Benzthiazide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60 to 70% |
| Protein binding | 30% |
| Biological half-life | 5 to 15 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.874 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
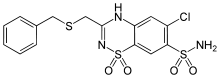
| Formula | C15H14ClN3O4S3 |
| Molar mass | 431.94 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Benzthiazide (BAN/INN, also known as benzothiazide; trade names Aquatag, Dihydrex, Diucen, Edemax, Exna, Foven and others[1]) is a thiazide diuretic used in the treatment of high blood pressure and edema. It is no longer available in the United States.
In the United Kingdom, it was also sold in combination with the potassium-sparing diuretic triamterene under the trade name Dytide.[2] The same combination is still available in Switzerland as Dyrenium compositum.[3]
References
- ↑ David J. Triggle; C. R. Ganellin; F. MacDonald (1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. 1. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC. p. 246. ISBN 0-412-46630-9. Retrieved on August 29, 2008 through Google Book Search.
- ↑ "Triamterene and Benzthiazide". PatientUK. 2005. Retrieved 2008-08-29.
- ↑ "Dyrenium compositum". Doetsch Grether. n.d. Archived from the original on February 11, 2007. Retrieved 2008-08-29.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.