Flavivirus
| Flavivirus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| A TEM micrograph of the yellow fever virus | |
| Virus classification | |
| Group: | Group IV ((+)ssRNA) |
| Family: | Flaviviridae |
| Genus: | Flavivirus |
| Type species | |
| Yellow fever virus [1] | |
| Species | |
|
(see list in article) | |
Flavivirus is a genus of viruses in the family Flaviviridae. This genus includes the West Nile virus, dengue virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, yellow fever virus, Zika virus and several other viruses which may cause encephalitis,[2] as well as insect-specific flaviviruses (ISFs) such as cell fusing agent virus (CFAV), Palm Creek virus (PCV), and Parramatta River virus (PaRV).[3]
Flaviviruses are named from the yellow fever virus, the type virus for the family; the word flavus means "yellow" in Latin. The name yellow fever in turn originated from its propensity to cause yellow jaundice in victims.[4]
Flaviviruses share several common aspects: common size (40–65 nm), symmetry (enveloped, icosahedral nucleocapsid), nucleic acid (positive-sense, single-stranded RNA around 10,000–11,000 bases), and appearance in the electron microscope.
Most of these viruses are transmitted by the bite from an infected arthropod (mosquito or tick) and hence, classified as arboviruses. Human infections with most of these arboviruses are incidental, as humans are unable to replicate the virus to high enough titers to reinfect the arthropods needed to continue the virus lifecycle – humans are then a dead end host. The exceptions to this are the yellow fever, dengue, and zika viruses. These three viruses still require mosquito vectors, but are well-enough adapted to humans as to not necessarily depend upon animal hosts (although they continue to have important animal transmission routes, as well).
Other virus transmission routes for arboviruses include handling infected animal carcasses, blood transfusion, child birth and through consumption of unpasteurised milk products. Transmission from nonhuman vertebrates to humans without an intermediate vector arthropod is thought to be unlikely. For example, early tests with yellow fever showed that the disease is not contagious.
The known non-arboviruses of the flavivirus family reproduce in either arthropods or vertebrates, but not both, with one odd member of the genus affecting a nematode.[5]
Taxonomy
Group: ssRNA(+)
- Family: Flaviviridae
- Genus: Flavivirus
- Apoi virus
- Aroa virus
- Bagaza virus
- Banzi virus
- Bouboui virus
- Bukalasa bat virus
- Cacipacore virus
- Carey Island virus
- Cowbone Ridge virus
- Dakar bat virus
- Dengue virus
- Edge Hill virus
- Entebbe bat virus
- Gadgets Gully virus
- Ilheus virus
- Israel turkey meningoencephalomyelitis virus
- Japanese encephalitis virus
- Jugra virus
- Jutiapa virus
- Kadam virus
- Kedougou virus
- Kokobera virus
- Koutango virus
- Kyasanur Forest disease virus
- Langat virus
- Louping ill virus
- Meaban virus
- Modoc virus
- Montana myotis leukoencephalitis virus
- Murray Valley encephalitis virus
- Ntaya virus
- Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus
- Phnom Penh bat virus
- Powassan virus
- Rio Bravo virus
- Royal Farm virus
- Saboya virus
- Sal Vieja virus
- San Perlita virus
- Saumarez Reef virus
- Sepik virus
- St. Louis encephalitis virus
- Tembusu virus
- Tick-borne encephalitis virus
- Tyuleniy virus
- Uganda S virus
- Usutu virus
- Wesselsbron virus
- West Nile virus
- Yaounde virus
- Yellow fever virus
- Yokose virus
- Zika virus
Structure
Viruses in Flavivirus are enveloped, with icosahedral and spherical geometries. The diameter is around 50 nm. Genomes are linear positive-sense RNA and non-segmented, around 10-11kb in length.[7]
| Genus | Structure | Symmetry | Capsid | Genomic arrangement | Genomic segmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavivirus | Icosahedral-like | Pseudo T=3 | Enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
Life cycle
Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment of the viral envelope protein E to host receptors, which mediates clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Replication follows the positive stranded RNA virus replication model. Positive stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. Humans, mammals, mosquitoes, and ticks serve as the natural host. Transmission routes are zoonosis and bite.[7]
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavivirus | Humans; mammals; mosquitoes; ticks | Epithelium: skin; epithelium: kidney; epithelium: intestine; epithelium: testes | Clathrin-mediated endocytosis | Secretion | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Zoonosis; arthropod bite |
Replication
Flaviviruses have a (+) sense RNA genome and replicate in the cytoplasm of the host cells. The genome mimics the cellular mRNA molecule in all aspects except for the absence of the poly-adenylated (poly-A) tail. This feature allows the virus to exploit cellular apparatus to synthesise both structural and non-structural proteins, during replication. The cellular ribosome is crucial to the replication of the flavivirus, as it translates the RNA, in a similar fashion to cellular mRNA, resulting in the synthesis of a single polyprotein. In general, the genome encodes 3 structural proteins (Capsid, prM, and Envelope) and 7 non-structural proteins (NS1, NS2A, NS2B, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5).[8] The genomic RNA is modified at the 5′ end of positive-strand genomic RNA with a cap-1 structure (me7-GpppA-me2).
