Food coloring



Food coloring, or color additive, is any dye, pigment or substance that imparts color when it is added to food or drink. They come in many forms consisting of liquids, powders, gels, and pastes. Food coloring is used both in commercial food production and in domestic cooking. Food colorants are also used in a variety of non-food applications including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, home craft projects, and medical devices.[2]
Purpose of food coloring
People associate certain colors with certain flavors, and the color of food can influence the perceived flavor in anything from candy to wine.[3] Sometimes the aim is to simulate a color that is perceived by the consumer as natural, such as adding red coloring to glacé cherries (which would otherwise be beige), but sometimes it is for effect, like the green ketchup that Heinz launched in 1999. Color additives are used in foods for many reasons including:[4][5]
- To make food more attractive, appealing, appetizing, and informative
- Offset color loss due to exposure to light, air, temperature extremes, moisture and storage conditions
- Correct natural variations in color
- Enhance colors that occur naturally
- Provide color to colorless and "fun" foods
- Allow consumers to identify products on sight, like candy flavors or medicine dosages
History of artificial food colorants
The addition of colorants to foods is thought to have occurred in Egyptian cities as early as 1500 BC, when candy makers added natural extracts and wine to improve the products' appearance.[6] During the Middle Ages, the economy in the European countries was based on agriculture, and the peasants were accustomed to producing their own food locally or trading within the village communities. Under feudalism, aesthetic aspects were not considered, at least not by the vast majority of the generally very poor population.[7] This situation changed with urbanization at the beginning of the Modern Age, when trade emerged—especially the import of precious spices and colors. One of the very first food laws, created in Augsburg, Germany, in 1531, concerned spices or colorants and required saffron counterfeiters to be burned.[8]
With the onset of the industrial revolution, people became dependent on foods produced by others.[7] These new urban dwellers demanded food at low cost. Analytical chemistry was still primitive and regulations few. The adulteration of foods flourished.[7] Heavy metal and other inorganic element-containing compounds turned out to be cheap and suitable to "restore" the color of watered-down milk and other foodstuffs, some more lurid examples being:[9]
- Red lead (Pb3O4) and vermillion (HgS) were routinely used to color cheese and confectionery.
- Copper arsenite (CuHAsO3) was used to recolor used tea leaves for resale. It also caused two deaths when used to color a dessert in 1860.
Sellers at the time offered more than 80 artificial coloring agents, some invented for dyeing textiles, not foods.[9]
...Thus, with potted meat, fish and sauces taken at breakfast he would consume more or less Armenian bole, red lead, or even bisulphuret of mercury. At dinner with his curry or cayenne he would run the chance of a second dose of lead or mercury; with pickles, bottled fruit and vegetables he would be nearly sure to have copper administrated to him; and while he partook of bon-bons at dessert, there was no telling of the number of poisonous pigments he might consume. Again his tea if mixed or green, he would certainly not escape without the administration of a little Prussian blue...[10]
Many color additives had never been tested for toxicity or other adverse effects. Historical records show that injuries, even deaths, resulted from tainted colorants. In 1851, about 200 people were poisoned in England, 17 of them fatally, directly as a result of eating adulterated lozenges.[7] In 1856, mauveine, the first synthetic color, was developed by Sir William Henry Perkin and by the turn of the century, unmonitored color additives had spread through Europe and the United States in all sorts of popular foods, including ketchup, mustard, jellies, and wine.[11][12] Originally, these were dubbed 'coal-tar' colors because the starting materials were obtained from bituminous coal.[13][5]
Many synthesized dyes were easier and less costly to produce and were superior in coloring properties when compared to naturally derived alternatives.[9] Some synthetic food colorants are diazo dyes. Diazo dyes are prepared by coupling of a diazonium compound with a second aromatic hydrocarbons.[14][15] The resulting compounds contain conjugated systems that efficiently absorb light in the visible parts of the spectrum, i.e. they are deeply colored. The attractiveness of the synthetic dyes is that their color, lipophilicity, and other attributes can be engineered by the design of the specific dyestuff. The color of the dyes can be controlled by selecting the number of azo-groups and various substituents. Yellow shades are often achieved by using acetoacetanilide. Red colors are often azo compounds.[15] The pair indigo and indigo carmine exhibit the same blue color, but the former is soluble in lipids, and the latter is water-soluble because it has been fitted with sulfonate functional groups.
