Fuzhou dialect
| Fuzhou dialect | |
|---|---|
|
福州話 / Hók-ciŭ-uâ 福州語 / Hók-ciŭ-ngṳ̄ 平話 / Bàng-uâ | |
| Native to | China (Fuzhou and its surrounding counties) and Taiwan (Matsu Islands), Thailand (Chandi Town and Lamae), Singapore, Malaysia (Sibu, Miri, Sarikei, Bintulu, Yong Peng, Sitiawan and Ayer Tawar) and Indonesia (Semarang, Magelang and Surabaya), as well as some other Chinese communities in Southeast Asia and in the West, particularly in the Chinatowns of New York City. |
| Ethnicity | Fuzhounese (Han Chinese) |
Native speakers | < 10 million (date missing) |
|
Sino-Tibetan
| |
Early forms | |
| Chinese characters and Foochow Romanized | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | none |
Recognised minority language in |
one of the statutory languages for public transport announcements in the Matsu Islands, Republic of China[1] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| ISO 639-6 |
fzho |
| Glottolog |
fuzh1239[2] |
|
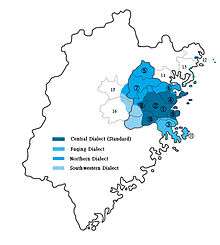
Fuzhou dialect in Fujian Province, regions where the standard form is spoken are deep blue. 1: Fuzhou City Proper, 2: Minhou, 3: Fuqing, 4: Lianjiang, 5: Pingnan 6: Luoyuan, 7: Gutian, 8: Minqing, 9: Changle, 10: Yongtai, 11: Pingtan 12: Regions in Fuding, 13: Regions in Xiapu, 14: Regions in Ningde 15: Regions in Nanping, 16: Regions in Youxi | |
| Fuzhounese | |||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 福州話 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 福州话 | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 福州語 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 福州语 | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Everyday language | |||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 平話 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 平话 | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
The Fuzhou dialect, (simplified Chinese: 福州话; traditional Chinese: 福州話; pinyin: Fúzhōuhuà; FR: ![]() Hók-ciŭ-uâ ) also Fuzhounese, Foochow or Hok-chiu, is the prestige variety of the Eastern Min branch of Min Chinese spoken mainly in eastern Fujian province. Like many other varieties of Chinese, the Fuzhou dialect is dominated by monosyllabic morphemes which carry lexical tones,[3] and has a mainly analytic syntax. While the Eastern Min branch that it belongs to is closer to Southern Min than to other Sinitic branches such as Mandarin or Hakka, they are still not mutually intelligible.
Hók-ciŭ-uâ ) also Fuzhounese, Foochow or Hok-chiu, is the prestige variety of the Eastern Min branch of Min Chinese spoken mainly in eastern Fujian province. Like many other varieties of Chinese, the Fuzhou dialect is dominated by monosyllabic morphemes which carry lexical tones,[3] and has a mainly analytic syntax. While the Eastern Min branch that it belongs to is closer to Southern Min than to other Sinitic branches such as Mandarin or Hakka, they are still not mutually intelligible.
Centered in Fuzhou City, the Fuzhou dialect covers eleven cities and counties: Fuzhou City Proper, Pingnan, Gutian, Luoyuan, Minqing, Lianjiang (including Matsu), Minhou, Changle, Yongtai, Fuqing and Pingtan. It is also the second local language in many northern and middle Fujian cities and counties such as Nanping, Shaowu, Shunchang, Sanming and Youxi.[4]
Fuzhou dialect is also widely spoken in some regions abroad, especially in Southeastern Asian countries like Malaysia and Indonesia. The city of Sibu in Malaysia is called "New Fuzhou" due to the influx of immigrants there in the late 19th century and early 1900s. Similarly, quite a significant number of Fuzhounese have emigrated to Singapore, Taiwan, United States, Canada, United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand in the decades since China's economic reform.
Name
In older works, the variety is called "Foochow dialect", based on the Chinese postal romanization of Fuzhou. In Chinese, it is sometimes called 福州語 (Hók-ciŭ-ngṳ̄; pinyin: Fúzhōuyǔ). Native speakers also refer to it as Bàng-uâ (平話), meaning "the everyday language."
In Singapore and Malaysia, it is often referred to as "Hokchiu" ([hɔk̚˥t͡ɕiu˦]), which is the pronunciation of Fuzhou in the Southern Min Hokkien language, or "Huchiu" ([hu˨˩t͡ɕiu˥]), which is the pronunciation of Fuzhou in the Eastern Min language of Fuzhou itself. Eastern Min and Southern Min are both spoken in the same Fujian province, but the name Hokkien, while etymologically derived from the same characters as Fujian (福建), is used in Southeast Asia and the English press to refer specifically to Southern Min, which has a larger number of speakers both within Fujian and in the Chinese diaspora of Southeast Asia.
History
Formation

After the Qin Dynasty conquered the Minyue kingdom of southeast China in 110 BC, Han Chinese people began settling what is now Fujian province. The Old Chinese language brought by the mass influx of Han immigrants from Northern area, along with the influences of local languages, became the early Proto-Min language from which Eastern Min, Southern Min, and other Min languages arose.[5] Within this Min branch of Chinese, Eastern Min and Southern Min both form part of a Coastal Min subgroup, and are thus closer to each other than to Inland Min groups such as Northern Min and Central Min.