Cellular RNA cap structures are formed via the action of an RNA triphosphatase, with guanylyltransferase, N7-methyltransferase and 2′-O methyltransferase. The virus encodes these activities in its non-structural proteins. The NS3 protein encodes a RNA triphosphatase within its helicase domain. It uses the helicase ATP hydrolysis site to remove the γ-phosphate from the 5′ end of the RNA. The N-terminal domain of the non-structural protein 5 (NS5) has both the N7-methyltransferase and guanylyltransferase activities necessary for forming mature RNA cap structures. RNA binding affinity is reduced by the presence of ATP or GTP and enhanced by S-adenosyl methionine.[9] This protein also encodes a 2′-O methyltransferase.
Once translated, the polyprotein is cleaved by a combination of viral and host proteases to release mature polypeptide products.[10] Nevertheless, cellular post-translational modification is dependent on the presence of a poly-A tail; therefore this process is not host-dependent. Instead, the polyprotein contains an autocatalytic feature which automatically releases the first peptide, a virus specific enzyme. This enzyme is then able to cleave the remaining polyprotein into the individual products. One of the products cleaved is a polymerase, responsible for the synthesis of a (-) sense RNA molecule. Consequently, this molecule acts as the template for the synthesis of the genomic progeny RNA.
Flavivirus genomic RNA replication occurs on rough endoplasmic reticulum membranes in membranous compartments.
New viral particles are subsequently assembled. This occurs during the budding process which is also responsible for the accumulation of the envelope and cell lysis.
A G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (also known as ADRBK1) appears to be important in entry and replication for several Flaviviridae.[11]
RNA secondary structure elements
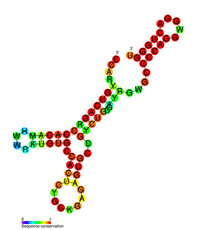
| Flavivirus 3'UTR stem loop IV | |
|---|---|
|
Predicted secondary structure of the Flavivirus 3'UTR stem loop IV | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | Flavivirus_SLIV |
| Rfam | RF01415 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-reg |
| Domain(s) | Flaviviridae |
| SO | 0005836 |
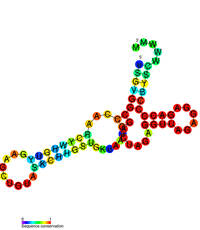
| Flavivirus DB element | |
|---|---|
|
Predicted secondary structure of the Flavivirus DB element | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | Flavivirus_DB |
| Rfam | RF00525 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-reg |
| Domain(s) | Flaviviridae |
| SO | 0000233 |
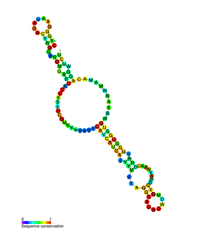
| Flavivirus 3' UTR cis-acting replication element (CRE) | |
|---|---|
|
Predicted secondary structure of the Flavivirus 3' UTR cis-acting replication element (CRE) | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | Flavi_CRE |
| Alt. Symbols | Flavi_pk3 |
| Rfam | RF00185 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-reg |
| Domain(s) | Flaviviridae |
| SO | 0000205 |
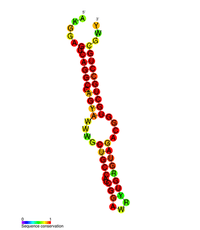
| Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) hairpin structure | |
|---|---|
|
Predicted secondary structure of the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) hairpin structure | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | JEV_hairpin |
| Rfam | RF00465 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-reg |
| Domain(s) | Flaviviridae |
| SO | 0000233 |
The (+) sense RNA genome of Flavivirus contains 5' and 3' untranslated regions (UTRs).
5'UTR
The 5'UTRs are 95–101 nucleotides long in Dengue virus.[12] There are two conserved structural elements in the Flavivirus 5'UTR, a large stem loop (SLA) and a short stem loop (SLB). SLA folds into a Y-shaped structure with a side stem loop and a small top loop.[12][13] SLA is likely to act as a promoter, and is essential for viral RNA synthesis.[14][15] SLB is involved in interactions between the 5'UTR and 3'UTR which result in the cyclisation of the viral RNA, which is essential for viral replication.[16]
3'UTR
The 3'UTRs are typically 0.3–0.5 kb in length and contain a number of highly conserved secondary structures which are conserved and restricted to the flavivirus family. The majority of analysis has been carried out using West Nile virus (WNV) to study the function the 3'UTR.
