.
It is sometimes possible to identify the presence of an imaginary unit in a physical equation. Such units arise from one of the many quantities in the real algebra that square to , and these have geometric significance because of the properties of the algebra and the interaction of its various subspaces.
In , a further familiar case occurs. Given a canonical basis consisting of orthonormal vectors of , the set of all -vectors is spanned by
Labelling these , and (momentarily deviating from our uppercase convention), the subspace generated by -vectors and -vectors is exactly . This set is seen to be a subalgebra, and furthermore is -algebra isomorphic to the quaternions, another important algebraic system.
Dual basis
Let be a basis of , i.e. a set of linearly independent vectors that span the -dimensional vector space . The basis that is dual to is the set of elements of the dual vector space that forms a biorthogonal system with this basis, thus being the elements denoted satisfying
where is the Kronecker delta.
Given a nondegenerate quadratic form on , becomes naturally identified with , and the dual basis may be regarded as elements of , but are not in general the same set as the original basis.
Given further a GA of , let
be the pseudoscalar (which does not necessarily square to ) formed from the basis . The dual basis vectors may be constructed as
where the denotes that the th basis vector is omitted from the product.
Extensions of the inner and exterior products
It is common practice to extend the exterior product on vectors to the entire algebra. This may be done through the use of the grade projection operator:
- (the exterior product)
This generalization is consistent with the above definition involving antisymmetrization. Another generalization related to the exterior product is the commutator product:
The regressive product is the dual of the exterior product:
with the unit pseudoscalar of the algebra. The regressive product, like the exterior product, is associative.[9]
The inner product on vectors can also be generalized, but in more than one non-equivalent way. The paper (Dorst 2002) gives a full treatment of several different inner products developed for geometric algebras and their interrelationships, and the notation is taken from there. Many authors use the same symbol as for the inner product of vectors for their chosen extension (e.g. Hestenes and Perwass). No consistent notation has emerged.
Among these several different generalizations of the inner product on vectors are:
- (the left contraction)
- (the right contraction)
- (the scalar product)
- (the "(fat) dot" product)[lower-alpha 2]
Dorst (2002) makes an argument for the use of contractions in preference to Hestenes's inner product; they are algebraically more regular and have cleaner geometric interpretations. A number of identities incorporating the contractions are valid without restriction of their inputs. For example,
Benefits of using the left contraction as an extension of the inner product on vectors include that the identity is extended to for any vector and multivector , and that the projection operation is extended to for any blade and any multivector (with a minor modification to accommodate null , given below).
Terminology specific to geometric algebra
Some terms are used in geometric algebra with a meaning that differs from the use of those terms in other fields of mathematics. Some of these are listed here:
- Vector
- In GA this refers to an element of the -vector subspace unless otherwise clear from the context, despite the entire algebra forming a vector space.
- Grade
- When used in GA, this is a synonym for degree of a homogeneous element under the grading as an algebra with the exterior product (a -grading), and not under the geometric product.[lower-alpha 3]
- Outer product
- When used in GA, this is a synonym for exterior product, the term used by many authors. It is not the outer product of linear algebra.
- Inner product
- When used in GA, this is synonym for the scalar product of a pseudo-Euclidean vector space, and refers to the symmetric bilinear form on the -vector subspace, not the inner product on a normed vector space. Some authors may extend the meaning of inner product to the entire algebra, but there is little consensus on this. Even in texts on geometric algebras, the term is not universally used.
- Versor
- In GA this refers to an element of the algebra that can be constructed as the geometric product of any number of non-null vectors; an element of the Clifford group. Elsewhere, the term versor may refer to a unit quaternion, which is analogous to a rotor in GA.
- Outermorphism
- In GA this refers to the extension of a linear map on the vector subspace that preserves the exterior product. It is unrelated to the contraction of outer automorphism that is sometimes used in group theory.
Geometric interpretation
Projection and rejection
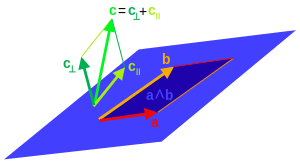
For any vector and any invertible vector ,
where the projection of onto (or the parallel part) is
and the rejection of onto (or the perpendicular part) is
Using the concept of a -blade as representing a subspace of and every multivector ultimately being expressed in terms of vectors, this generalizes to projection of a general multivector onto any invertible -blade as[lower-alpha 4]
with the rejection being defined as
The projection and rejection generalize to null blades by replacing the inverse with the pseudoinverse with respect to the contractive product.[lower-alpha 5] The outcome of the projection coincides in both cases for non-null blades.[10][11] For null blades , the definition of the projection given here with the first contraction rather than the second being onto the pseudoinverse should be used,[lower-alpha 6] as only then is the result necessarily in the subspace represented by .[10] The projection generalizes through linearity to general multivectors .[lower-alpha 7] The projection is not linear in and does not generalize to objects that are not blades.