The famous book Qī Lín Bāyīn, which was compiled in the 17th century, is the first and the most full-scale rime book that provides a systematic guide to character reading for people speaking or learning the Fuzhou dialect. It once served to standardize the language and is still widely quoted as an authoritative reference book in modern academic research in Min Chinese phonology.
Studies by Western missionaries

In 1842, Fuzhou was open to Westerners as a treaty port after the signing of the Treaty of Nanjing. But due to the language barrier, however, the first Christian missionary base in this city did not take place without difficulties. In order to convert Fuzhou people, those missionaries found it very necessary to make a careful study of the Fuzhou dialect. Their most notable works are listed below:[6]
- 1856, M. C. White: The Chinese language spoken at Fuh Chau
- 1870, R. S. Maclay & C. C. Baldwin: An alphabetic dictionary of the Chinese language in the Foochow dialect
- 1871, C. C. Baldwin: Manual of the Foochow dialect
- 1891, T. B. Adam: An English-Chinese Dictionary of the Foochow Dialect
- 1893, Charles Hartwell: Three Character Classic of Gospel in the Foochow Colloquial
- 1898, R. S. Maclay & C. C. Baldwin: An Alphabetic Dictionary of the Chinese Language of the Foochow Dialect, 2nd edition
- 1905, T. B. Adam: An English-Chinese Dictionary of the Foochow Dialect, 2nd edition]
- 1906, The Foochow translation of the complete Bible
- 1923, T. B. Adam & L. P. Peet: An English-Chinese dictionary of the Foochow dialect, 2nd edition
- 1929, R. S. Maclay & C. C. Baldwin (revised and enlarged by S. H. Leger): Dictionary of the Foochow dialect
Studies by Japanese scholars

During the Second World War, some Japanese scholars became passionate about studying Fuzhou dialect, believing that it could be beneficial to the rule of the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere. One of their most famous works was the Japanese-Chinese Translation: Fuzhou Dialect (日華對譯: 福州語) published in 1940 in Taipei, in which katakana was used to represent Fuzhou pronunciation.
Status quo

By the end of the Qing Dynasty, Fuzhou society had been largely monolingual. But for decades the Chinese government has discouraged the use of the vernacular in school education and in media, so the number of Mandarin speakers has been greatly boosted. Recent reports indicate that less than 50% of young people in Fuzhou are able to speak Fuzhou dialect.[7]
In Mainland China, the Fuzhou dialect has been officially listed as an Intangible Cultural Heritage[8] and promotion work is being systematically carried out to preserve its use. In Matsu, currently controlled by the Republic of China located in Taiwan, the teaching of Fuzhou dialect has been successfully introduced into elementary schools.
Phonology
- This section is about Standard Fuzhou dialect only. See Regional variations for a discussion of other dialects.
Like all Chinese varieties, the Fuzhou dialect is a tonal language, and has extensive sandhi rules in the initials, rimes, and tones. These complicated rules make Fuzhou dialect one of the most difficult Chinese varieties.[9]
Tones
There are seven original tones in Fuzhou dialect, compared with the eight tones of Middle Chinese:
| Name | Tone contour | Description | Example | five-scale IPA (李1994)[10] | five-scale IPA (冯1998)[11] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dark-level (Ĭng-bìng 陰平) | ˥ | high level | 君 | 44 | 55 |
| Rising tone (Siōng-siăng 上聲) | ˧ | middle level | 滾 | 31 | 33 |
| Dark-departing (Ĭng-ké̤ṳ 陰去) | ˨˩˧ | low falling and rising | 貢 | 213 | 212 |
| Dark-entering (Ĭng-ĭk 陰入) | ˨˦ | middle rising stopped | 谷 | 23 | 24 |
| Light-level (Iòng-bìng 陽平) | ˥˧ | high falling | 群 | 53 | 53 |
| Light-departing (Iòng-ké̤ṳ 陽去) | ˨˦˨ | middle rising and falling | 郡 | 353 | 242 |
| Light-entering (Iòng-ĭk 陽入) | ˥ | high level stopped | 掘 | 5 | 5 |
The sample characters are taken from the Qī Lín Bāyīn.
In Qī Lín Bāyīn, the Fuzhou dialect is described as having eight tones, which explains how the book got its title (Bāyīn means "eight tones"). That name, however, is somewhat misleading, because Ĭng-siōng (陰上) and Iòng-siōng (陽上) are identical in tone contour; therefore, only seven tones exist.
Ĭng-ĭk and Iòng-ĭk (or so-called entering tone) syllables end with either velar stop [k] or a glottal stop [ʔ]. However, they are both now realized as a glottal stop, though the two phonemes maintain distinct sandhi behavior in connected speech.
Besides those seven tones listed above, two new tonal values, "˨˩" (Buáng-ĭng-ké̤ṳ, 半陰去) and ˧˥ (Buáng-iòng-ké̤ṳ, 半陽去) occur in connected speech (see Tonal sandhi below).
Tonal sandhi
The rules of tonal sandhi in Fuzhou dialect are complicated, even compared with those of other Min dialects. When two or more than two morphemes combine into a word, the tonal value of the last morpheme remains stable but in most cases those of the preceding morphemes change. For example, "獨", "立" and "日" are words of Iòng-ĭk (陽入) with the same tonal value ˥, and are pronounced [tuʔ˥], [liʔ˥], and [niʔ˥], respectively. When combined together as the phrase "獨立日" (Independence Day), "獨" changes its tonal value to ˨˩, and "立" changes its to ˧, therefore the pronunciation as a whole is [tuʔ˨˩ liʔ˧ niʔ˥].