Regulation
History of regulation
Concerns over food safety led to numerous regulations throughout the world. German food regulations released in 1882 stipulated the exclusion of dangerous minerals such as arsenic, copper, chromium, lead, mercury and zinc, which were frequently used as ingredients in colorants.[16] In contrast to today, these first laws followed the principle of a negative listing (substances not allowed for use); they were already driven by the main principles of today's food regulations all over the world, since all of these regulations follow the same goal: the protection of consumers from toxic substances and from fraud.[7] In the United States, the Pure Food and Drug Act of 1906 reduced the permitted list of synthetic colors from 700 down to seven.[17] The seven dyes initially approved were Ponceau 3R (FD&C Red No. 1), amaranth (FD&C Red No. 2), erythrosine (FD&C Red No. 3), indigotine (FD&C Blue No. 2), Light Green SF (FD&C Green No. 2), Naphthol yellow 1 (FD&C Yellow No. 1), and Orange 1 (FD&C Orange No. 1). Even with updated food laws, adulteration continued for many years and this, together with more recent adverse press comments on food colors and health, has continued to contribute to consumer concern about color addition to foodstuffs.
In the 20th century, the improvement of chemical analysis and the development of trials to identify the toxic features of substances added to foods led to the replacement of the negative lists by lists of substances allowed to be used for the production and the improvement of foods. This principle is called a positive listing, and almost all recent legislations are based on it.[7] Positive listing implies that substances meant for human consumption have been tested for their safety, and that they have to meet specified purity criteria prior to their approval by the corresponding authorities. In 1962, the first EU directive (62/2645/EEC) approved 36 colorants, of which 20 were naturally derived and 16 were synthetic.[18] This directive did not list which food products the colorants could or could not be used in. At that time, each member state could designate where certain colors could and could not be used. In Germany, for example, quinoline yellow was allowed in puddings and desserts, but tartrazine was not. The reverse was true in France.[8] This was updated in 1989 with 89/107/EEC, which concerned food additives authorized for use in foodstuffs.[19]
Current regulation
While naturally derived colors are not required to be certified by a number of regulatory bodies throughout the world (including the U.S. FDA), they still need to be approved for use in that country. Food colorings are tested for safety by various bodies around the world and sometimes different bodies have different views on food color safety.
FDA's permitted colors are classified as subject to certification or exempt from certification in Code of Federal Regulations - Title 21 Part 73 & 74, both of which are subject to rigorous safety standards prior to their approval and listing for use in foods.[20]
- Certified colors are synthetically produced and are used widely because they impart an intense, uniform color, are less expensive, and blend more easily to create a variety of hues. There are nine certified color additives approved for use in the United States. Certified food colors generally do not add undesirable flavors to foods.
- Colors that are exempt from certification include pigments derived from natural sources such as vegetables, minerals, or animals. Nature derived color additives are typically more expensive than certified colors and may add unintended flavors to foods. Examples of exempt colors include annatto, beet extract, caramel, beta-carotene, turmeric and grape skin extract. This list contains substances which may have synthetic origins, such as nature identical beta-carotene.
In the United States, FD&C numbers (which indicate that the FDA has approved the colorant for use in foods, drugs and cosmetics) are given to approved synthetic food dyes that do not exist in nature, while in the European Union, E numbers are used for all additives, both synthetic and natural, that are approved in food applications. The food colors are known by E numbers that begin with a 1, such as E100 (turmeric) or E161b (lutein).[21] The safety of food colors and other food additives in the EU is evaluated by the European Food Safety Authority. Color Directive 94/36/EC, enacted by the European Commission in 1994, outlines permitted natural and artificial colors with their approved applications and limits in different foodstuffs.[8] This is binding to all member countries of the EU. Any changes have to be implemented into their national laws within a given time frame. In non-EU member states, food additives are regulated by their national authorities, which usually, but not in all cases, try to harmonize with the laws adopted by the EU. Most other countries have their own regulations and list of food colors which can be used in various applications, including maximum daily intake limits.