Currently 8 secondary structures have been identified within the 3'UTR of WNV and are (in the order in which they are found with the 3'UTR) SL-I, SL-II, SL-III, SL-IV, DB1, DB2 and CRE.[17][18] Some of these secondary structures have been characterised and are important in facilitating viral replication and protecting the 3'UTR from 5' endonuclease digestion. Nuclease resistance protects the downstream 3' UTR RNA fragment from degradation and is essential for virus-induced cytopathicity and pathogenicity.
- SL-II
SL-II has been suggested to contribute to nuclease resistance.[18] It may be related to another hairpin loop identified in the 5'UTR of the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) genome.[19] The JEV hairpin is significantly over-represented upon host cell infection and it has been suggested that the hairpin structure may play a role in regulating RNA synthesis.
- SL-IV
This secondary structure is located within the 3'UTR of the genome of Flavivirus upstream of the DB elements. The function of this conserved structure is unknown but is thought to contribute to ribonuclease resistance.
- DB1/DB2
These two conserved secondary structures are also known as pseudo-repeat elements. They were originally identified within the genome of Dengue virus and are found adjacent to each other within the 3'UTR. They appear to be widely conserved across the Flaviviradae. These DB elements have a secondary structure consisting of three helices and they play a role in ensuring efficient translation. Deletion of DB1 has a small but significant reduction in translation but deletion of DB2 has little effect. Deleting both DB1 and DB2 reduced translation efficiency of the viral genome to 25%.[17]
- CRE
CRE is the Cis-acting replication element, also known as the 3'SL RNA elements, and is thought to be essential in viral replication by facilitating the formation of a "replication complex".[20] Although evidence has been presented for an existence of a pseudoknot structure in this RNA, it does not appear to be well conserved across flaviviruses.[21] Deletions of the 3' UTR of flaviviruses have been shown to be lethal for infectious clones.
Conserved hairpin cHP
A conserved hairpin (cHP) structure was later found in several Flavivirus genomes and is thought to direct translation of capsid proteins. It is located just downstream of the AUG start codon.[22]
The role of RNA secondary structures in sfRNA production
Subgenomic flavivirus RNA (sfRNA) is an extension of the 3' UTR and has been demonstrated to play a role in flavivirus replication and pathogenesis.[23] sfRNA is produced by incomplete degradation of genomic viral RNA by the host cells 5'-3' exoribonuclease 1 (XRN1).[24] As the XRN1 degrades viral RNA, it stalls at stemloops formed by the secondary structure of the 5' and 3' UTR.[25] This pause results in an undigested fragment of genome RNA known as sfRNA. sfRNA influences the life cycle of the flavivirus in a concentration dependent manner. Accumulation of sfRNA causes (1) antagonization of the cell's innate immune response, thus decreasing host defense against the virus[26] (2) inhibition of XRN1 and Dicer activity to modify RNAi pathways that destroy viral RNA[27] (3) modification of the viral replication complex to increase viral reproduction.[28] Overall, sfRNA is implied in multiple pathways that compromise host defenses and promote infection by flaviviruses.
Evolution
The flaviviruses can be divided into 2 clades: one with the vector borne viruses and the other with no known vector.[29] The vector clade in turn can be subdivided into a mosquito borne clade and a tick borne clade. These groups can be divided again.[30]
The mosquito group can be divided into two branches: one branch contains the neurotropic viruses, often associated with encephalitic disease in humans or livestock. This branch tends to be spread by Culex species and to have bird reservoirs. The second branch is the non-neurotropic viruses which are associated with haemorrhagic disease in humans. These tend to have Aedes species as vectors and primate hosts.
The tick-borne viruses also form two distinct groups: one is associated with seabirds and the other - the tick-borne encephalitis complex viruses - is associated primarily with rodents.
The viruses that lack a known vector can be divided into three groups: one closely related to the mosquito-borne viruses which is associated with bats; a second, genetically more distant, is also associated with bats; and a third group is associated with rodents.
It seems likely that tick transmission may have been derived from a mosquito borne group.[31]
A partial genome of a flavivirus has been found in the sea spider Endeis spinosa.[32] The sequences are related to those in the insect specific flaviviruses. It is not presently clear how this sequence fits into the evolution of this group of viruses.
Estimates of divergence times have been made for several of these viruses.[33] The origin of these viruses appears to be at least 9400 to 14,000 years ago. The Old World and New World dengue strains diverged between 150 and 450 years ago. The European and Far Eastern tick borne encephalitis strains diverged about 1087 (1610–649) years ago. European tick borne encephalitis and louping ill viruses diverged about 572 (844–328) years ago. This latter estimate is consistent with historical records. Kunjin virus diverged from West Nile virus approximately 277 (475–137) years ago. This time corresponds to the settlement of Australia from Europe. The Japanese encephalitis group appears to have evolved in Africa 2000–3000 years ago and then spread initially to South East Asia before migrating to the rest of Asia.