The two-syllable tonal sandhi rules are shown in the table below (the rows give the first syllable's original citation tone, while the columns give the citation tone of the second syllable):
| Ĭng-bìng (陰平 ˥) |
Iòng-bìng (陽平 ˥˧) |
Siōng-siăng (上聲 ˧) |
Ĭng-ké̤ṳ (陰去 ˨˩˧) | |
|
Ĭng-bìng (陰平 ˥) |
|
|
|
|
|
Iòng-bìng (陽平 ˥˧) |
|
|
|
|
|
Siōng-siăng (上聲 ˧) |
|
|
|
|
Ĭng-ĭk-gák (陰入甲) are Ĭng-ĭk (陰入) syllables ending with /k/ and Ĭng-ĭk-ék (陰入乙) are those with /ʔ/.[12] Both are usually realized as the glottal stop by most modern speakers of the Fuzhou dialect, but the distinction is made both in the above tone sandhi behavior and in initial assimilation.
The three patterns of tone sandhi exhibited in the Fuzhou dialect may be a reflex of the voicing split from Middle Chinese into different registers, especially on comparison with the tonal sandhi system of the subdialect of Lianjiang, a very similar but more conservative Eastern Min variety. The historical registers ("Yin" from unvoiced consonants in Middle Chinese; "Yang" from voiced consonants in Middle Chinese; and "Shang" tone from the Middle Chinese "rising tone" 上聲 where the Yin and Yang registers have merged) on the penultimate syllables interact with the tonal category of the final syllable to form the sandhi pattern in Lianjiang.[13][14] Although the effect of the historical registers is clear in Lianjiang, the Fuzhou tonal sandhi system has deviated from the older pattern, in that the tone Iòng-ké̤ṳ 陽去˨˦˨, which is from the historical "Yang" register, follows the sandhi rules for the "Yin" register, and part of the tone Ĭng-ĭk 陰入˨˦, Ĭng-ĭk-gák 陰入乙, which is from the historical "Yin" register, follow the sandhi rules for the merged "Shang" tone.
However, the tonal sandhi rules of more than two syllables display further complexities.
Initials
There are fifteen initials, including a zero initial realized as a glottal stop [ʔ]:
| Bilabial | Alveolar | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | /m/ (蒙) | /n/ (日) | /ŋ/ (語) | ||
| Plosive | aspiration | /pʰ/ (波) | /tʰ/ (他) | /kʰ/ (氣) | |
| plain | /p/ (邊) | /t/ (低) | /k/ (求) | /ʔ/ (鶯) | |
| Fricative | /s/ (時) | /h/ (喜) | |||
| Affricate | aspiration | /tsʰ/ (出) | |||
| plain | /ts/ (曾) | ||||
| Lateral | /l/ (柳) | ||||
The Chinese characters in the brackets are also sample characters from Qī Lín Bāyīn.
Some speakers find it difficult to distinguish between the initials /n/ and /l/.
No labiodental phonemes, such as /f/ or /v/, exist in Fuzhou dialect, which is one of the most conspicuous characteristics shared by all branches in the Min Family.
[β] and [ʒ] exist only in connected speech (see Initial assimilation below).
Initial assimilation
In Fuzhou dialect, there are various kinds of initial assimilation, all of which are progressive. When two or more than two syllables combine into a word, the initial of the first syllable stays unchanged while those of the following syllables, in most cases, change to match its preceding phoneme, i.e., the coda of its preceding syllable. As with the rime changes, initial assimilation is not as mandatory as tone sandhi in connected speech, and its presence and absence may indicate different parts of speech, different meanings of a single word, or different relationships between groups of words syntactically.[15]
| The Coda of the Former Syllable | The Initial Assimilation of the Latter Syllable |
|---|---|
| Null coda or /-ʔ/ |
|
| /-ŋ/ |
|
| /-k/ | All initials remain unchanged. |
Rimes
The table below shows the seven vowel phonemes of Fuzhou dialect.
