Gemini 5
 View of Cape Kennedy, Florida from Gemini V | |
| Operator | NASA |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 1965-068A[1] |
| SATCAT no. | 1516[2] |
| Mission duration | 7 days, 22 hours, 55 minutes, 14 seconds |
| Distance travelled | 5,242,682 kilometers (3,257,652 miles) |
| Orbits completed | 120 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Gemini SC5 |
| Manufacturer | McDonnell |
| Launch mass | 3,605 kilograms (7,948 lb) |
| Crew | |
| Crew size | 2 |
| Members |
L. Gordon Cooper, Jr. Charles "Pete" Conrad, Jr. |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | August 21, 1965, 13:59:59 UTC |
| Rocket | Titan II GLV, s/n 62-12560 |
| Launch site | Cape Kennedy LC-19 |
| End of mission | |
| Recovered by | USS Lake Champlain |
| Landing date | August 29, 1965, 12:55:13 UTC |
| Landing site | 29°47′N 69°45.4′W / 29.783°N 69.7567°W |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee | 170 kilometers (92 nautical miles) |
| Apogee | 330 kilometers (180 nautical miles) |
| Inclination | 32.5 degrees |
| Period | 89.5 minutes |
| Epoch | August 23, 1965[2] |
  (L-R) Conrad, Cooper | |
Gemini 5 (officially Gemini V)[3] was a 1965 manned spaceflight in NASA's Gemini program. It was the third manned Gemini flight, the eleventh manned American flight, and the nineteenth spaceflight of all time, including two X-15 flights above 100 kilometers (54 nmi). It was also the first time an American manned space mission held the world record for duration, set on August 26, 1965, by breaking the Soviet Union's previous record set by Vostok 5 in 1963.[4]
Crew
| Position | Astronaut | |
|---|---|---|
| Command Pilot | L. Gordon Cooper, Jr. Second and last spaceflight | |
| Pilot | Charles "Pete" Conrad, Jr. First spaceflight | |
Backup crew
| Position | Astronaut | |
|---|---|---|
| Command Pilot | Neil A. Armstrong | |
| Pilot | Elliot M. See, Jr. | |
Support crew
- Edwin E. "Buzz" Aldrin (Houston CAPCOM)
- Neil A. Armstrong (Houston CAPCOM)
- Virgil I. "Gus" Grissom (Cape CAPCOM)
- James A. McDivitt (Houston CAPCOM)
Mission parameters
- Mass: 3,605 kilograms (7,948 lb)
- Perigee: 162 kilometers (87 nmi)
- Apogee: 350.1 kilometers (189.0 nmi)
- Inclination: 32.61°
- Period: 89.59 min
- REP (Rendezvous Evaluation Pod) sub-satellite:
On August 21, 1965 at 16:07:15 UTC, the REP was released into orbit from the Gemini 5 spacecraft.
Objectives
Gemini 5 doubled the U.S space-flight record of the Gemini 4 mission to eight days, the length of time it would take to fly to the Moon, land and return. This was possible due to new fuel cells that generated enough electricity to power longer missions, a pivotal innovation for future Apollo flights, instead of the chemical batteries used on previous manned spacecraft. Cooper and Conrad were to have made a practice space rendezvous with a "pod" deployed from the spacecraft, but problems with the electrical supply forced a switch to a simpler "phantom rendezvous," whereby the Gemini craft maneuvered to a predetermined position in space. Command Pilot and Mercury veteran Gordon Cooper was the first person to fly two Earth orbital missions. He and Conrad took high-resolution photographs for the United States Department of Defense, but problems with the fuel cells and maneuvering system forced the cancellation of several other experiments. The astronauts found themselves marking time in orbit, and Conrad later lamented that he had not brought along a book. On-board medical tests, however, continued to show the feasibility of longer flights.
| Gemini 5 | REP |
|---|---|
| REP | Rendezvous Evaluation Pod |
| NSSDC ID: | 1965-068C |
| Mass | 34.5 kilograms (76 lb) |
| Launch date | August 21, 1965 |
| Release time | 16:07:15 UTC |
| Perigee | 162 kilometers (87 nmi) |
| Apogee | 350.1 kilometers (189.0 nmi) |
| Period | 89.59 min |
| Inclination | 32.61° |
| Reentered | August 27, 1965 |
Conrad, who had a reputation for frequently having a punchline on hand, called the mission "Eight days in a garbage can." (the garbage can referring to the small size of the Gemini cabin, which was about the size of the front seat of a Volkswagen Beetle)
Flight