Reflection
Simple reflections in a hyperplane are readily expressed in the algebra through conjugation with a single vector. These serve to generate the group of general rotoreflections and rotations.[lower-alpha 8]

The reflection of a vector along a vector , or equivalently in the hyperplane orthogonal to , is the same as negating the component of a vector parallel to . The result of the reflection will be
This is not the most general operation that may be regarded as a reflection when the dimension . A general reflection may be expressed as the composite of any odd number of single-axis reflections. Thus, a general reflection of a vector may be written
where
- and
If we define the reflection along a non-null vector of the product of vectors as the reflection of every vector in the product along the same vector, we get for any product of an odd number of vectors that, by way of example,
and for the product of an even number of vectors that
Using the concept of every multivector ultimately being expressed in terms of vectors, the reflection of a general multivector using any reflection versor may be written
where is the automorphism of reflection through the origin of the vector space () extended through linearity to the whole algebra.
Rotations

If we have a product of vectors then we denote the reverse as
As an example, assume that we get
Scaling so that then
so leaves the length of unchanged. We can also show that
so the transformation preserves both length and angle. It therefore can be identified as a rotation or rotoreflection; is called a rotor if it is a proper rotation (as it is if it can be expressed as a product of an even number of vectors) and is an instance of what is known in GA as a versor (presumably for historical reasons).
There is a general method for rotating a vector involving the formation of a multivector of the form that produces a rotation in the plane and with the orientation defined by a -blade .
Rotors are a generalization of quaternions to -dimensional spaces.
For more about reflections, rotations and "sandwiching" products like see Plane of rotation.
Hypervolume of a parallelotope spanned by vectors
For vectors and spanning a parallelogram we have
with the result that is linear in the product of the "altitude" and the "base" of the parallelogram, that is, its area.
Similar interpretations are true for any number of vectors spanning an -dimensional parallelotope; the exterior product of vectors , that is , has a magnitude equal to the volume of the -parallelotope. An -vector does not necessarily have a shape of a parallelotope – this is a convenient visualization. It could be any shape, although the volume equals that of the parallelotope.
Linear functions
An important class of functions of multivectors are the linear functions that map multivectors to multivectors. The geometric algebra of an -dimensional vector space is spanned by a basis of elements. If a multivector is represented by a real column matrix in terms of a basis, then all linear transformations of the multivector can be expressed as the matrix multiplication by a real matrix. However, such a general linear transformation allows arbitrary exchanges among grades, such as a "rotation" of a scalar into a vector, which has no evident geometric interpretation.
A general linear transformation from vectors to vectors is of interest. With the natural restriction to preserving the induced exterior algebra, the outermorphism of the linear transformation is its unique extension. If is a linear function that maps vectors to vectors, then its outermorphism is the function that obeys the rule
for a blade, extended to the whole algebra through linearity.
In the cases of reflections and rotations, their outermorphisms have a particularly simple algebraic form. Specifically, a mapping of vectors of the form
extends to the outermorphism
Examples and applications
Intersection of a line and a plane

We may define the line parametrically by where and are position vectors for points T and P and is the direction vector for the line.
Then
- and
so
and
Rotating systems
The mathematical description of rotational forces such as torque and angular momentum often makes use of the cross product of vector calculus in three dimensions with a convention of orientation (handedness).

The cross product can be viewed in terms of the exterior product allowing a more natural geometric interpretation of the cross product as a bivector using the dual relationship
For example, torque is generally defined as the magnitude of the perpendicular force component times distance, or work per unit angle.
Suppose a circular path in an arbitrary plane containing orthonormal vectors and is parameterized by angle.
By designating the unit bivector of this plane as the imaginary number
this path vector can be conveniently written in complex exponential form
and the derivative with respect to angle is
So the torque, the rate of change of work , due to a force , is
Unlike the cross product description of torque, , the geometric algebra description does not introduce a vector in the normal direction; a vector that does not exist in two and that is not unique in greater than three dimensions. The unit bivector describes the plane and the orientation of the rotation, and the sense of the rotation is relative to the angle between the vectors and .