Permitted colorants
E.U.
E numbers 102-143 cover the range of artificial colors. For an overview of currently allowed additives see here . Some artificial dyes approved for food use in the EU include:
- E104: Quinoline Yellow
- E122: Carmoisine
- E124: Ponceau 4R
- E131: Patent Blue V
- E142: Green S
U.S.
In the US, the following seven artificial colorings are generally permitted in food (the most common in bold) as of 2016. The lakes of these colorings are also permitted except the lake of Red No. 3.[22]
- FD&C Blue No. 1 – Brilliant Blue FCF, E133 (blue shade)
- FD&C Blue No. 2 – Indigotine, E132 (indigo shade)
- FD&C Green No. 3 – Fast Green FCF, E143 (turquoise shade)
- FD&C Red No. 3 – Erythrosine, E127 (pink shade, commonly used in glacé cherries)[23]
- FD&C Red No. 40 – Allura Red AC, E129 (red shade)
- FD&C Yellow No. 5 – Tartrazine, E102 (yellow shade)
- FD&C Yellow No. 6 – Sunset Yellow FCF, E110 (orange shade)
Two dyes are allowed by the FDA for limited applications:
- Citrus Red 2 (orange shade) - allowed only to color orange peels.
- Orange B (red shade) - allowed only for use in hot dog and sausage casings (not produced after 1978, but never delisted)
Many dyes have been delisted for a variety of reasons, ranging from poor coloring properties to regulatory restrictions.[24] Some of these delisted food colorants are:
- FD&C Red No. 2 – Amaranth, E123
- FD&C Red No. 4[25][26]
- FD&C Red No. 32 was used to color Florida oranges.[24][25][27]
- FD&C Orange Number 1 was one of the first water-soluble dyes to be commercialized, and one of seven original food dyes allowed under the Pure Food and Drug Act of June 30, 1906.[24][25]
- FD&C Orange No. 2 was used to color Florida oranges.[24]
- FD&C Yellow No. 1, 2, 3, and 4[25]
- FD&C Violet No. 1[25]
Global harmonization
Since the beginning of the 1960s, JECFA has promoted the development of international standards for food additives, not only by its toxicological assessments, which are continuously published by the WHO in a "Technical Report Series", but furthermore by elaborating appropriate purity criteria, which are laid down in the two volumes of the "Compendium of Food Additive Specifications" and their supplements. These specifications are not legally binding but very often serve as a guiding principle, especially in countries where no scientific expert committees have been established.[7]
In order to further regulate the use of these evaluated additives, in 1962 the WHO and FAO created an international commission, the Codex Alimentarius, which is composed of authorities, food industry associations and consumer groups from all over the world. Within the Codex organization, the Codex Committee for Food Additives and Contaminants is responsible for working out recommendations for the application of food additives, the General Standard for Food Additives. In the light of the World Trade Organizations General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), the Codex Standard, although not legally binding, influences food color regulations all over the world.[7]
Natural food dyes

Carotenoids (E160, E161, E164), chlorophyllin (E140, E141), anthocyanins (E163), and betanin (E162) comprise four main categories of plant pigments grown to color food products.[28] Other colorants or specialized derivatives of these core groups include:
- Annatto (E160b), a reddish-orange dye made from the seed of the achiote
- Caramel coloring (E150a-d), made from caramelized sugar
- Carmine (E120), a red dye derived from the cochineal insect, Dactylopius coccus
- Elderberry juice (E163)
- Lycopene (E160d)
- Paprika (E160c)
- Turmeric (E100)
Blue colors are especially rare.[29] One feasible blue dye currently in use is derived from spirulina.
To ensure reproducibility, the colored components of these substances are often provided in highly purified form. For stability and convenience, they can be formulated in suitable carrier materials (solid and liquids). Hexane, acetone, and other solvents break down cell walls in the fruit and vegetables and allow for maximum extraction of the coloring. Traces of these may still remain in the finished colorant, but they do not need to be declared on the product label. These solvents are known as carry-over ingredients.