Phylogenetic studies of the West Nile Virus have shown that it emerged as a distinct virus around 1000 years ago.[34] This initial virus developed into two distinct lineages, lineage 1 and its multiple profiles is the source of the epidemic transmission in Africa and throughout the world. Lineage 2 was considered an Africa zoonosis. However, in 2008, lineage 2, previously only seen in horses in sub-Saharan Africa and Madagascar, began to appear in horses in Europe, where the first known outbreak affected 18 animals in Hungary in 2008.[35] Lineage 1 West Nile virus was detected in South Africa in 2010 in a mare and her aborted fetus; previously, only lineage 2 West Nile virus had been detected in horses and humans in South Africa.[36] A 2007 fatal case in a killer whale in Texas broadened the known host range of West Nile virus to include cetaceans.[37]
Omsk haemorrhagic fever virus appears to have evolved within the last 1000 years.[38] The viral genomes can be divided into 2 clades — A and B. Clade A has five genotypes and clade B has one. These clades separated about 700 years ago. This separation appears to have occurred in the Kurgan province. Clade A subsequently underwent division into clade C, D and E 230 years ago. Clade C and E appear to have originated in the Novosibirsk and Omsk Provinces respectively. The muskrat Ondatra zibethicus which is highly susceptible to this virus was introduced into this area in the 1930s.
Species
Tick-borne viruses
Mammalian tick-borne virus group
- Greek goat encephalitis virus (GGEV)
- Kadam virus (KADV)
- Krasnodar virus (KRDV)
- Mogiana tick virus (MGTV)
- Ngoye virus (NGOV)
- Sokuluk virus (SOKV)
- Spanish sheep encephalomyelitis virus (SSEV)
- Turkish sheep encephalitis virus (TSE)
- Tick-borne encephalitis virus serocomplex
- Absettarov virus
- Deer tick virus (DT)
- Gadgets Gully virus (GGYV)
- Karshi virus
- Kyasanur Forest disease virus (KFDV)
- Alkhurma hemorrhagic fever virus (ALKV)
- Langat virus (LGTV)
- Louping ill virus (LIV)
- Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus (OHFV)
- Powassan virus (POWV)
- Royal Farm virus (RFV)
- Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV)
Seabird tick-borne virus group
- Kama virus (KAMV)
- Meaban virus (MEAV)
- Saumarez Reef virus (SREV)
- Tyuleniy virus (TYUV)
Mosquito-borne viruses
- Without known vertebrate host
- Aedes flavivirus
- Barkedji virus
- Calbertado virus
- Cell fusing agent virus
- Chaoyang virus
- Culex flavivirus
- Culex theileri flavivirus
- Culiseta flavivirus
- Donggang virus
- Ilomantsi virus
- Kamiti River virus
- Lammi virus
- Marisma mosquito virus
- Nounané virus
- Nhumirim virus
- Nienokoue virus
- Spanish Culex flavivirus
- Spanish Ochlerotatus flavivirus
- Quang Binh virus
- Aroa virus group
- Aroa virus (AROAV)
- Bussuquara virus (BSQV)
- Iguape virus (IGUV)
- Naranjal virus (NJLV)
- Dengue virus group
- Dengue virus (DENV)
- Kedougou virus (KEDV)
- Japanese encephalitis virus group
- Cacipacore virus (CPCV)
- Koutango virus (KOUV)
- Kunjin virus
- Ilheus virus (ILHV)
- Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV)
- Murray Valley encephalitis virus (MVEV)
- Alfuy virus
- St. Louis encephalitis virus (SLEV)
- Usutu virus (USUV)
- West Nile virus (WNV)
- Yaounde virus (YAOV)
- Kokobera virus group
- Kokobera virus (KOKV)
- New Mapoon virus (NMV)
- Stratford virus (STRV)
- Ntaya virus group
- Bagaza virus (BAGV)
- Baiyangdian virus (BYDV)
- Duck egg drop syndrome virus (DEDSV)
- Ilheus virus (ILHV)
- Israel turkey meningoencephalomyelitis virus (ITV)
- Jiangsu virus (JSV)
- Layer flavivirus
- Ntaya virus (NTAV)
- Rocio virus (ROCV)
- Sitiawan virus (STWV)
- T'Ho virus
- Tembusu virus (TMUV)
- Spondweni virus group
- Spondweni virus (SPOV)
- Zika virus (ZIKV)
- Yellow fever virus group
- Banzi virus (BANV)
- Bamaga virus (BGV)
- Bouboui virus (BOUV)
- Edge Hill virus (EHV)
- Fitzroy river virus
- Jugra virus (JUGV)
- Saboya virus (SABV)
- Sepik virus (SEPV)