| Front | Back | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| unrounded | rounded | ||
| Close | /i/ [i~ɛi] |
/y/ [y~œy] |
/u/ [u~ɔu] |
| Mid | /e/ [e~a] |
/ø/ [ø~ɔ] |
/o/ [o~ɔ] |
| Open | /a/ | ||
In Fuzhou dialect codas /-m/, /-n/, and /-ŋ/ have all merged as /-ŋ/; and /-p/, /-t/, /-k/ have all merged as /-ʔ/. Seven vowel phonemes, together with the codas /-ŋ/ and /-ʔ/, are organized into forty-six rimes.[16]
| Monophthongs | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /a/ | /e/ | /ø/ | /o/ | /i/ | /u/ | /y/ | |
| Open syllable | [a] (蝦, 罷) |
[e, a] (街, 細) |
[ø, ɔ] (驢, 告) |
[o, ɔ] (哥, 抱) |
[i, ɛi] (喜, 氣) |
[u, ɔu] (苦, 怒) |
[y, œy] (豬, 箸) |
| Nasal Coda /-ŋ/ | [aŋ] (三, 汗) |
[iŋ, ɛiŋ] (人, 任) |
[uŋ, ɔuŋ] (春, 鳳) |
[yŋ, œyŋ] (銀, 頌) | |||
| Glottal Coda /-ʔ/ | [aʔ] (盒, 鴨) |
[eʔ] (漬) |
[øʔ] (扔) |
[oʔ, ɔʔ] (樂, 閣) |
[iʔ, ɛiʔ] (力, 乙) |
[uʔ, ɔuʔ] (勿, 福) |
[yʔ, œyʔ] (肉, 竹) |
| Rising diphthongs | Falling diphthongs | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /ia/ | /ie/ | /ua/ | /uo/ | /yo/ | /ai/ | /au/ | /eu/ | /ei/ | /ou/ | /øy/ | /iu/ | /ui/ | |
| Open syllable | [ia] (寫, 夜) |
[ie] (雞, 毅) |
[ua] (花, 話) |
[uo] (科, 課) |
[yo] (橋, 銳) |
[ai] (紙, 再) |
[au] (郊, 校) |
[eu, au] (溝, 構) |
[øy, ɔy] (催, 罪) |
[iu] (秋, 笑) |
[ui] (杯, 歲) | ||
| Nasal Coda /-ŋ/ | [iaŋ] (驚, 命) |
[ieŋ] (天, 見) |
[uaŋ] (歡, 換) |
[uoŋ] (王, 象) |
[yoŋ] (鄉, 樣) |
[eiŋ, aiŋ] (恒, 硬) |
[ouŋ, ɔuŋ] (湯, 寸) |
[øyŋ, ɔyŋ] (桶, 洞) |
|||||
| Glottal Coda /-ʔ/ | [iaʔ] (擲, 察) |
[ieʔ] (熱, 鐵) |
[uaʔ] (活, 法) |
[uoʔ] (月, 郭) |
[yoʔ] (藥, 弱) |
[eiʔ, aiʔ] (賊, 黑) |
[ouʔ, ɔuʔ] (學, 骨) |
[øyʔ, ɔyʔ] (讀, 角) |
|||||
| Triphthong | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /uai/ | ||||
| Open syllable | [uai] (我, 怪) | |||
As has been mentioned above, there are theoretically two different entering tonal codas in Fuzhou dialect: /-k/ and /-ʔ/. But for most Fuzhou dialect speakers, those two codas are only distinguishable when in the tonal sandhi or initial assimilation.
Close/Open rimes
Some rimes come in pairs in the above table: the one to the left represents a close rime (緊韻), while the other represents an open rime (鬆韻). The close/open rimes are closely related with the tones. As single syllables, the tones of Ĭng-bìng (陰平), Siōng-siăng (上聲), Iòng-bìng (陽平) and Iòng-ĭk (陽入) have close rimes while Ĭng-ké̤ṳ (陰去), Ĭng-ĭk (陰入) and Iòng-ké̤ṳ (陽去) have the open rimes. In connected speech, an open rime shifts to its close counterpart in the tonal sandhi.
For instance, "福" (hók) is a Ĭng-ĭk syllable and is pronounced [hɔuʔ˨˦] and "州" (ciŭ) a Ĭng-bìng syllable with the pronunciation of [tsiu˥]. When these two syllables combine into the word "福州" (Hók-ciŭ, Fuzhou), "福" changes its tonal value from ˨˦ to ˨˩ and, simultaneously, shifts its rime from [-ɔuʔ] to [-uʔ], so the phrase is pronounced [huʔ˨˩ tsiu˥]. While in the word "中國" [tyŋ˥˧ kuoʔ˨˦] (Dṳ̆ng-guók, China), "中" is a Ĭng-bìng syllable and therefore its close rime never changes, though it does change its tonal value from ˥ to ˥˧ in the tonal sandhi.
As with initial assimilation, the closing of open rimes in connected speech is not as compulsory than tone sandhi. It has been described as "a sort of switch that flips on and off to indicate different things", so its presence or absence can indicate different meanings or different syntactic functions.[15]
The phenomenon of close/open rimes is nearly unique to the Fuzhou dialect and this feature makes it especially intricate and hardly intelligible even to speakers of other Min varieties.
Other phonological features
Neutral tone
The neutral tone is attested in the Fuzhou dialect, as well as being found in the Southern Min group and in varieties of Mandarin Chinese, including Beijing-based Standard Mandarin. It is commonly found in some modal particles, aspect markers, and some question-forming negative particles that come after units made up of one tone sandhi domain, and in some adverbs, aspect markers, conjunctions etc. that come before such units. These two types, the post-nucleus and the pre-nucleus neutral tone, exhibit different tone sandhi behavior. Disyllabic neutral tone words are also attested, as are some inter-nuclei neutral tones, mainly connected to the use of 蜀 siŏh /suoʔ˥/ in verbal reduplication.[17]
Vocabulary
Most words in Fuzhou dialect have cognates in other varieties of Chinese, so a non-Fuzhou speaker would find it much easier to understand Fuzhou dialect written in Chinese characters than spoken in conversation. However, false friends do exist: for example, "莫細膩" (mŏ̤h sá̤-nê) means "don't be too polite" or "make yourself at home", "我對手汝洗碗" (nguāi dó̤i-chiū nṳ̄ sā̤ uāng) means "I help you wash dishes", "伊共伊老媽嚟冤家" (ĭ gâe̤ng ĭ lâu-mā lā̤ uŏng-gă) means "he and his wife are quarreling (with each other)", etc. Mere knowledge of Mandarin vocabulary does not help one catch the meaning of these sentences.