Criticism and health implications
Widespread public belief that artificial food coloring cause hyperactivity in children originated with Benjamin Feingold a pediatric allergist from California, who proposed in 1973 that salicylates, artificial colors, and artificial flavors cause hyperactivity in children;[30] however, there is no evidence to support broad claims that food coloring causes food intolerance and ADHD-like behavior in children.[31]:452[32] It is possible that certain food coloring may act as a trigger in those who are genetically predisposed, but the evidence is weak.[33][34]
After concerns were expressed that food colorings may cause ADHD-like behavior in children,[33] the collective evidence do not support this assertion.[35] The US FDA and other food safety authorities to regularly review the scientific literature, and led the UK Food Standards Agency (FSA) to commission a study by researchers at Southampton University of the effect of a mixture of six food dyes (Tartrazine, Allura Red, Ponceau 4R, Quinoline Yellow WS, Sunset Yellow and Carmoisine (dubbed the "Southampton 6")) on children in the general population. These colorants are found in beverages.[33][36] The study found "a possible link between the consumption of these artificial colours and a sodium benzoate preservative and increased hyperactivity" in the children;[33][36] the advisory committee to the FSA that evaluated the study also determined that because of study limitations, the results could not be extrapolated to the general population, and further testing was recommended".[33] The U.S. FDA did not make changes following the publication of the Southampton study, but following a citizen petition filed by the Center for Science in the Public Interest in 2008, requesting the FDA ban several food additives, the FDA reviewed the available evidence, and still made no changes.[33]
The European regulatory community, with an emphasis on the precautionary principle, required labelling and temporarily reduced the acceptable daily intake (ADI) for the food colorings; the UK FSA called for voluntary withdrawal of the colorings by food manufacturers.[33][36] However, in 2009 the EFSA re-evaluated the data at hand and determined that "the available scientific evidence does not substantiate a link between the color additives and behavioral effects" for any of the dyes.[33][37][38][39][40]
Chemical structures of representative colorants
- Food colorants, natural
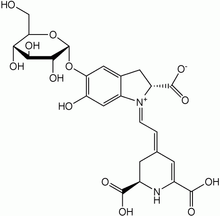 Betanin, a magenta dye, mainly produced from beets.
Betanin, a magenta dye, mainly produced from beets. Anthocyanin, a red to blue dye depending on functional groups and pH.
Anthocyanin, a red to blue dye depending on functional groups and pH. beta-Carotene, a yellow to orange colorant.
beta-Carotene, a yellow to orange colorant.
- Food colorants, synthetic
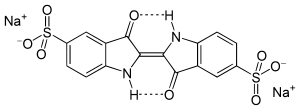 Indigo Carmine, which is blue.
Indigo Carmine, which is blue. Allura Red AC, which is red.
Allura Red AC, which is red.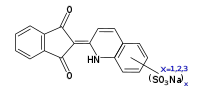 Quinoline Yellow WS, which is yellow.
Quinoline Yellow WS, which is yellow.
See also
References
- ↑ Ian P. Freeman, "Margarines and Shortenings" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_145
- ↑ CFR Title 21 Part 70: Color Additive Regulations, FDA, retrieved Feb 15, 2012
- ↑ Jeannine Delwiche (2003). "The impact of perceptual interactions on perceived flavor" (PDF). Food Quality and Preference. 14 (2): 137–146. doi:10.1016/S0950-3293(03)00041-7.
- ↑ "Food Ingredients & Colors". International Food Information Council. June 29, 2010. Retrieved Feb 15, 2012.
- 1 2 Barrows, Julie N.; Lipman, Arthur L.; Bailey, Catherine J. (17 Dec 2009). "Color Additives: FDA's Regulatory Process and Historical Perspectives". FDA (Reprinted from Food Safety Magazine October/November 2003 issue). Retrieved 2 Mar 2012.
Although certifiable color additives have been called coal-tar colors because of their traditional origins, today they are synthesized mainly from raw materials obtained from petroleum.