Electrodynamics and special relativity
In physics, the main applications are the geometric algebra of Minkowski 3+1 spacetime, Cl1,3, called spacetime algebra (STA),[5] or less commonly, Cl3, called the algebra of physical space (APS) where Cl3 is isomorphic to the even subalgebra of the 3+1 Clifford algebra, Cl0
3,1.
While in STA points of spacetime are represented simply by vectors, in APS, points of -dimensional spacetime are instead represented by paravectors: a -dimensional vector (space) plus a -dimensional scalar (time).
In spacetime algebra the electromagnetic field tensor has a bivector representation .[12] Here, the is the unit pseudoscalar (or four-dimensional volume element), is the unit vector in time direction, and and are the classic electric and magnetic field vectors (with a zero time component). Using the four-current , Maxwell's equations then become
Formulation Homogeneous equations Non-homogeneous equations Fields Potentials (any gauge) Potentials (Lorenz gauge)
In geometric calculus, juxtapositioning of vectors such as in indicate the geometric product and can be decomposed into parts as . Here is the covector derivative in any spacetime and reduces to in flat spacetime. Where plays a role in Minkowski -spacetime which is synonymous to the role of in Euclidean -space and is related to the d'Alembertian by . Indeed, given an observer represented by a future pointing timelike vector we have
Boosts in this Lorentzian metric space have the same expression as rotation in Euclidean space, where is the bivector generated by the time and the space directions involved, whereas in the Euclidean case it is the bivector generated by the two space directions, strengthening the "analogy" to almost identity.
Relationship with other formalisms
may be directly compared to vector algebra.
The even subalgebra of is isomorphic to the complex numbers, as may be seen by writing a vector in terms of its components in an orthonormal basis and left multiplying by the basis vector , yielding
where we identify since
Similarly, the even subalgebra of with basis is isomorphic to the quaternions as may be seen by identifying , and .
Every associative algebra has a matrix representation; the Pauli matrices are a representation of and the Dirac matrices are a representation of , showing the equivalence with matrix representations used by physicists.
Geometric calculus
Geometric calculus extends the formalism to include differentiation and integration including differential geometry and differential forms.[13]
Essentially, the vector derivative is defined so that the GA version of Green's theorem is true,
and then one can write
as a geometric product, effectively generalizing Stokes' theorem (including the differential form version of it).
In when is a curve with endpoints and , then
reduces to
or the fundamental theorem of integral calculus.
Also developed are the concept of vector manifold and geometric integration theory (which generalizes Cartan's differential forms).
Conformal geometric algebra (CGA)
A compact description of the current state of the art is provided by Bayro-Corrochano & Scheuermann (2010), which also includes further references, in particular to Dorst, Fontijne & Mann (2007). Other useful references are Li (2008) and Bayro-Corrochano (2010).

Working within GA, Euclidean space is embedded projectively in the CGA via the identification of Euclidean points with -d subspaces in the -d null cone of the -d CGA vector subspace, and adding a point at infinity. This allows all conformal transformations to be done as rotations and reflections and is covariant, extending incidence relations of projective geometry to circles and spheres.
Specifically, we add orthogonal basis vectors and such that and to the basis of and identify null vectors
- as an ideal point (point at infinity) (see Compactification) and
- as the point at the origin, giving
- .
This procedure has some similarities to the procedure for working with homogeneous coordinates in projective geometry and in this case allows the modeling of Euclidean transformations as orthogonal transformations.
A fast changing and fluid area of GA, CGA is also being investigated for applications to relativistic physics.
History
- Before the 20th century
Although the connection of geometry with algebra dates as far back at least to Euclid's Elements in the third century B.C. (see Greek geometric algebra), GA in the sense used in this article was not developed until 1844, when it was used in a systematic way to describe the geometrical properties and transformations of a space. In that year, Hermann Grassmann introduced the idea of a geometrical algebra in full generality as a certain calculus (analogous to the propositional calculus) that encoded all of the geometrical information of a space.[14] Grassmann's algebraic system could be applied to a number of different kinds of spaces, the chief among them being Euclidean space, affine space, and projective space. Following Grassmann, in 1878 William Kingdon Clifford examined Grassmann's algebraic system alongside the quaternions of William Rowan Hamilton in (Clifford 1878). From his point of view, the quaternions described certain transformations (which he called rotors), whereas Grassmann's algebra described certain properties (or Strecken such as length, area, and volume). His contribution was to define a new product — the geometric product – on an existing Grassmann algebra, which realized the quaternions as living within that algebra. Subsequently, Rudolf Lipschitz in 1886 generalized Clifford's interpretation of the quaternions and applied them to the geometry of rotations in dimensions. Later these developments would lead other 20th-century mathematicians to formalize and explore the properties of the Clifford algebra.