- Uganda S virus (UGSV)
- Wesselsbron virus (WESSV)
- Yellow fever virus (YFV)
- Others
- Batu cave virus
- Bukulasa bat virus
- Nanay virus
- Rabensburg virus (RABV)
- Sitiawan virus
Viruses with no known arthropod vector
- Tamana bat virus (TABV)
- Entebbe virus group
- Entebbe bat virus (ENTV)
- Sokoluk virus
- Yokose virus (YOKV)
- Entebbe bat virus (ENTV)
- Modoc virus group
- Apoi virus (APOIV)
- Cowbone Ridge virus (CRV)
- Jutiapa virus (JUTV)
- Modoc virus (MODV)
- Sal Vieja virus (SVV)
- San Perlita virus (SPV)
- Rio Bravo virus group
- Bukalasa bat virus (BBV)
- Carey Island virus (CIV)
- Dakar bat virus (DBV)
- Montana myotis leukoencephalitis virus (MMLV)
- Phnom Penh bat virus (PPBV)
- Rio Bravo virus (RBV)
Non vertebrate viruses
- Assam virus
- Bamaga virus[39]
- Cuacua virus
- Hanko virus
- Mediterranean Ochlerotatus flavivirus
- Menghai flavivirus
- Nakiwogo virus (NAKV)
- Ochlerotatus caspius flavivirus
- Palm Creek virus
- Parramatta River virus
- Soybean cyst nematode virus 5[5]
- Xishuangbanna Aedes flavivirus
Viruses known only from sequencing
- Aedes flavivirus
- Aedes cinereus flavivirus
- Aedes vexans flavivirus
- Culex theileri flavivirus
Vaccines
The very successful yellow fever 17D vaccine, introduced in 1937, produced dramatic reductions in epidemic activity.
Effective inactivated Japanese encephalitis and Tick-borne encephalitis vaccines were introduced in the middle of the 20th century. Unacceptable adverse events have prompted change from a mouse-brain inactivated Japanese encephalitis vaccine to safer and more effective second generation Japanese encephalitis vaccines. These may come into wide use to effectively prevent this severe disease in the huge populations of Asia - North, South and Southeast.
The dengue viruses produce many millions of infections annually due to transmission by a successful global mosquito vector. As mosquito control has failed, several dengue vaccines are in varying stages of development. CYD-TDV, sold under the trade name Dengvaxia, is a tetravalent chimeric vaccine that splices structural genes of the four dengue viruses onto a 17D yellow fever backbone.[40][41] Dengvaxia is approved in five countries.[42]
References
- ↑ International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (20 March 2010). "ICTV 2009 Master Species List Version 4".
- ↑ Shi, P-Y (editor) (2012). Molecular Virology and Control of Flaviviruses. Caister Academic Press. ISBN 978-1-904455-92-9.
- ↑ McLean, Breeanna J.; Hobson-Peters, Jody; Webb, Cameron E.; Watterson, Daniel; Prow, Natalie A.; Nguyen, Hong Duyen; Hall-Mendelin, Sonja; Warrilow, David; Johansen, Cheryl A.; Jansen, Cassie C.; van den Hurk, Andrew F.; Beebe, Nigel W.; Schnettler, Esther; Barnard, Ross T.; Hall, Roy A. (2015). "A novel insect-specific flavivirus replicates only in Aedes-derived cells and persists at high prevalence in wild Aedes vigilax populations in Sydney, Australia" (PDF). Virology. 486: 272–283. PMID 26519596. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2015.07.021.
- ↑ The earliest mention of "yellow fever" appears in a manuscript of 1744 by Dr. John Mitchell of Virginia; copies of the manuscript were sent to Mr. Cadwallader Colden, a physician in New York, and to Dr. Benjamin Rush of Philadelphia; the manuscript was eventually reprinted in 1814. See:
(Dr. John Mitchell) (written: 1744 ; reprinted: 1814) "Account of the Yellow fever which prevailed in Virginia in the years 1737, 1741, and 1742, in a letter to the late Cadwallader Colden, Esq. of New York, from the late John Mitchell, M.D.F.R.S. of Virginia," American Medical and Philosophical Register … , 4 : 181-215. The term "yellow fever" appears on p. 186. On p. 188, Mitchell mentions "… the distemper was what is generally called the yellow fever in America." However, on pages 191–192, he states "… I shall consider the cause of the yellowness which is so remarkable in this distemper, as to have given it the name of the Yellow Fever."