The majority of Fuzhou dialect vocabulary dates back to more than 1,200 years ago. Some daily-used words are even preserved as they were in the Tang Dynasty, which can be illustrated by a poem of a famous Chinese poet Gu Kuang.[18] In his poem Jiǎn (囝), Gu Kuang explicitly noted:
囝,音蹇。閩俗呼子為囝,父為郎罷。
"囝 is pronounced as 蹇. In Fujian vernacular son is called 囝, and father 郎罷."
In Fuzhou dialect, "囝" (giāng) and "郎罷" (nòng-mâ) are still in use today.
Words from Old Chinese
Quite a few words from Old Chinese have retained the original meanings for thousands of years, while their counterparts in Mandarin Chinese have either fallen out of daily use or varied to different meanings.
This table shows some Fuzhou dialect words from Old Chinese, as contrasted to Mandarin Chinese:
| Meaning | Fuzhou dialect | Foochow Romanized | Mandarin | Pinyin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eye | 目睭/目珠 | mĕ̤k-ciŭ [møyʔ˥ tsiu˥] | 眼睛 | yǎnjīng |
| you | 汝 | nṳ̄ [ny˧] | 你 | nǐ |
| chopstick | 箸 | dê̤ṳ [tøy˨˦˨] | 筷子 | kuàizi |
| to chase | 逐 | dṳ̆k [tyʔ˥] | 追 | zhuī |
| to look, to watch | 覷/覰/䁦 | ché̤ṳ [tsʰœy˨˩˧] | 看1 | kàn |
| wet | 潤 | nóng [nɔuŋ˨˩˧] | 濕 | shī |
| black | 烏 | ŭ [u˥] | 黑 | hēi |
| to feed | 豢 | huáng [huaŋ˨˩˧] | 養² | yǎng |
- 1 "看" (káng) is also used as the verb "to look" in Fuzhou dialect.
- 2 "養" (iōng) in Fuzhou dialect means "give birth to (a child)".
This table shows some words that are used in Fuzhou dialect close to as they were in Classical Chinese, while the meanings in Mandarin Chinese have altered:
| Word | Foochow Romanized | Meaning in Classical Chinese and Fuzhou dialect | Pinyin | Meaning in Mandarin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 細 | sá̤ [sa˨˩˧] | tiny, small, young | xì | thin, slender |
| 說 | suók/siók [suoʔ˨˦] | to explain, to clarify | shuō | to speak, to talk |
| 懸 | gèng [keiŋ˥˧] | tall, high | xuán | to hang, to suspend (v.) |
| 喙 | chói [tsʰui˨˩˧] | mouth | huì | beak |
Words from Ancient Minyue language
Some daily used words, shared by all Min varieties, came from the ancient Minyue language. Such as follows:
| Word | Foochow Romanized | Southern Min / Taiwanese POJ | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| 骹 | kă ([kʰa˥]) | kha ([kʰa˥]) | foot and leg |
| 囝 | giāng [kiaŋ˧] | kiáⁿ ([kiã˥˩]) | son, child, whelp, a small amount |
| 睏 | káung [kʰauŋ˨˩˧] | khùn [kʰun˨˩] | to sleep |
| 骿 | piăng [pʰiaŋ˥] | phiaⁿ [pʰiã˥] | back, dorsum |
| 儂 | nè̤ng [nøyŋ˥˧] | lâng [laŋ˨˦] | human |
| 厝 | chuó/chió [tsʰuo˨˩˧] | chhù [tsʰu˨˩] | home, house |
| 刣 | tài [tʰai˥˧] | thâi [tʰai˨˦] | to kill, to slaughter |
Literary and colloquial readings
The literary and colloquial readings is a feature commonly found in all Chinese dialects throughout China. Literary readings are mainly used in formal phrases and written language, while the colloquial ones are basically used in vulgar phrases and spoken language.
This table displays some widely used characters in Fuzhou dialect which have both literary and colloquial readings:
| Character | Literary reading | Phrase | Meaning | Colloquial reading | Phrase | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 行 | hèng [heiŋ˥˧] | 行李 hèng-lī | luggage | giàng [kiaŋ˥˧] | 行墿 giàng-duô | to walk |
| 生 | sĕng [seiŋ˥] | 生態 sĕng-tái | zoology, ecology | săng [saŋ˥] | 生囝 săng-giāng | childbearing |
| 江 | gŏng [kouŋ˥] | 江蘇 Gŏng-sŭ | Jiangsu | gĕ̤ng [køyŋ˥] | 閩江 Mìng-gĕ̤ng | Min River |
| 百 | báik [paiʔ˨˦] | 百科 báik-kuŏ | encyclopedical | báh [paʔ˨˦] | 百姓 báh-sáng | common people |
| 飛 | hĭ [hi˥] | 飛機 hĭ-gĭ | aeroplane | buŏi [pui˥] | 飛鳥 buŏi-cēu | flying birds |
| 寒 | hàng [haŋ˥˧] | 寒食 Hàng-sĭk | Cold Food Festival | gàng [kaŋ˥˧] | 天寒 tiĕng gàng | cold, freezing |
| 廈 | hâ [ha˨˦˨] | 大廈 dâi-hâ | mansion | â [a˨˦˨] | 廈門 Â-muòng | Amoy (Xiamen) |
Loan words from English
The First Opium War, also known as the First Anglo-Chinese War, was ended in 1842 with the signing of the Treaty of Nanjing, which forced the Qing government to open Fuzhou to all British traders and missionaries. Since then, quite a number of churches and Western-style schools have been established. Consequently, some English words came into Fuzhou dialect, but without fixed written forms in Chinese characters. The most frequently used words are listed below:[19]
- kŏk, [kʰouʔ˥], noun, meaning "an article of dress", is from the word "coat";
- nă̤h, [neʔ˥], noun, meaning "a meshwork barrier in tennis or badminton", is from the word "net";
- pèng, [pʰeiŋ˥˧], noun, meaning "oil paint", is from the word "paint";
- pĕng-giāng, [pʰeiŋ˥˧ ŋiaŋ˧], noun, meaning "a small sum of money", is from the word "penny";
- tă̤h, [tʰeʔ˥], noun, meaning "money", is from the word "take";
- sò̤, [so˥˧], verb, meaning "to shoot (a basket)", is from the word "shoot";
- ă-gì, [a˥ ki˥˧], verb, meaning "to pause (usually a game)", is from the word "again".
