Radio occultation

Radio occultation (RO) is a remote sensing technique used for measuring the physical properties of a planetary atmosphere or ring system.
Atmospheric radio occultation
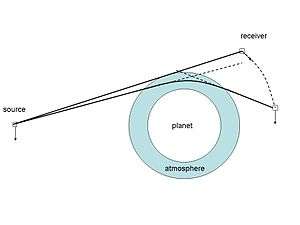
Atmospheric radio occultation relies on the detection of a change in a radio signal as it passes through a planet's atmosphere, i.e. as it is occulted by the atmosphere. When electromagnetic radiation (light) passes through the atmosphere, it is refracted (or bent). The magnitude of the refraction depends on the gradient of refractivity normal to the path, which in turn depends on the density gradient. The effect is most pronounced when the radiation traverses a long atmospheric limb path. At radio frequencies the amount of bending cannot be measured directly; instead the bending can be calculated using the Doppler shift of the signal given the geometry of the emitter and receiver. The amount of bending can be related to the refractive index by using an Abel transform on the formula relating bending angle to refractivity. In the case of the neutral atmosphere (below the ionosphere) information on the atmosphere's temperature, pressure and water vapour content can be derived giving radio occultation data applications in meteorology.
GNSS radio occultation
GNSS or GPS radio occultation (GNSS-RO, GPS-RO, GPSRO) is a type of radio occultation that relies on radio transmissions from GPS (Global Positioning System), or more generally from GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System), satellites.[1][2] This is a relatively new technique (first applied in 1995) for performing atmospheric measurements. It is used as a weather forecasting tool, and could also be harnessed in monitoring climate change. The technique involves a low-Earth orbit satellite receiving a signal from a GPS satellite. The signal has to pass through the atmosphere and gets refracted along the way. The magnitude of the refraction depends on the temperature and water vapor concentration in the atmosphere.[3]
GPS Radio occultation amounts to an almost instantaneous depiction of the atmospheric state. The relative position between the GPS satellite and the low-Earth orbit satellite changes over time, allowing for a vertical scanning of successive layers of the atmosphere.[4]
GPSRO observations can also be conducted from aircraft.[5] or on high mountaintops.[6]
Planetary satellite missions
Current missions include:
- REX on New Horizons
- For past missions, see Special:WhatLinksHere/Radio occultation.
Satellite missions
- FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC
- CHAMP
- GRACE
- GRAS sensor onboard MetOp satellite
- CLARREO
See also
References
- ↑ Melbourne et al. 1994. The application of spacebourne GPS to atmospheric limb sounding and global change monitoring. Publication 94-18, Jet Propulsion Laboratory
- ↑ Kursinski et al. 1997. Observing the Earth's atmosphere with radio occultation measurements using the Global Positioning System. J. Geophys. Res. 102:23.429-23.465.
- ↑ "GPS 'thermometer' could flag up climate change". Retrieved 2008-02-16.
- ↑ "GPS Space-Based & GPS Radio occultation". Retrieved 2008-02-16.
- ↑ Xie, F.; Haase, J. S.; Syndergaard, S. (2008). "Profiling the atmosphere using the airborne GPS occultation technique: A sensitivity study". IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. 46 (11).
- ↑ Zuffada, C.; Hajj, G. A.; Kursinski, E. R. (1999). "A novel approach to atmospheric profiling with a mountain-based or airborne GPS receiver". Journal of Geophysical Research. 104: 24435. Bibcode:1999JGR...10424435Z. doi:10.1029/1999JD900766.
External links
- COSMIC Project Website
- GeoOptics LLC Website - First commercial operational RO Constellation
- PlanetIQ Website
- ROM SAF monitoring
- ROM SAF website
- ECMWF monitoring