The launch went perfectly except for a few seconds of Pogo oscillation (axial vibration of the rocket). This was measured at +0.38 g (3.7 m/s²) during first stage flight, exceeding the permitted +0.25 g (2.5 m/s²) for a total of about 13 seconds. Conrad and Cooper found their vision and speech momentarily impaired by the strong vibrations. The cause was traced to improper gas levels in an oxidizer standpipe, and severe oscillations did not affect any subsequent Gemini flights. The initial orbit was 101x216 miles (163x349 kilometers).
Film of the launch revealed a series of unexplained light flashes in the first stage exhaust plume, but telemetry data failed to indicate anything that could have caused them. Subsequent review of previous Gemini launches as well as film of Titan II ICBM tests also showed the presence of these light flashes. This phenomenon was thought to be caused by duct tape securing desiccant bags to the turbine exhaust pipe.
The top half of the Titan II's first stage, comprising the nitrogen tetroxide tank and its surrounding fuselage, was found floating on the surface of the Atlantic Ocean and retrieved; it is now on display at the US Space and Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama.

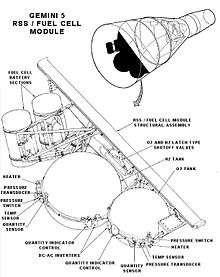
The first major event on the mission was the ejection of the Rendezvous Evaluation Pod (REP) at 2 hours and 13 minutes into the flight. The radar showed that the pod was moving a relative speed of two meters per second. While out of radio contact with the ground, the crew found that the pressure in one fuel cell had dropped from 850 to 65 pounds per square inch (5,860 to 450 kPa) 4 hours and 22 minutes into the flight. This was still above the 22.2 psi (153 kPa) minimum but Cooper decided to shut the fuel cells down. With only battery power, they would be unable to rendezvous with the REP, and it could also mean a premature end to the mission. The cause of this mishap was believed to be a short circuit in the oxygen tank heater that tripped a breaker.
Tests on the ground found that it was possible for the fuel cell to work, even with low oxygen pressure. However, with the fuel cells off, they would only be able to stay in orbit for a day and still have enough battery power for reentry.
It was decided to turn the fuel cells back on and test them by using equipment that required more and more power. These showed that the fuel cells were stable and the crew could continue the mission.
In the meantime, Buzz Aldrin had been working out an alternative rendezvous test. He had a doctorate in orbital mechanics[5] and worked out a scheme where the crew could rendezvous with a given point in space.
The crew became cold as they drifted. Even with the coolant pipes in the suits turned off and the airflow on low, they still shivered. Stars slowly drifting by the windows also proved disorienting, so the crew put covers on the windows.
As with Gemini 4, the crew had difficulty sleeping in alternate rest periods. They still had little rest when they decided to take their sleep periods together.
The phantom rendezvous came on the third day. It went perfectly, even though it was the first precision maneuver on a spaceflight. They tried four maneuvers—apogee adjust, phase adjust, plane change, and coelliptical maneuver—using the orbit attitude and maneuvering system (OAMS).
The next day, flight controllers discovered another problem with the fuel cells: they were producing waste water not suitable for drinking, as it was too acidic, in 20% higher quantity than expected. The cells discharged into a storage tank on board used for both potable and non-potable water, separated by a bladder wall. However, as the astronauts would be draining the potable water for drinking, it was soon determined that there would still be room left over at the end of the mission. In general, the fuel cells were successful at producing cool drinking water, but the astronauts reported that it had a high quantity of gas bubbles in it.
On the fifth day, a major problem occurred when one of the OAMS thruster blocks (comprising thrusters 5, 6, 7, and 8) malfunctioned repeatedly. The exact reason for these problems was unclear and a variety of possible causes were suggested. This meant the cancellation of all experiments requiring the use of the thrusters and the crew were not able to get them operating again.