- Mā-lăk-gă, [ma˨˩ laʔ˥ ka˥], meaning "Southeastern Asian (esp. Singapore and Malaysia)", is from the word "Malacca".
Examples
Some common phrases in Fuzhou dialect:
- Fuzhou dialect: 福州話 Hók-ciŭ-uâ [huʔ˨˩ tsiu˥˧ ua˨˦˨]
- Hello: 汝好
 Nṳ̄ hō̤ [ny˧ ho˧]
Nṳ̄ hō̤ [ny˧ ho˧] - Good-bye: 再見
 Cái-giéng [tsai˥˧ kieŋ˨˩˧]
Cái-giéng [tsai˥˧ kieŋ˨˩˧] - Please: 請
 Chiāng [tshiaŋ˧]; 起動
Chiāng [tshiaŋ˧]; 起動  Kī-dâe̤ng [khi˥ lɔyŋ˨˦˨]
Kī-dâe̤ng [khi˥ lɔyŋ˨˦˨] - Thank you: 謝謝
 Siâ-siâ [sia˥˧ lia˨˦˨]; 起動 Kī-dâe̤ng [khi˥ lɔyŋ˨˦˨]
Siâ-siâ [sia˥˧ lia˨˦˨]; 起動 Kī-dâe̤ng [khi˥ lɔyŋ˨˦˨] - Sorry: 對不住
 Dó̤i-bók-cê̤ṳ [tøy˨˩ puʔ˥ tsøy˨˦˨]
Dó̤i-bók-cê̤ṳ [tøy˨˩ puʔ˥ tsøy˨˦˨] - This: 嚽
 Cuòi [tsui˥˧]; 啫
Cuòi [tsui˥˧]; 啫  Ciā [tsia˧]; 茲
Ciā [tsia˧]; 茲  Cī [tsi˧]
Cī [tsi˧] - That: 噲
 Huòi [hui˥˧]; 嘻
Huòi [hui˥˧]; 嘻  Hiā [hia˧]; 許
Hiā [hia˧]; 許  Hī [hi˧]
Hī [hi˧] - How much?: 偌
 Nuâi (niŏh-uâi) [nuai˨˦˨] ([nuoʔ˨˩ uai˨˦˨])
Nuâi (niŏh-uâi) [nuai˨˦˨] ([nuoʔ˨˩ uai˨˦˨]) - Yes: 正是
 Ciáng-sê [tsiaŋ˥˧ nɛi˨˦˨]; 無綻
Ciáng-sê [tsiaŋ˥˧ nɛi˨˦˨]; 無綻  Mò̤ dâng [mo˨˩ laŋ˨˦˨]; 著
Mò̤ dâng [mo˨˩ laŋ˨˦˨]; 著  Diŏh (Duŏh) [tyoʔ˥] ([tuoʔ˥])
Diŏh (Duŏh) [tyoʔ˥] ([tuoʔ˥]) - No: 伓是
 Ng-sê [ŋ˥˧ nɛi˨˦˨]; 綻
Ng-sê [ŋ˥˧ nɛi˨˦˨]; 綻  Dâng [taŋ˨˦˨]; 賣著
Dâng [taŋ˨˦˨]; 賣著  Mâ̤ diŏh (Mâ̤ duŏh) [me˥ tyoʔ˥] ([me˥ tuoʔ˥])
Mâ̤ diŏh (Mâ̤ duŏh) [me˥ tyoʔ˥] ([me˥ tuoʔ˥]) - I don't understand: 我賣會意
 Nguāi mâ̤ huôi-é [ŋuai˧ me˨˩ hui˥˧ ɛi˨˩˧]
Nguāi mâ̤ huôi-é [ŋuai˧ me˨˩ hui˥˧ ɛi˨˩˧] - What's his name?: 伊名什乇?
 Ĭ miàng sié-nó̤h? [i˥ miaŋ˥˧ sie˨˩ nɔʔ˨˦]
Ĭ miàng sié-nó̤h? [i˥ miaŋ˥˧ sie˨˩ nɔʔ˨˦] - Where's the hotel?: 賓館洽底所?
 Bĭng-guāng găk diē-nē̤? [piŋ˥˧ kuaŋ˧ kaʔ˥ tie˨˦ nø˧]
Bĭng-guāng găk diē-nē̤? [piŋ˥˧ kuaŋ˧ kaʔ˥ tie˨˦ nø˧] - How can I go to the school?: 去學校怎樣行?