Dr. Mitchell misdiagnosed the disease that he observed and treated, and the disease was probably Weil's disease or hepatitis. See: Saul Jarcho (1957) "John Mitchell, Benjamin Rush, and Yellow fever". Bulletin of the History of Medicine, 31 (2) : 132–6. - 1 2 Bekal S, Domier LL, Gonfa B, McCoppin NK, Lambert KN, Bhalerao K. "A novel flavivirus in the soybean cyst nematode". PubMed. 95: 1272–1280. doi:10.1099/vir.0.060889-0.
- ↑ ICTV. "Virus Taxonomy: 2014 Release". Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- 1 2 "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- ↑ Rice, C.; Lenches, E.; Eddy, S.; Shin, S.; Sheets, R.; Strauss, J. (23 August 1985). "Nucleotide sequence of yellow fever virus: implications for flavivirus gene expression and evolution" (PDF). Science. 229 (4715): 726–33. PMID 4023707. doi:10.1126/science.4023707. Retrieved 14 November 2016.
- ↑ Henderson BR, Saeedi BJ, Campagnola G, Geiss BJ (2011). Jeang, K.T, ed. "Analysis of RNA binding by the Dengue virus NS5 RNA capping enzyme". PLoS ONE. 6 (10): e25795. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...625795H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025795.
- ↑ Sun, G.; Larsen, C.; Baumgarth, N.; Klem, E; Scheuermann, R. (26 January 2017). "Comprehensive Annotation of Mature Peptides and Genotypes for Zika Virus". PLoS ONE. 12: e0170462. PMC 5268401
 . PMID 28125631. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0170462. Retrieved 20 February 2017.
. PMID 28125631. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0170462. Retrieved 20 February 2017. - ↑ Le Sommer C, Barrows NJ, Bradrick SS, Pearson JL, Garcia-Blanco MA (2012). Michael, Scott F, ed. "G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 promotes flaviviridae entry and replication". PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 6 (9): e1820. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0001820.
- 1 2 Gebhard LG, Filomatori CV, Gamarnik AV (2011). "Functional RNA elements in the dengue virus genome". Viruses. 3 (9): 1739–56. PMC 3187688
 . PMID 21994804. doi:10.3390/v3091739.
. PMID 21994804. doi:10.3390/v3091739. - ↑ Brinton MA, Dispoto JH (1988). "Sequence and secondary structure analysis of the 5'-terminal region of flavivirus genome RNA". Virology. 162 (2): 290–9. PMID 2829420. doi:10.1016/0042-6822(88)90468-0.
- ↑ Filomatori CV, Lodeiro MF, Alvarez DE, Samsa MM, Pietrasanta L, Gamarnik AV (2006). "A 5' RNA element promotes dengue virus RNA synthesis on a circular genome". Genes Dev. 20 (16): 2238–49. PMC 1553207
 . PMID 16882970. doi:10.1101/gad.1444206.
. PMID 16882970. doi:10.1101/gad.1444206. - ↑ Yu L, Nomaguchi M, Padmanabhan R, Markoff L (2008). "Specific requirements for elements of the 5' and 3' terminal regions in flavivirus RNA synthesis and viral replication". Virology. 374 (1): 170–85. PMC 3368002
 . PMID 18234265. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2007.12.035.
. PMID 18234265. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2007.12.035. - ↑ Alvarez DE, Lodeiro MF, Ludueña SJ, Pietrasanta LI, Gamarnik AV (2005). "Long-range RNA-RNA interactions circularize the dengue virus genome". J Virol. 79 (11): 6631–43. PMC 1112138
 . PMID 15890901. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.11.6631-6643.2005.
. PMID 15890901. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.11.6631-6643.2005. - 1 2 Chiu WW, Kinney RM, Dreher TW (July 2005). "Control of Translation by the 5′- and 3′-Terminal Regions of the Dengue Virus Genome". J. Virol. 79 (13): 8303–15. PMC 1143759
 . PMID 15956576. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.13.8303-8315.2005.
. PMID 15956576. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.13.8303-8315.2005. - 1 2 Pijlman GP, Funk A, Kondratieva N, et al. (December 2008). "A highly structured, nuclease-resistant, noncoding RNA produced by flaviviruses is required for pathogenicity". Cell Host Microbe. 4 (6): 579–91. PMID 19064258. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2008.10.007.
- ↑ Lin KC, Chang HL, Chang RY (May 2004). "Accumulation of a 3′-Terminal Genome Fragment in Japanese Encephalitis Virus-Infected Mammalian and Mosquito Cells". J. Virol. 78 (10): 5133–8. PMC 400339
 . PMID 15113895. doi:10.1128/JVI.78.10.5133-5138.2004.
. PMID 15113895. doi:10.1128/JVI.78.10.5133-5138.2004. - ↑ Zeng L, Falgout B, Markoff L (September 1998). "Identification of Specific Nucleotide Sequences within the Conserved 3′-SL in the Dengue Type 2 Virus Genome Required for Replication". J. Virol. 72 (9): 7510–22. PMC 109990
 . PMID 9696848.
