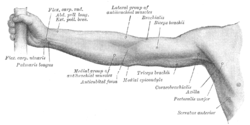
Flexor carpi radialis muscle
| Flexor carpi radialis muscle | |
|---|---|
|
Anterior view of the left forearm. Superficial muscles. (Flexor carpi radialis and its tendon visible in blue.) | |
|
Anterior view of right upper extremity. (Flex. carp. rad. labeled at upper left.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | medial epicondyle of humerus (common flexor tendon) |
| Insertion | Bases of second and third metacarpal bones |
| Artery | Radial Artery |
| Nerve | Median nerve |
| Actions | Flexion and abduction at wrist |
| Antagonist | Extensor carpi ulnaris muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus flexor carpi radialis |
| Dorlands /Elsevier | m_22/12549030 |
| TA | A04.6.02.028 |
| FMA | 38459 |
In anatomy, flexor carpi radialis is a muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and (radial) abduct the hand. The Latin carpus means wrist, and carpi "of the wrist." Hence flexor carpi is a flexor of the wrist.
Origin and insertion
This muscle originates on the medial epicondyle of the humerus. It runs just laterally of flexor digitorum superficialis and inserts on the anterior aspect of the base of the second metacarpal, and has small slips to both the third metacarpal and trapezial tuberosity.[1]
On the anterior aspect of a person's forearm, proximal to the wrist, flexor carpi radialis is the most lateral (closest to the thumb) tendon visible when the wrist is brought into flexion.
Nerve and artery
As are most of the flexors of the hand, FCR is innervated by the median nerve. It gets its blood from the radial artery.
Exercises
The muscle, like all flexors of the forearm, can be strengthened by exercises that resist its flexion. A wrist roller can be used and wrist curls with dumbbells can also be performed.
See also
Additional images
- Cross-section through the middle of the forearm.
 Transverse section across distal ends of radius and ulna.
Transverse section across distal ends of radius and ulna.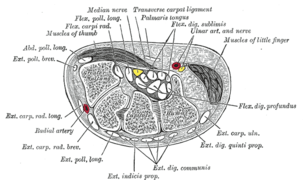 Transverse section across the wrist and digits.
Transverse section across the wrist and digits. The mucous sheaths of the tendons on the front of the wrist and digits.
The mucous sheaths of the tendons on the front of the wrist and digits. The muscles of the thumb.
The muscles of the thumb. The muscles of the left hand. Palmar surface.
The muscles of the left hand. Palmar surface.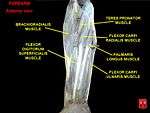 Flexor carpi radialis muscle
Flexor carpi radialis muscle