Shichidō garan

Shichidō garan is a Japanese Buddhist term indicating the seven halls composing the ideal Buddhist temple compound. This compound word is composed by the word shichidō (七堂), literally meaning "seven halls", and garan (伽藍), meaning "temple". The term is often shortened to just garan. Which seven halls the term refers to varies, and it is also pointed out that 七堂 is possibly a misinterpretation of shitsudō (悉堂), meaning a complete temple.[1][2][3] In practice, shichidō garan often simply means a large temple with many buildings.[4] See below for more details about what are the possible seven buildings included.
Etymology and history of the term
Garan (伽藍)[5] in Japanese is an abbreviated form of the expression sōgya ranma (僧伽藍摩), itself a transliteration of the Sanskrit saMghaaraama (सँघाराम), literally meaning "garden for monks".[6] A Japanese garan was originally just a park where monks gathered together with their teacher, but the term later came to mean "Buddhist temple".
The word garan can be found in a record in Nihon Shoki dated 552, although no monastery of this time survives, so we don't know what they were like.[6]
The compound word shichidō garan (七堂伽藍 seven hall temple) is found in a much more recent literature of Edo period,[2][7] referring to a complex that had a complete set of buildings forming an ideal Buddhist temple.
Early garan layout
A record dated 577 in the Nihon Shoki states that a mission including among others a temple architect and a Buddhist image maker was sent by King Seong of Baekje (聖王) to Japan, with more Buddhist related artisans sent over in the following years.[8] Excavations carried out between 1979-1980 on the temple site of Jeongnimsa in Buyeo, capital of Baekje from 538 to 663, revealed that the original temple was laid out in a typical north-to-south style with key buildings put on the center axis,[9] which was an arrangement closely adhered to at Shitennō-ji in Ōsaka.[6]
Composition of a shichidō garan
What is counted in the group of seven buildings, or shichidō, can vary greatly from temple to temple, from sect to sect, and from time to time. As mentioned above, shichidō garan could mean a complete temple or even simply a large temple complex.
According to a 13th-century text,[10] "a garan is a temple with a kon-dō (main hall), a tō (pagoda), a kō-dō (lecture hall), a shōrō (bellfry), a jiki-dō (refectory), a sōbō (monks' living quarters), and a kyōzō (scriptures deposit, library)."[2] These are the seven listed as shichidō elements of a Nanto Rokushū (南都六宗 Nara six sects)[11] temple.[1]
A 15th-century text[12] describes how Zen school temples (Sōtō (曹洞), Rinzai (臨済))[13] included a butsuden or butsu-dō (main hall), a hattō (lecture hall), a kuin (kitchen/office), a sō-dō (building dedicated to Zazen), a sanmon (main gate), a tōsu (toilet) and a yokushitsu (bath).
Loss of importance of the pagoda within the garan

Because of the relics they contained, wooden pagodas used to be the centerpiece of the garan, the seven edifices considered indispensable for a temple.[14] They gradually lost of importance and were replaced by the kondō (golden hall), because of the magic powers believed to lie within the images the building housed. This loss of status was so complete that the Zen sects, which arrived late in Japan from China, normally do not build any pagoda at all. The layout of four early temples clearly illustrates this trend: they are in chronological order Asuka-dera, Shitennō-ji, Hōryū-ji, and Yakushi-ji.[14] In the first, the pagoda was at the very center of the garan surrounded by three small kondō (see the reconstruction of the temple's original layout). In the second, a single kondō is at the center of the temple and the pagoda lies in front of it. At Hōryū-ji, they are one next to the other. Yakushi-ji has a single, large kondō at the center with two pagodas on the sides. The same evolution can be observed in Buddhist temples in China.
Examples of garan
Hōryū-ji