- ↑ Meggos, H. (1995). "Food colours: an international perspective". The Manufacturing Confectioner. pp. 59–65.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Arlt, Ulrike (29 Apr 2011). "The Legislation of Food Colours in Europe". The Natural Food Colours Association. Retrieved 18 Feb 2014.
- 1 2 3 Cook, Jim. "Colorants Compliance". The World of Food Ingredients. Arnhem, The Netherlands: CNS Media BV (Sept 2013): 41–43. ISSN 1566-6611.
- 1 2 3 Downham, Alison; Collins, Paul (2000). "Colouring our foods in the last and next millennium" (PDF). International Journal of Food Science and Technology. Blackwell Science Ltd. 35: 5–22. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2621.2000.00373.x. Retrieved 18 Feb 2014.
- ↑ Hassel, A.H. (1960). Amos, Arthur James, ed. Pure Food and Pure Food Legislation. Butterworths, London. p. 12.
- ↑ Walford, J. (1980). "Historical Development of Food Colouration". Developments in Food Colours. London: Applied Science Publishers. 1: 1–25.
- ↑ Sharma, Vinita; McKone, Harold T.; Markow, Peter G. (2011). "A Global Perspective on the History, Use, and Identification of Synthetic Food Dyes". Journal of Chemical Education. 88: 24–28. doi:10.1021/ed100545v.
- ↑ Hancock, Mary (1997). "Potential for Colourants from Plant Sources in England & Wales" (PDF). UK Central Science Laboratory. Retrieved 20 January 2013.
The use of natural dyes in the UK and the rest of the Western economies has been replaced commercially by synthetic dyes, based mainly on aniline and using petroleum or coal tar as the raw stock.
- ↑ Klaus Hunger, Peter Mischke, Wolfgang Rieper, Roderich Raue, Klaus Kunde, Aloys Engel: "Azo Dyes" in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.doi:10.1002/14356007.a03_245.
- 1 2 König, J. (2015), "Food colour additives of synthetic origin", in Scotter, Michael J., Colour Additives for Foods and Beverages, Elsevier, pp. 35–60, ISBN 978-1-78242-011-8, doi:10.1016/B978-1-78242-011-8.00002-7
- ↑ Hastings, Robert W. (January–March 1898). Hamilton, John B., ed. "Human Food Laws". Journal of the American Medical Association. Chicago: American Medical Association. 30 (1-13): 419–421. doi:10.1001/jama.1898.72440600019002e. Retrieved 17 Feb 2014.
- ↑ Meadows, Michelle (2006). "A Century of Ensuring Safe Foods and Cosmetics". FDA Consumer magazine. FDA (January–February). Retrieved 21 Feb 2014.
- ↑ EEC: Council Directive on the approximation of the rules of the Member States concerning the colouring matters authorized for use in foodstuffs intended for human consumption OJ 115, 11.11.1962, p. 2645–2654 (DE, FR, IT, NL) English special edition: Series I Volume 1959-1962 p. 279–290
- ↑ Council Directive 89/107/EEC of 21 December 1988 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States concerning food additives authorized for use in foodstuffs intended for human consumption OJ L 40, 11.2.1989, p. 27–33 (ES, DA, DE, EL, EN, FR, IT, NL, PT)
- ↑ Barrows, Julie N.; Lipman, Arthur L.; Bailey, Catherine J. Cianci, Sebastian, ed. "Color Additives: FDA's Regulatory Process and Historical Perspectives". Food Safety Magazine. No. October/November 2003. Food Safety Magazine. Retrieved 24 July 2016.
- ↑ "Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers". Food Standards Agency. 26 Nov 2010. Retrieved 20 Feb 2012.
- ↑ US FDA Color Additive Status List
- ↑ "Red No. 3 and Other Colorful Controversies". FDA. Archived from the original on 2007-08-09. Retrieved 2007-08-26.
FDA terminated the provisional listings for FD&C Red No. 3 on January 29, 1990, at the conclusion of its review of the 200 straight colors on the 1960 provisional list. Commonly called erythrosine, FD&C Red No. 3 is a tint that imparts a watermelon-red color and was one of the original seven colors on Hesse's list.