Nevertheless, another revolutionary development of the 19th-century would completely overshadow the geometric algebras: that of vector analysis, developed independently by Josiah Willard Gibbs and Oliver Heaviside. Vector analysis was motivated by James Clerk Maxwell's studies of electromagnetism, and specifically the need to express and manipulate conveniently certain differential equations. Vector analysis had a certain intuitive appeal compared to the rigors of the new algebras. Physicists and mathematicians alike readily adopted it as their geometrical toolkit of choice, particularly following the influential 1901 textbook Vector Analysis by Edwin Bidwell Wilson, following lectures of Gibbs.
In more detail, there have been three approaches to geometric algebra: quaternionic analysis, initiated by Hamilton in 1843 and geometrized as rotors by Clifford in 1878; geometric algebra, initiated by Grassmann in 1844; and vector analysis, developed out of quaternionic analysis in the late 19th century by Gibbs and Heaviside. The legacy of quaternionic analysis in vector analysis can be seen in the use of , , to indicate the basis vectors of : it is being thought of as the purely imaginary quaternions. From the perspective of geometric algebra, quaternions can be identified as Cl03,0(R), the even part of the Clifford algebra on Euclidean 3-space, which unifies the three approaches.
- 20th century and present
Progress on the study of Clifford algebras quietly advanced through the twentieth century, although largely due to the work of abstract algebraists such as Hermann Weyl and Claude Chevalley. The geometrical approach to geometric algebras has seen a number of 20th-century revivals. In mathematics, Emil Artin's Geometric Algebra[15] discusses the algebra associated with each of a number of geometries, including affine geometry, projective geometry, symplectic geometry, and orthogonal geometry. In physics, geometric algebras have been revived as a "new" way to do classical mechanics and electromagnetism, together with more advanced topics such as quantum mechanics and gauge theory.[2] David Hestenes reinterpreted the Pauli and Dirac matrices as vectors in ordinary space and spacetime, respectively, and has been a primary contemporary advocate for the use of geometric algebra.
In computer graphics and robotics, geometric algebras have been revived in order to efficiently represent rotations and other transformations. For applications of GA in robotics (screw theory, kinematics and dynamics using versors), computer vision, control and neural computing (geometric learning) see Bayro (2010).
Software
GA is a very application-oriented subject. There is a reasonably steep initial learning curve associated with it, but this can be eased somewhat by the use of applicable software.
The following is a list of freely available software that does not require ownership of commercial software or purchase of any commercial products for this purpose:
- GA Viewer Fontijne, Dorst, Bouma & Mann
- galgebra modules for sympy Alan Bromborsky
The link provides a manual, introduction to GA and sample material as well as the software.
- CLUViz Perwass
Software allowing script creation and including sample visualizations, manual and GA introduction.
- Gaigen Fontijne
For programmers, this is a code generator with support for C, C++, C# and Java.
- Cinderella Visualizations Hitzer and Dorst.
- Gaalop Standalone GUI-Application that uses the Open-Source Computer Algebra Software Maxima to break down CLUViz code into C/C++ or Java code.
- Gaalop Precompiler Precompiler based on Gaalop integrated with CMake.
- Gaalet, C++ Expression Template Library Seybold.
- Versor Colapinto, A lightweight templated C++ Library with an OpenGL interface for efficient geometric algebra programming in arbitrary metrics, including conformal
- Clifford Algebra with Mathematica clifford.m
See also
- Comparison of vector algebra and geometric algebra
- Clifford algebra
- Spacetime algebra
- Spinor
- Quaternion
- Algebra of physical space (wikibooks:Physics in the Language of Geometric Algebra. An Approach with the Algebra of Physical Space)
- Universal geometric algebra
Notes
- ↑ Given , we have that , showing that is idempotent, and that , showing that it is a nonzero zero divisor.
- ↑ This should not be confused with Hestenes's irregular generalization , where the distinguishing notation is from Dorst, Fontijne & Mann (2007), §B.1 p. 590, which makes the point that scalar components must be handled separately with this product.
- ↑ When referring to grading under the geometric product, the literature generally only focuses on a -grading, meaning the split into even and odd -grades. is a subgroup of the full -grading of the geometric product.