Hōryū-ji (法隆寺) is a Buddhist temple of the "Shōtoku" sect in Ikaruga, Nara Prefecture, Japan. Its garan is composed of (see plan on the right):
A Chūmon (中門)
In a temple, the gate after the naindaimon connected to a kairō[1]
B Kairō (回廊・廻廊)
A long and roofed portico-like passage surrounding the kondō and the pagoda.[15]
C Kon-dō (金堂)
The main hall of a garan, housing the main object of worship.[15]
D Tō
A pagoda, which is an evolution of the stupa (a kind of reliquary) . After reaching China, the stupa evolved into a tower with an odd number of tiers (three, five, seven, nine, thirteen).[15]
E Kōdō (講堂)
The lecture hall of a non-Zen garan.[1]
F Kyōzō (経蔵)
Lit. "scriptures deposit". Repository of sūtras and books about the temple's history.[15] Also called kyōdō.
G Shōrō (鐘楼)
A bellfry
Zuiryū-ji
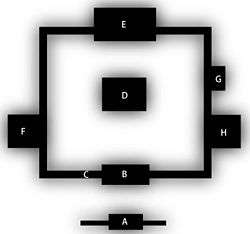
Zuiryū-ji is a Zen temple of the Sōtō sect in Takaoka, Toyama Prefecture.
A Sōmon (総門)
The gate at the entrance of a temple.[1] It precedes the bigger and more important sanmon.
B Sanmon (三門 or 山門)
The gate in front of the butsuden,[15] most commonly having two stories (nijūmon). The name is short for Sangedatsumon (三解脱門), lit. gate of the three liberations.[15] Its openings (kūmon (空門), musōmon (無相門) and muganmon (無願門)) symbolize the three gates to enlightenment.[15] Entering, one can symbolically free him or herself from the three passions of ton (貪 greed), shin (瞋 hatred), and chi (癡 foolishness).[16]
C Kairō (回廊)
See above
D Butsuden (仏殿)
Lit. "Hall of Buddha". A building enshrining the statue of Buddha or of a bodhisattva and dedicated to prayer.[1]
E Hōdō (法堂)
Lit. "Dharma hall". A building dedicated to lectures by the chief priest on Buddhism's scriptures (the hō).[1]
F Zendō (禅堂)
Lit. "hall of Zen".[15] The building where monks practice zazen, and one of the main structures of a Zen garan.[15]
G Shōrō (鐘楼)
A bellfry
H Kuri (庫裏)
A building hosting the galleys, the kitchen, and the offices of a Zen garan.[1]
Another typical Zen garan, of which Kenchō-ji's is a good example, begins with the sōmon followed by the sanmon, the main hall (the butsuden), the lecture hall (hattō), and the chief abbot's residence (hōjō) all aligned more or less on a north to south axis, with the bath house (yokushitsu) and the sūtra repository (kyōzō) to its east, and the monks' hall (sodō) to its west.
See also
- For an explanation of terms concerning Japanese Buddhism, Japanese Buddhist art, and Japanese Buddhist temple architecture, see the Glossary of Japanese Buddhism.
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Iwanami Kōjien
- 1 2 3 Kōsetsu Bukkyō Daijiten (広説仏教語大辞典)
- ↑ The Japanese character 七 can also be pronounced shitsu.
- ↑ Imaizumi, Yoshio (1999). Nihon Bukkyo Shi Jiten. City: Yoshikawa Kobunkan. ISBN 978-4-642-01334-5.
- ↑ Also called sōen (僧園) shūen (衆園) and shōja (精舎)
- 1 2 3 JAANUS, garan
- ↑ Nihon Kokugo Daijiten
- ↑ Grayson, James Huntley (2002). Korea: a religious history. London: RoutledgeCurzon. p. 33. ISBN 0-7007-1605-X.
- ↑ "National Research Institute of Cultural Heritage". Retrieved 2010-06-30.
- ↑ Shōtoku Taishi Denkokonmokurokushō (聖徳太子伝古今目録抄)
- ↑ The six Buddhist schools 南都六宗, introduced to Japan during the Asuka and Nara periods
- ↑ Sekiso Ōrai (尺素往来)
- ↑ The Obaku School (黃檗) arrived in Japan in the 17th century.
- 1 2
- Tamura, Yoshiro (2000). Japanese Buddhism - A Cultural History (First ed.). Tokyo: Kosei Publishing Company. pp. 40–41 pages. ISBN 4-333-01684-3.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 JAANUS entry of the same name
- ↑ Zōjō-ji accessed on May 1, 2009
References
- Japanese Art Net User System Dictionary of Japanese Architectural and Art Historical Terminology accessed on April 27, 2009
- Iwanami Kōjien (広辞苑) Japanese dictionary, 6th Edition (2008), DVD version
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Shichidō garan. |