- 1 2 3 4 "News of Food; U.S. May Outlaw Dyes Used to Tint Oranges and Other Foods". New York Times. January 19, 1954.
The use of artificial colors to make foods more attractive to the eye may be sharply curtailed by action of the United States Food and Drug Administration. Three of the most extensively used food colorants are being considered for removal from the Government's list of colors certified as safe for internal and external use and consumption.
(Subscription required.) - 1 2 3 4 5 "Food coloring". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2007-08-21.
Among the colours that have been “delisted,” or disallowed, in the United States are FD&C Orange No. 1; FD&C Red No. 32; FD&C Yellows No. 1, 2, 3, and 4; FD&C Violet No. 1; and FD&C Reds No. 2 and 4. Many countries with similar food colouring controls (including Canada and Great Britain) also ban the use of Red No. 40, and Yellow No. 5 is also undergoing testing.
- ↑ CFR Title 21 Part 81.10: Termination of provisional listings of color additives.
- ↑ Deshpande, S.S., ed. (2002), "8.5.3 Toxicological Characteristics of Colorants Subject to Certification", Handbook of Food Toxicology, Food Science and Technology, CRC Press, p. 234, ISBN 9780824707606
- ↑ Delia B Rodriguez-Amaya "Natural food pigments and colorants" Current Opinion in Food Science 2016, Volume 7, Pages 20–26. doi:10.1016/j.cofs.2015.08.004
- ↑ Newsome, A. G.,; Culver, C. A.;van Breemen, R. B. "Nature’s palette: the search for natural blue colorants" J Agric Food Chem 2014, volume 62, pp. 6498-6511. doi:10.1021/jf501419q
- ↑ Feingold, B.F. (1973). Introduction to clinical allergy. Charles C. Thomas. ISBN 0-398-02797-8.
- ↑ Tomaska LD and Brooke-Taylor, S. Food Additives - General pp 449-454 in Encyclopedia of Food Safety, Vol 2: Hazards and Diseases. Eds, Motarjemi Y et al. Academic Press, 2013. ISBN 9780123786135
- ↑ Kavale KA, Forness SR (1983). "Hyperactivity and Diet Treatment: A Meta-Analysis of the Feingold Hypothesis". Journal of Learning Disabilities. 16 (6): 324–330. ISSN 0022-2194. doi:10.1177/002221948301600604.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 FDA. Background Document for the Food Advisory Committee: Certified Color Additives in Food and Possible Association with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Children: March 30-31, 2011
- ↑ Millichap JG, Yee MM (February 2012). "The diet factor in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder". Pediatrics. 129 (2): 330–337. PMID 22232312. doi:10.1542/peds.2011-2199.
- ↑ Amchova, Petra; Kotolova, Hana; Ruda-Kucerova, Jana "Health safety issues of synthetic food colorants" Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology (2015), 73(3), 914-922.doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2015.09.026
- 1 2 3 Sarah Chapman of Chapman Technologies on behalf of Food Standards Agency in Scotland. March 2011 [Guidelines on approaches to the replacement of Tartrazine, Allura Red, Ponceau 4R, Quinoline Yellow, Sunset Yellow and Carmoisine in food and beverages]
- ↑ EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to food (ANS) Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of Sunset Yellow FCF (E 110) as a food additive. EFSA Journal 2009; 7(11):1330 doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1330
- ↑ EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS) 091113 efsa.europa.eu Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of Ponceau 4R (E 124) as a food additive EFSA Journal 2009; 7(11):1328
- ↑ EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to food (ANS). Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of Quinoline Yellow (E 104) as a food additive. EFSA Journal 2009; 7(11):1329 [40 pp.]. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1329
- ↑ EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (ANS) (November 2009). "Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation Tartrazine (E 102)". EFSA Journal. 7 (11): 1331–1382. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1331.
External links
- Food coloring at Encyclopædia Britannica
- FDA/CFSAN Food Color Facts
- Natural Food Colors (Food-Info)
- Report on the Certification of Color Additives by US FDA
- NATCOL: What are natural food colours?
- CSPI: Food Dyes Pose Rainbow of Risks