- ↑ This definition follows Dorst (2007) and Perwass (2009) – the left contraction used by Dorst replaces the ("fat dot") inner product that Perwass uses, consistent with Perwass's constraint that grade of may not exceed that of .
- ↑ Dorst appears to merely assume such that , whereas Perwass (2009) defines , where is the conjugate of , equivalent to the reverse of up to a sign.
- ↑ That is to say, the projection must be defined as and not as , though the two are equivalent for non-null blades .
- ↑ This generalization to all is apparently not considered by Perwass or Dorst.
- ↑ Perwass also claims here that David Hestenes coined the term "versor", where he is presumably referring to the GA context (the term versor appears to have been used by Hamilton to refer to a related object of the quaternion algebra).
Citations
- ↑ Hestenes 2003.
- 1 2 Doran 1994.
- ↑ Lasenby, Lasenby & Doran 2000.
- ↑ Hildenbrand et al. 2004.
- 1 2 Hestenes 1966.
- 1 2 Hestenes, David (2005), Introduction to Primer for Geometric Algebra
- ↑ Penrose 2007.
- ↑ Wheeler & Misner 1973, p. 83.
- ↑ Vaz & da Rocha 2016, §2.8.
- 1 2 Dorst 2007, §3.6 p. 85.
- ↑ Perwass 2009, §3.2.10.2 p. 83.
- ↑ "Electromagnetism using Geometric Algebra versus Components". Retrieved 2013-03-19.
- ↑ Hestenes & Sobczyk 1984.
- ↑ Grassmann 1844.
- ↑ Artin 1957.
References and further reading
- Grassmann, Hermann (1844), Die lineale Ausdehnungslehre ein neuer Zweig der Mathematik: dargestellt und durch Anwendungen auf die übrigen Zweige der Mathematik, wie auch auf die Statik, Mechanik, die Lehre vom Magnetismus und die Krystallonomie erläutert, Leipzig: O. Wigand, OCLC 20521674
- Artin, Emil (1957), Geometric algebra, Wiley Classics Library, New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc. (published 1988), ISBN 0-471-60839-4, MR 1009557 (Reprint of the 1957 original)
- Hestenes, David (1966), Space–time Algebra, New York: Gordon and Breach, ISBN 978-0-677-01390-9, OCLC 996371
- Wheeler, J. A.; Misner, C.; Thorne, K. S. (1973), Gravitation, W.H. Freeman & Co, ISBN 0-7167-0344-0
- Bourbaki, Nicolas (1980), Eléments de Mathématique. Algèbre, Hermann, Ch. 9 "Algèbres de Clifford"
- Hestenes, David; Sobczyk, Garret (1984), Clifford Algebra to Geometric Calculus, a Unified Language for mathematics and Physics, Springer Netherlands
- Doran, Chris J. L. (1994), Geometric Algebra and its Application to Mathematical Physics (PhD thesis), University of Cambridge, OCLC 53604228, archived from the original on 2014-11-29
- Baylis, W. E., ed. (1996), Clifford (Geometric) Algebra with Applications to Physics, Mathematics, and Engineering, Birkhäuser
- Hestenes, David (1999), New Foundations for Classical Mechanics (2 ed.), Springer Verlag, ISBN 978-0-7923-5302-7
- Lasenby, Joan; Lasenby, Anthony N.; Doran, Chris J. L. (2000), "A Unified Mathematical Language for Physics and Engineering in the 21st Century" (PDF), Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, pp. 1–18, 358 (A 358): 21, Bibcode:2000RSPTA.358...21L, doi:10.1098/rsta.2000.0517
- Baylis, W. E. (2002), Electrodynamics: A Modern Geometric Approach (2 ed.), Birkhäuser, ISBN 978-0-8176-4025-5
- Dorst, Leo (2002), The inner products of geometric algebra, Boston, MA: Birkhäuser Boston, pp. 35−46
- Hestenes, David (2003), "Oersted Medal Lecture 2002: Reforming the Mathematical Language of Physics" (PDF), Am. J. Phys., 71 (2): 104–121, Bibcode:2003AmJPh..71..104H, doi:10.1119/1.1522700
- Doran, Chris J. L.; Lasenby, Anthony N. (2003), Geometric algebra for physicists (PDF), Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-71595-9
- Hildenbrand, Dietmar; Fontijne, Daniel; Perwass, Christian; Dorst, Leo (2004), "Geometric Algebra and its Application to Computer Graphics" (PDF), Proceedings of Eurographics 2004
- Bain, J. (2006), "Spacetime structuralism: §5 Manifolds vs. geometric algebra", in Dennis Dieks, The ontology of spacetime, Elsevier, p. 54 ff, ISBN 978-0-444-52768-4