. PMID 9696848. - ↑ Shi PY, Brinton MA, Veal JM, Zhong YY, Wilson WD (April 1996). "Evidence for the existence of a pseudoknot structure at the 3' terminus of the flavivirus genomic RNA". Biochemistry. 35 (13): 4222–30. PMID 8672458. doi:10.1021/bi952398v.
- ↑ Clyde K, Harris E; (2006). "RNA Secondary Structure in the Coding Region of Dengue Virus Type 2 Directs Translation Start Codon Selection and Is Required for Viral Replication". J Virol. 80 (5): 2170–2182. PMC 1395379
 . PMID 16474125. doi:10.1128/JVI.80.5.2170-2182.2006.
. PMID 16474125. doi:10.1128/JVI.80.5.2170-2182.2006. - ↑ Bidet, Katell; Garcia-Blanco, Mariano A. (2014-09-01). "Flaviviral RNAs: weapons and targets in the war between virus and host". Biochemical Journal. 462 (2): 215–230. ISSN 0264-6021. PMID 25102029. doi:10.1042/BJ20140456.
- ↑ Chapman, Erich G.; Costantino, David A.; Rabe, Jennifer L.; Moon, Stephanie L.; Wilusz, Jeffrey; Nix, Jay C.; Kieft, Jeffrey S. (2014-04-18). "The Structural Basis of Pathogenic Subgenomic Flavivirus RNA (sfRNA) Production". Science. 344 (6181): 307–310. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 4163914
 . PMID 24744377. doi:10.1126/science.1250897.
. PMID 24744377. doi:10.1126/science.1250897. - ↑ Funk, Anneke; Truong, Katherine; Nagasaki, Tomoko; Torres, Shessy; Floden, Nadia; Melian, Ezequiel Balmori; Edmonds, Judy; Dong, Hongping; Shi, Pei-Yong (2010-11-01). "RNA Structures Required for Production of Subgenomic Flavivirus RNA". Journal of Virology. 84 (21): 11407–11417. ISSN 0022-538X. PMC 2953152
 . PMID 20719943. doi:10.1128/JVI.01159-10.
. PMID 20719943. doi:10.1128/JVI.01159-10. - ↑ Chang, Ruey-Yi; Hsu, Ta-Wen; Chen, Yen-Lin; Liu, Shu-Fan; Tsai, Yi-Jer; Lin, Yun-Tong; Chen, Yi-Shiuan; Fan, Yi-Hsin (2013-09-27). "Japanese encephalitis virus non-coding RNA inhibits activation of interferon by blocking nuclear translocation of interferon regulatory factor 3". Veterinary Microbiology. 166 (1–2): 11–21. doi:10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.04.026.
- ↑ Moon, Stephanie L.; Anderson, John R.; Kumagai, Yutaro; Wilusz, Carol J.; Akira, Shizuo; Khromykh, Alexander A.; Wilusz, Jeffrey (2012-11-01). "A noncoding RNA produced by arthropod-borne flaviviruses inhibits the cellular exoribonuclease XRN1 and alters host mRNA stability". RNA. 18 (11): 2029–2040. ISSN 1355-8382. PMC 3479393
 . PMID 23006624. doi:10.1261/rna.034330.112.
. PMID 23006624. doi:10.1261/rna.034330.112. - ↑ Clarke, B. D.; Roby, J. A.; Slonchak, A.; Khromykh, A. A. (2015-08-03). "Functional non-coding RNAs derived from the flavivirus 3′ untranslated region". Virus Research. Special Issue: Functions of the ends of positive strand RNA virus genomes. 206: 53–61. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2015.01.026.
- ↑ Kuno G, Chang GJ, Tsuchiya KR, Karabatsos N, Cropp CB (1998). "Phylogeny of the genus Flavivirus". J Virol. 72 (1): 73–83. PMC 109351
 . PMID 9420202.
. PMID 9420202. - ↑ Gaunt MW, Sall AA, de Lamballerie X, Falconar AK, Dzhivanian TI, Gould EA (2001). "Phylogenetic relationships of flaviviruses correlate with their epidemiology, disease association and biogeography". J Gen Virol. 82 (8): 1867–1876.
- ↑ Cook S, Holmes EC (2006). "A multigene analysis of the phylogenetic relationships among the flaviviruses (Family: Flaviviridae) and the evolution of vector transmission". Arch Virol. 151 (2): 309–325. PMID 16172840. doi:10.1007/s00705-005-0626-6.
- ↑ Conway MJ (2015). "Identification of a flavivirus sequence in a marine arthropod". PLOS ONE. 10 (12): e0146037. PMC 4699914
 . PMID 26717191. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0146037.