 Kó̤ hăk-hâu cuōng-iông giàng? [kho˥˧ haʔ˨˩ hau˨˦˨ tsuoŋ˥ yoŋ˨˦˨ kiaŋ˥˧]
Kó̤ hăk-hâu cuōng-iông giàng? [kho˥˧ haʔ˨˩ hau˨˦˨ tsuoŋ˥ yoŋ˨˦˨ kiaŋ˥˧] - Do you speak Fuzhou dialect?: 汝會講福州話賣?
 Nṳ̄ â̤ gōng Hók-ciŭ-uâ mâ̤? [ny˧ e˥˧ kouŋ˧ huʔ˨˩ tsiu˥˧ ua˨˦˨ ma˨˦˨]
Nṳ̄ â̤ gōng Hók-ciŭ-uâ mâ̤? [ny˧ e˥˧ kouŋ˧ huʔ˨˩ tsiu˥˧ ua˨˦˨ ma˨˦˨] - Do you speak English?: 汝會講英語賣?
 Nṳ̄ â̤ gōng Ĭng-ngṳ̄ mâ̤? [ny˧ e˥˧ kouŋ˧ iŋ˥˧ ŋy˧ ma˨˦˨]
Nṳ̄ â̤ gōng Ĭng-ngṳ̄ mâ̤? [ny˧ e˥˧ kouŋ˧ iŋ˥˧ ŋy˧ ma˨˦˨]
Writing system
Chinese characters

Most of the words of Fuzhou dialect stem from Old Chinese and can therefore be written in Chinese characters. Many books published in Qing Dynasty have been written in this traditional way, such as the famous Mǐndū Biéjì (閩都別記, Foochow Romanized: Mìng-dŭ Biék-gé). However, Chinese characters as the writing system for Fuzhou dialect do have many shortcomings.
Firstly, a great number of words are unique to Fuzhou dialect, so that they can only be written in informal ways. For instance, the word "mâ̤", a negative word, has no common form. Some write it as "賣" or "袂", both of which share with it an identical pronunciation but has a totally irrelevant meaning; and others prefer to use a newly created character combining "勿" and "會", but this character is not included in most fonts.
Secondly, Fuzhou dialect has been excluded from the educational system for many decades. As a result, many if not all take for granted that Fuzhou dialect does not have a formal writing system and when they have to write it, they tend to misuse characters with a similar Mandarin Chinese enunciation. For example, "會使 (â̤ sāi)", meaning "okay", are frequently written as "阿塞" because they are uttered almost in the same way.
Foochow Romanized

Foochow Romanized, also known as Bàng-uâ-cê (平話字, BUC for short) or Hók-ciŭ-uâ Lò̤-mā-cê (福州話羅馬字), is a romanized orthography for Fuzhou dialect adopted in the middle of 19th century by American and English missionaries. It had varied at different times, and became standardized several decades later. Foochow Romanized was mainly used inside of Church circles, and was taught in some Mission Schools in Fuzhou.[20]
Mǐnqiāng Kuàizì
Mǐnqiāng Kuàizì (閩腔快字, Foochow Romanized: Mìng-kiŏng Kuái-cê), literally meaning "Fujian Colloquial Fast Characters", is a Qieyin System (切音系統) for Fuzhou dialect designed by Chinese scholar and calligrapher Li Jiesan (力捷三) in 1896.
Example text
Below are Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights written in the Fuzhou dialect, using both Foochow Romanized (left) and Chinese characters (center).
| BUC version | Hanzi version | English version |
|---|---|---|
| Lièng-hăk-guók sié-gái ìng-guòng sŏng-ngiòng | 聯合國世界人權宣言 | Universal Declaration of Human Rights |
| Dâ̤-ék dèu | 第一條 | Article 1 |
| Sū-iū nè̤ng sĕng giâ lì cêu sê cê̤ṳ-iù gì, | 所有儂生下來就是自由其, | All human beings are born free |
| bêng-chiă diŏh cŏng-ngièng gâe̤ng guòng-lĭk siông ék-lŭk bìng-dēng. | 並且著尊嚴共權利上一律平等。 | and equal in dignity and rights. |
| Ĭ-gáuk-nè̤ng ô lī-séng gâe̤ng liòng-sĭng, | 伊各儂有理性共良心, | They are endowed with reason and conscience |
| bêng-chiă éng-gāi ī hiăng-diê guăng-hiê gì cĭng-sìng lì hô-siŏng dó̤i-dái. | 並且應該以兄弟關係其精神來互相對待。 | and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood. |
Literary and art forms
See also
- Fuqing dialect
- Chinatown, Brooklyn
- Chinatown, Flushing
- Chinatown, Manhattan
- Manhattan's Little Fuzhou
References
- ↑ 大眾運輸工具播音語言平等保障法
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Fuzhou". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ "WALS Online - Language Fuzhou". World Atlas of Language Structures. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ↑ 陈泽平. (1998). 福州方言研究: 福建人民出版社, 福州.
- ↑ Li Rulong, Liang Yuzhang: Fuzhou Dialect Records, 2001, ISBN 7-80597-361-X
- ↑ Li, Zhuqing: A study of the "Qī Lín Bāyīn", University of Washington, 1993
- ↑ Survey by Fuzhou Evening Paper Showing Less Than Half of Fuzhou Youth Able to Speak Fuzhou Dialect (in Chinese)
- ↑ Fuzhou Dialect Protected as Intangible Cultural Heritage (in Chinese)
- ↑ Yuan Jiahua: Summary of Chinese Dialects, 2nd Edition, 2003, ISBN 978-7-80126-474-9
- ↑ 李如龙, & 梁玉璋. (Eds.). (1994) 福州方言词典. 福州: 福建人民出版社.