- Dorst, Leo; Fontijne, Daniel; Mann, Stephen (2007), Geometric algebra for computer science: an object-oriented approach to geometry, Amsterdam: Elsevier/Morgan Kaufmann, ISBN 978-0-12-369465-2, OCLC 132691969
- Penrose, Roger (2007), The Road to Reality, Vintage books, ISBN 0-679-77631-1
- Li, Hongbo (2008), Invariant Algebras and Geometric Reasoning, Singapore: World Scientific. Extract online at http://www.worldscibooks.com/etextbook/6514/6514_chap01.pdf
- Vince, John A. (2008), Geometric Algebra for Computer Graphics, Springer, ISBN 978-1-84628-996-5
- Perwass, Christian (2009), Geometric Algebra with Applications in Engineering, Springer Science & Business Media, ISBN 978-3-540-89068-3
- Bayro-Corrochano, Eduardo (2010), Geometric Computing for Wavelet Transforms, Robot Vision, Learning, Control and Action, Springer Verlag
- Bayro-Corrochano, E.; Scheuermann, Gerik, eds. (2010), Geometric Algebra Computing in Engineering and Computer Science, Springer Extract online at http://geocalc.clas.asu.edu/html/UAFCG.html #5 New Tools for Computational Geometry and rejuvenation of Screw Theory
- Goldman, Ron (2010), Rethinking Quaternions: Theory and Computation, Morgan & Claypool Publishers, Part III. Rethinking Quaternions and Clifford Algebras, ISBN 978-1-60845-420-4
- Macdonald, Alan (2011), Linear and Geometric Algebra, Charleston: CreateSpace, ISBN 9781453854938, OCLC 704377582
- Snygg, John (2011), A New Approach to Differential Geometry using Clifford's Geometric Algebra, Springer Science & Business Media, ISBN 978-0-8176-8282-8
- Hildenbrand, Dietmar (2013), Foundations of Geometric Algebra Computing, Springer Science & Business Media, ISBN 978-3-642-31793-4
- Vaz, Jayme; da Rocha, Roldão (2016), An Introduction to Clifford Algebras and Spinors, ISBN 978-0-19-878292-6
External links
- A Survey of Geometric Algebra and Geometric Calculus Alan Macdonald, Luther College, Iowa.
- Imaginary Numbers are not Real – the Geometric Algebra of Spacetime. Introduction (Cambridge GA group).
- Geometric Algebra 2015, Masters Course in Scientific Computing, from Dr. Chris Doran (Cambridge).
- Maths for (Games) Programmers: 5 – Multivector methods. Comprehensive introduction and reference for programmers, from Ian Bell.
- "Geometric Algebra". PlanetMath.
- Clifford algebra, geometric algebra, and applications Douglas Lundholm, Lars Svensson Lecture notes for a course on the theory of Clifford algebras, with special emphasis on their wide range of applications in mathematics and physics.
- IMPA Summer School 2010 Fernandes Oliveira Intro and Slides.
- University of Fukui E.S.M. Hitzer and Japan GA publications.
- Google Group for GA
- Geometric Algebra Primer Introduction to GA, Jaap Suter.
- Geometric Algebra Resources curated wiki, Pablo Bleyer.
English translations of early books and papers
- G. Combebiac, "calculus of tri-quaternions" (Doctoral dissertation)
- M. Markic, "Transformants: A new mathematical vehicle. A synthesis of Combebiac's tri-quaternions and Grassmann's geometric system. The calculus of quadri-quaternions"
- C. Burali-Forti, "The Grassmann method in projective geometry" A compilation of three notes on the application of exterior algebra to projective geometry
- C. Burali-Forti, "Introduction to Differential Geometry, following the method of H. Grassmann" Early book on the application of Grassmann algebra
- H. Grassmann, "Mechanics, according to the principles of the theory of extension" One of his papers on the applications of exterior algebra.
Research groups
- Geometric Calculus International. Links to Research groups, Software, and Conferences, worldwide.
- Cambridge Geometric Algebra group. Full-text online publications, and other material.
- University of Amsterdam group
- Geometric Calculus research & development (Arizona State University).
- GA-Net blog and newsletter archive. Geometric Algebra/Clifford Algebra development news.
- Geometric Algebra for Perception Action Systems. Geometric Cybernetics Group (CINVESTAV, Campus Guadalajara, Mexico).