. PMID 26717191. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0146037. - ↑ Moureau G, Cook S, Lemey P, Nougairede A, Forrester NL, Khasnatinov M, Charrel RN, Firth AE, Gould EA, de Lamballerie X (2015) New insights into Flavivirus evolution, taxonomy and biogeographic history, extended by analysis of canonical and alternative coding sequences. PLoS One https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117849
- ↑ Galli M, Bernini F, Zehender G (July 2004). "Alexander the Great and West Nile virus encephalitis". Emerging Infect. Dis. 10 (7): 1330–2; author reply 1332–3. PMID 15338540. doi:10.3201/eid1007.040396.
- ↑ West, Christy (2010-02-08). "Different West Nile Virus Genetic Lineage Evolving?". The Horse. Retrieved 2010-02-10. From statements by Orsolya Kutasi, DVM, of the Szent Istvan University, Hungary at the 2009 American Association of Equine Practitioners Convention, December 5–9, 2009.
- ↑ Venter M, Human S, van Niekerk S, Williams J, van Eeden C, Freeman F (August 2011). "Fatal neurologic disease and abortion in mare infected with lineage 1 West Nile virus, South Africa". Emerging Infect. Dis. 17 (8): 1534–6. PMC 3381566
 . PMID 21801644. doi:10.3201/eid1708.101794.
. PMID 21801644. doi:10.3201/eid1708.101794. - ↑ St Leger J, Wu G, Anderson M, Dalton L, Nilson E, Wang D (2011). "West Nile virus infection in killer whale, Texas, USA, 2007". Emerging Infect. Dis. 17 (8): 1531–3. PMC 3381582
 . PMID 21801643. doi:10.3201/eid1708.101979.
. PMID 21801643. doi:10.3201/eid1708.101979. - ↑ Karan LS, Ciccozzi M, Yakimenko VV, Presti AL, Cella E, Zehender G, Rezza G, Platonov AE (2013) The deduced evolution history of Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus. J Med Virol doi:10.1002/jmv.23856
- ↑ van den Hurk, Andrew F.; Suen, Willy W.; Hall, Roy A.; O'Brien, Caitlin A.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, Helle; Hobson-Peters, Jody; Colmant, Agathe M. G. (2016). "A newly discovered flavivirus in the yellow fever virus group displays restricted replication in vertebrates". Journal of General Virology. 97 (5): 1087–1093. PMID 26878841. doi:10.1099/jgv.0.000430.
- ↑ Thisyakorn, U. (2014). "Latest developments and future directions in dengue vaccines". Therapeutic Advances in Vaccines. 2 (1): 3–9. doi:10.1177/2051013613507862.
- ↑ Yauch, Lauren E. (2014). "Dengue Virus Vaccine Development". Advances in Virus Research: 315–372. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-800098-4.00007-6.
- ↑ "WHO Questions and Answers on Dengue Vaccines". WHO.int. Retrieved 2016-10-01.
Further reading
- Kuno G, Chang GJ, Tsuchiya KR, Karabatsos N, Cropp CB (Jan 1998). "Phylogeny of the genus Flavivirus". J Virol. 72 (1): 73–83. PMC 109351
 . PMID 9420202.
. PMID 9420202. - Zanotto, P. M.; Gould, E. A.; Gao, G. F.; Harvey, P. H.; Holmes, E. C. (1996). "Population dynamics of flaviviruses revealed by molecular phylogenies.". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 93 (2): 548–553. Bibcode:1996PNAS...93..548Z. PMC 40088
 . PMID 8570593. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.2.548.
. PMID 8570593. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.2.548. - Kalitzky, Matthias (2006). Molecular Biology of the Flavivirus. Wymondham: Horizon Bioscience. ISBN 1-904933-22-X.
- Shi, Pei-Yong (2012). Molecular Virology and Control of Flaviviruses. Norfolk, UK: Caister Academic Press. ISBN 978-1-904455-92-9.
- Murray, Catherine L.; Jones, Christopher T.; Rice, Charles M. (2008). "Architects of assembly: roles of Flaviviridae non-structural proteins in virion morphogenesis". Nature Reviews Microbiology. 6 (9): 699–708. PMC 2764292
 . PMID 18587411. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1928.
. PMID 18587411. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1928.
External links
- MicrobiologyBytes: Flaviviruses
- Novartis Institute for Tropical Diseases (NITD) - Dengue Fever research at the Novartis Institute for Tropical Diseases (NITD)
- Dengueinfo.org - Depository of dengue virus genomic sequence data
- Viralzone: Flavivirus
- Virus Pathogen Database and Analysis Resource (ViPR): Flaviviridae
- Rfam entry for Flavivirus 3'UTR stem loop IV
- Rfam entry for Flavivirus DB element
- Rfam entry for Flavivirus 3' UTR cis-acting replication element (CRE)
- Rfam entry for the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) hairpin structure