Seventeen experiments were planned, with one cancelled, as it involved photography of the REP. Experiment D-1 involved the crew photographing celestial objects, and D-6 was a ground photography experiment. Experiments D-4/D-7 involved making brightness measurements of celestial and terrestrial backgrounds and of rocket plumes. Experiments S-8/D-13 investigated whether the crew's eyesight changed during the mission.
All of the medical experiments from Gemini 4 were performed, as well as experiment M-1 into the performance of the heart. This involved Conrad wearing inflatable leg cuffs. Experiment M-9 also investigated whether the astronauts' ability to measure horizontally changed.
The astronauts did not experience much of an appetite during the mission and averaged about 1000 calories a day, well below the intended 2700 calorie per day food intake. They reported dandruff to be a persistent problem to the point where their loose skin flakes would settle on the Gemini's instrument panel and partially obscure some instrument readouts. This condition was believed to be due to very low ambient humidity in the cabin causing the astronauts' skin to become dry and flaky. Postflight medical examinations showed some loss of red blood cells and plasma. Conrad's circulatory system returned to normal values within two days after the mission while Cooper took over four days.
S-1 involved Cooper taking the first photographs of the zodiacal light and the gegenschein from orbit. There was also syntopic photography of Earth. One photograph of the Zagros Mountains revealed greater detail than the official geologic map of Iran. Experiment S-7, the Cloud-Top Spectrometer revealed that the height of clouds could be determined from orbit.
Retrofire was initiated over Hawaii at 190 hours, 27 minutes, and 43 seconds into the mission. The astronauts controlled the reentry, creating drag and lift by rotating the capsule. Due to a computing error, the crew landed 80 miles (130 kilometers) short of the planned landing point in the Atlantic Ocean. Although the computer had worked perfectly, a programmer had entered the rate of the Earth's rotation as 360° per 24 hours instead of 360.98° See Sidereal day.
The Gemini 5 mission was supported by the following U.S. Department of Defense resources: 10,265 personnel, 114 aircraft and 19 ships. Recovery was by the aircraft carrier USS Lake Champlain.
Insignia

This was the first mission to have an insignia patch. After Gemini 3, NASA banned astronauts from naming their spacecraft. Cooper, having realized he had never been in a military organization without one, suggested a mission patch to symbolize the flight. NASA agreed, and the patches got the generic name of "Cooper patch."[6] Cooper chose the image of a covered wagon due to the pioneering nature of the flight. The slogan "8 Days or Bust" was emblazoned across the wagon, but NASA managers objected to this, feeling it placed too much emphasis on the mission length and not the experiments, and fearing the public might see the mission as a failure if it did not last the full duration. A piece of nylon cloth was sewn over the slogan.[7]
Spacecraft location
As of 2006, the spacecraft is on display at Space Center Houston, Houston, Texas.
See also

- Splashdown
- Space capsule
- Space exploration
- U.S. space exploration history on U.S. stamps
- Timeline of longest spaceflights
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
- ↑ "NSSDC Master Catalog: Gemini 5". NASA. Retrieved September 4, 2013.
- 1 2 "Satellite Catalog". Retrieved September 4, 2013.
- ↑ Hacker, Barton C.; Grimwood, James M. (September 1974). "Chapter 11 Pillars of Confidence". On the Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini. NASA History Series. SP-4203. NASA. p. 239. With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations.
- ↑ Sehlstedt, Albert "Gemini Nears Soviet Space Flight Mark" (August 26, 1965) The Baltimore Sun, p. 1
- ↑ "Astronaut Bio: Buzz Aldrin". nasa.gov.
- ↑ Cooper, Gordon; Bruce Henderson (2002). Leap of Faith: An Astronaut's Journey into the Unknown. HarperTorch. p. 320. ISBN 978-0-06-109877-2.
- ↑ French, Francis; Colin Burgess (2007). In the Shadow of the Moon. University of Nebraska Press. p. 44. ISBN 978-0-8032-1128-5.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gemini 5. |
- Gemini 5 Mission Report (PDF) October 1965
- NASA Gemini 5 press kit - August 12, 1965
- Gemini 5 in On The Shoulders of Titans: A History of Project Gemini
- Spaceflight Mission Patches: http://www.genedorr.com/patches/Intro.html
- NASA data sheet: http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/database/MasterCatalog?sc=1965-068A
- U.S. Space Objects Registry http://usspaceobjectsregistry.state.gov/search/index.cfm