- ↑ 冯爱珍, & 李荣. (Eds.). (1998) 福州方言词典. 江苏教育出版社.
- ↑ Nguāi Muōng Gōng Nṳ̄ Muōng Tiăng (我罔講汝罔聽), post of March 17th, 2006, retrieved December 26th, 2011.
- ↑ Wu, J., & Chen, Y. (2012). The Effect of Historical Tone Categories on Tone Sandhi in Lianjiang. Paper presented at the 20th Annual Conference of the IACL, Hongkong.https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271849974_The_Effect_of_Historical_Tone_Categories_on_Tone_Sandhi_in_Lianjiang
- ↑ Wu, J., & Chen, Y. (2012). An account of Lianjiang tone Sandhi: Pitch target, context, and historical tone categories. Paper presented at the Tone and Intonation Conference 2012 (TIE5), Londen.
- 1 2 Li Zhuping: Fuzhou Phonology and Grammar, Dunwoody Press (2002), page 6.
- ↑ Peng, Gongguan (2011). A phonetic study of Fuzhou Chinese (Thesis). City University of Hong Kong. Note that the thesis does not mention the open rimes for /e/, /ø/ and /eu/ and does not analyse phonemes independently from tonal allophones.
- ↑ Li Zhuping: Fuzhou Phonology and Grammar, Dunwoody Press (2002), page 106.
- ↑ Zhao Rihe: Fuzhou Dialect Rhyme Dictionary, 1998, MRXN-1998-0465
- ↑ Chen Zeping: Loan Words in Fuzhou dialect, Fujian Normal University, 1994
- ↑ 福州女校三鼎甲 (in Chinese)
Further reading
Missionary texts
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
- White, M.C. (1856). "The Chinese Language Spoken at Fuh Chau". The Methodist Review. 38: 352–381.
- Maclay, R.S.; Baldwin, C.C. (1870). An alphabetic dictionary of the Chinese language in the Foochow dialect. Foochow: Methodist Episcopal Mission Press.
- Baldwin, C.C. (1871). A manual of the Foochow dialect. Foochow: Methodist Episcopal Mission Press.
- Maclay, R.S.; Baldwin, C.C.; Leger, S.H. (1929). Dictionary of the Foochow dialect. Shanghai: Presbyterian Mission Press.
Modern studies
- Chen, Leo (1969). Foochow-English, English-Foochow glossary (PDF). San Francisco, CA: Asian Language Publication.
- Chen, Leo; Norman, Jerry (1965). An Introduction to the Foochow Dialect. San Francisco State College.
- Chen, Zeping 陈泽平 (1998). Fúzhōu fāngyán yánjiū 福州方言研究 [Studies of the Fuzhou dialect]. Fuzhou: Fujian People's Publishing House. ISBN 978-7-211-03080-4.
- —— (2010). Shíjiǔ shìjì yǐlái de fúzhōu fāngyán——chuánjiào shì fúzhōu tǔ bái wénxiàn zhī yǔyán xué yánjiū 十九世纪以来的福州方言——传教士福州土白文献之语言学研究 [Fuzhou dialect since the 19th century – missionary literature on the Fuzhou dialect]. Fuzhou: Fujian People's Publishing House. ISBN 978-7-211-06054-2.
- Dai, Ligang 戴黎刚 (2010). "Fúzhōuhuà shēngmǔ lèi huà lìwài de yuányīn" 福州话声母类化例外的原因. Fangyan. 3.
- Donohue, Cathryn (2013). Fuzhou tonal acoustics and tonology. LINCOM Europa. ISBN 978-3-86288-522-0.
- Feng, Aizhen 冯爱珍; Li, Rong, eds. (1998). Fúzhōu fāngyán cídiǎn 福州方言词典 [Fuzhou dialect dictionary]. Jiangsu Educational Press. ISBN 7-5343-3421-7.
- Li, Rulong 李如龙, ed. (2000). 福州话声母类化的制约条件. Xiamen University (Philosophy and Social Sciences).
- Li, Rulong 李如龙; Liang, Yuzhang 梁玉璋, eds. (1994). Fúzhōu fāngyán cídiǎn 福州方言词典 [Fuzhou dialect dictionary]. Fuzhou: Fujian People's Publishing House. ISBN 7-211-02354-6.
- Li, Zhuqing (1997). Fuzhou-English Dictionary. Dunwoody Press. ISBN 978-1-881265-52-8.
- —— (2002). Fuzhou Phonology and Grammar. Dunwoody Press. ISBN 978-1-881265-93-1.
- Liang, Yuzhang 梁玉璋 (1982). "Fúzhōu fāngyán de 'qiè jiǎo cí'" 福州方言的"切脚词". Fangyan. 1: 37–46.
External links
| Look up Appendix:Min Dong Swadesh list in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Min Dong Chinese edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fuzhou dialect. |
- Fuzhou Dialect Textbook: Elementary school textbook in Matsu.
- Fuzhou dialect phonology, by James Campbell.
- Five Languages Translator
- Fuzhou Dialect Resources
- Eastern Min Chinese (Speech variety #113): Globalrecordings.net. Eastern Min Chinese (Speech variety #113)
- OLAC resources in and about the Eastern Min Chinese language: OLAC. OLAC resources in and about the Eastern Min Chinese language